CYANOGEN
- CAS NO.:460-19-5
- Empirical Formula: C2N2
- Molecular Weight: 52.03
- MDL number: MFCD00040542
- EINECS: 207-306-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-03-14 15:18:25

What is CYANOGEN?
Description
Cyanogen, the dinitrile of oxalic acid, is an extremely poisonous gas. It was first prepared as a pure substance by J. L. Gay-Lussac in 1815. It is usually made in the lab by oxidizing cyanide ion in aqueous solution; the industrial process is gas-phase oxidation of HCN. Cyanogen has few industrial uses, although NASA has considered using it as a rocket fuel.
Description
Cyanogen is a colorless, flammable, compressed liquefied gas at room temperature. At deadly levelsonly, it has a pungent, almond-like odor. Molecular weight=52.04; Boiling point=221℃; Relative density(gas)=1.82; Freezing/Melting point=2 28℃; Vaporpressure=5.1 atm at 25℃; Relative vapor density(air=1)=1.82. Explosive limits: LEL=6.6%;UEL=32.0%. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704M Rating System): Health 4, Flammability 4, Reactivity 2.Soluble in water; solubility=1%.
Note: The irritant properties of cyanogen have been testedusing both human male and female subjects, 21-65 yearsof age. The distinctive bitter almond smell of cyanogencould not be detected at concentrations of 50, 100, and250 ppm. When exposed to 8 ppm for 6 min or 16 ppm for6-8 min, immediate eye and nose irritation occurred.
Chemical properties
Cyanogen is a colorless, flammable, com- pressed liquefied gas at room temperature. At deadly levels only, it has a pungent, almond-like odor.
The Uses of CYANOGEN
Cyanogen is used as a fumigant, as a fuel gas for welding and cutting metals, as a propellant, and in organic synthesis. It occurs in blast-furnace gases. It is also known to occur at varying concentrations in cassava flour consumed in northern Mozambique.
The Uses of CYANOGEN
Organic synthesis; fuel gas for welding and cutting heat-resistant metals; rocket and missile propellant; fumigant
Definition
ChEBI: A dinitrile that is ethane substituted by two cyano groups.
Definition
A toxic flammable gas prepared by heating mercury cyanide.
Definition
cyanogen: A colourless gas, (CN)2,with a pungent odour; soluble inwater, ethanol, and ether; d. 2.335g dm–3; m.p. –27.9°C; b.p. –20.7°C.The compound is very toxic. It maybe prepared in the laboratory byheating mercury(II) cyanide; industriallyit is made by gas-phase oxidationof hydrogen cyanide using air over asilver catalyst, chlorine over activatedsilicon(IV) oxide, or nitrogendioxide over a copper(II) salt.Cyanogen is an important intermediatein the preparation of various fertilizersand is also used as a stabilizerin making nitrocellulose. It is an exampleof a pseudohalogen.
Production Methods
Cyanogen can be prepared by slowly dropping potassium cyanide solution into copper sulfate solution or by heating mercury cyanide.
Production Methods
Cyanogen is prepared (1) by reaction of sodium cyanide and copper sulfate solutions, whereby one half the cyanogen is evolved as cyanogen gas and one half remains as cuprous cyanide. From the filtered cuprous cyanide, by treatment with ferric chloride solution, cyanogen is evolved with accompanying formation of ferrous chloride, (2) by heating ammonium oxalate COONH4·COONH4 with phosphorus pentoxide, water being abstracted. Small amounts of cyanogen are present in blast furnace gas and raw coal gas.
Reactions
Cyanogen (CN)2 is a colorless gas of marked characteristic odor, very poisonous, density 1.8 (air equal to 1.0), soluble. When passed into water at 0 °C, cyanogen forms hydrocyanic acid plus cyanic acid, but at ordinary temperatures the reaction is complex. With sodium hydroxide solution, there is formed with cyanogen sodium cyanide plus sodium cyanate, with dilute sulfuric acid oxamic acid COOH·CONH2, oxalic acid COOH·COOH. By reaction with tin and hydrochloric acid, cyanogen is reduced to ethylene diamine CH2·NH2·CH2·NH2. Cyanogen reacts with hydrogen to form hydrocyanic acid, and with metals, e.g., zinc, copper, lead, mercury, silver, to form cyanides.
Cyanogen, (1) when burned in air produces a violet flame forming carbon dioxide and nitrogen in the outer part and carbon monoxide and nitrogen in the inner part, (2) when exploded with oxygen produces carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide and nitrogen depending upon the ratio of oxygen to cyanogen (2 volumes oxygen plus 1 volume cyanogen yields 2 volumes carbon dioxide plus 1 volume nitrogen; 1 volume oxygen plus 1 volume cyanogen yields 2 volumes carbon monoxide plus 1 volume nitrogen). The flame spectrum contains characteristic bands in the blue and violet. By means of the electric spark, the electric arc or a red hot tube, cyanogen is decomposed into carbon plus nitrogen. When heated at ordinary pressure at about 300 °C, or under 300 atmospheres pressure at about 225°, cyanogen is converted into paracyanogen, a brown powder, also formed when mercuric cyanide is heated.
General Description
A colorless gas with an odor of almonds. Freezes at -28°C and boils at -20.7°C. Shipped as a liquid confined under its vapor pressure. The gas is heavier than air and a flame can travel back to the source of leak very easily. Prolonged exposure to fire or intense heat may cause the containers to violently rupture and rocket. Used to make other chemicals, as a fumigant, and as a rocket propellant.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Soluble in water and slowly decomposed by water to oxalic acid and ammonia.
Reactivity Profile
Colorless, flammable, highly toxic gas. CYANOGEN can react explosively with strong oxidants (dichlorine oxide, fluorene, oxygen, ozone). When heated to decomposition or on contact with acids, acid fumes, water or steam CYANOGEN will react to produce deadly hydrogen cyanide gas and oxides of nitrogen [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 945].
Health Hazard
Vapor irritates eyes and causes giddiness, headache, fatigue, and nausea if inhaled.
Health Hazard
Cyanogen is a highly poisonous gas having toxic symptoms similar to those of HCN. Acute exposure can result in death by asphyxia. The toxic routes are inhalation and percutaneous absorption. At sublethal concentrations the symptoms of acute toxicity are nausea, vomiting, headache, confusion, and weakness.
Rats exposed to cyanogen exhibited toxic symptoms of respiratory obstruction, lacrimation, and somnolence. Exposure to 350 ppm for 1 hour caused death to 50% of test animals. In humans, exposure to 16 ppm for 5 minutes produced irritation of eyes and nose. Toxicity of cyanogen is considerably lower than that of HCN. Lethal dose in test animals from subcutaneous injection varied between 10 and 15 mg/kg. Ernesto et al. (2002) have reported persistent konzo epidemics and subclinical upper motor neuron damage along with an elevated urinary thiocyanate concentration in school children in Mozambique who were exposed to high cyanogen concentrations from cassava flour.
A subchronic toxicity study conducted on male rhesus monkeys and male albino rats exposed over a period of 6 months (6 hours/day, 5 days/week) indicated marginal toxicity of cyanogen at 25 ppm (Lewis et al. 1984). Total lung moisture content and body weights were significantly lower. The odor threshold level for cyanogen is about 250 ppm.
Fire Hazard
Highly flammable, burns with a purpletinged flame; vapor density 1.8 (air = 1); the vapor may travel a considerable distance to an ignition source and flash back; fireextinguishing procedure: use a water spray to fight fire and keep fire-exposed containers cool; shut off the flow of gas.
Cyanogen forms an explosive mixture with air within the range of 6.6–32%. Liquid cyanogen can explode when mixed with liquid oxygen. When mixed with an acid or water or when heated to decomposition, it produces toxic fumes.
Safety Profile
: A poison by subcutaneous and possibly other routes. Moderately toxic by inhalation. Human systemic effects by inhalation: damage to the olfactory nerves and irritation of the conjunctiva. A systemic irritant by inhalation and subcutaneous routes. A human eyeirritant. Very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flames (sparks), or oxidizers. To fight fire, stop flow of gas. Potentially explosive reaction with powerful oxidants (e.g., dichlorine oxide, fluorine, oxygen, ozone). When heated to decomposition or on contact with acid, acid fumes, water, or steam will react to produce highly toxic fumes of NOx and CN-. See also other cyanogen entries and CYANIDE.
Potential Exposure
Cyanogen is currently used as an intermediate in organic syntheses; at one time, it was used in poison gas warfare.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is advised for 24-48 h. If frostbite hasoccurred, seek medical attention immediately; do NOT rubthe affected areas or flush them with water. In order to prevent further tissue damage, do NOT attempt to remove frozen clothing from frostbitten areas. If frostbite has NOToccurred, immediately and thoroughly wash contaminatedskin with soap and water.
cal attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is advised for 24-48 h. If frostbite hasoccurred, seek medical attention immediately; do NOT rubthe affected areas or flush them with water. In order to prevent further tissue damage, do NOT attempt to remove frozen clothing from frostbitten areas. If frostbite has NOToccurred, immediately and thoroughly wash contaminatedskin with soap and water. immediate work area and must be rapidly available. Kitingredients should be replaced every 1-2 years to ensurefreshness. Persons trained in the use of this kit, oxygen use,and CPR must be quickly available
storage
Cyanogen is stored outside or in a detached area: cool, dry, and well ventilated, and isolated from acid, acid fumes, and water. It is shipped in high-pressure metal cylinders of.
Shipping
UN1026 Cyanogen, Hazard Class: 2.3; Labels: 2.3-Poisonous gas, 2.1-Flammable gas, Inhalation Hazard Zone B. Cylinders must be transported in a secure upright position, in a well-ventilated truck. Protect cylinder and labels from physical damage. The owner of the compressed gas cylinder is the only entity allowed by federal law (49CFR) to transport and refill them. It is a violation of transportation regulations to refill compressed gas cylinders without the express written permission of the owner.
Incompatibilities
Chemically unstable in rising tempera- tures. May form explosive mixture with air. Explosive reac- tion with strong oxidizers (e.g., dichlorine oxide, fluorine). Forms toxic gases on contact with acids, including hydro- gen cyanide. Slowly hydrolyzed in water to form hydrogen cyanide, oxalic acid, and ammonia.
Waste Disposal
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier. Incineration; oxides, or nitrogen are removed from the effluent gas by scrubbers and/or ther- mal devices.
Properties of CYANOGEN
| Melting point: | -27.9° (also reported as -34.4°) |
| Boiling point: | bp -21.17° |
| Density | d4-21.17 0.9537 |
| vapor pressure | 520-570kPa at 21-25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.3780 (estimate) |
| solubility | slightly soluble in H2O, ethyl ether; soluble in ethanol |
| form | colorless gas |
| color | colorless |
| Water Solubility | 1.1–1.3g/100g H2O; 26 g/100g alcohol; 5g/100g ether [CIC73] |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 20 mg/m3 (10 ppm) (ACGIH). |
| Dielectric constant | 2.6(23℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 460-19-5 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cyanogen (460-19-5) |
Safety information for CYANOGEN
Computed Descriptors for CYANOGEN
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium 3-Bromopyrazole (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-hexahydro-5-Triethyl silyloxy-4-((E)-3-oxo-5-phenylpent-1- enyl)cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one. 1-Chlorocarbonyl-4-piperidinopiperidine 1-Bromo-4-phenyl-2-Butanone 4-Amino-2-fluoro-N-methylbenzamide 1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTIONRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![CYANOGEN BROMIDE, [14C]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure3/GIF/CB3781964.gif)

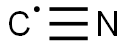

![TYPE II COLLAGEN CYANOGEN BROMIDE FRAGMENT CB10 (207-225) [BOS TAURUS]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)
You may like
-
![Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
Dimethyl [2-oxo-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]propyl]phosphonate 99%View Details
54094-19-8 -
 85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 99%View Details
85-81-4 -
 Cyclopentane carboxxylic acid 3400-45-1 99%View Details
Cyclopentane carboxxylic acid 3400-45-1 99%View Details
3400-45-1 -
![208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 (3aR,4R,5R,6aS)-5-(Benzoyloxy)hexahydro-4-[(1E)-3-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]-1-buten- 1-yl]-2H-cyclopenta[b]furan-2-one 99%View Details
208111-98-2 -
 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
Meldrums acid 2033-24-1 99%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
Cyaclopentane carboxylic acid 99%View Details
3400-45-1 -
 2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
2-Aminopyridine 504-29-0 99%View Details
504-29-0