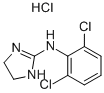
CLONIDINE
Synonym(s):2-(2,6-Dichloroanilino)-2-imidazoline
- CAS NO.:4205-90-7
- Empirical Formula: C9H9Cl2N3
- Molecular Weight: 230.09
- MDL number: MFCD00055059
- EINECS: 224-119-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
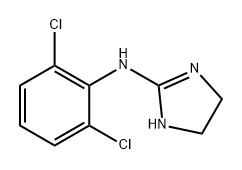
What is CLONIDINE?
Absorption
Clonidine reaches maximum concentration in 60-90 minutes after oral administration. Race and fasting status do not influence pharmacokinetics of clonidine.
A 100μg oral clonidine tablet reaches a Cmax of 400.72pg/mL with an AUC of 5606.78h*pg/mL and a bioavailability of 55-87%.
Toxicity
Oral LD50 is 126 mg/kg in rats. The TDLO is 70μg/kg in children, 126μg/kg in women, and 69μg/kg in men.
Symptoms of overdose include hypertension followed by hypotension, bradycardia, respiratory depression, hypothermia, drowsiness, decreased reflexes, weakness, irritability, and miosis. Severe overdoses can cause reversible cardiac conduction defects or dysrhythmias, apnea, coma, and seizures. Induction of vomiting is not recommended due to CNS depression but gastric lavage or activated charcoal may be useful in recent ingestion. Dialysis is also unlikely to be beneficial. Overdose can be treated with supportive measures such as atropine sulfate for bradycardia, intravenous fluids or vasopressors for hypotension, vasodilators for hypertension, naloxone for respiratory depression, and blood pressure monitoring.
The Uses of CLONIDINE
Clonidine may be useful in the treatment of acute opioid withdrawal. Epidural clonidine 1–2μgkg –1 increases the duration and potency of analgesia provided by epidural opioid or local anaesthetic drugs.
The Uses of CLONIDINE
Antihypertensive.
Background
Clonidine is an imidazole derivate that acts as an agonist of alpha-2 adrenoceptors. This activity is useful for the treatment of hypertension, severe pain, and ADHD.
Clonidine was granted FDA approval on 3 September 1974.
Indications
Clonidine tablets and transdermal systems are indicated for the treatment of hypertension alone or in combination with other medications. A clonidine injection is indicated for use with opiates in the treatment of severe cancer pain where opiates alone are insufficient. An extended release tablet of clonidine is indicated for the treatment of ADHD either alone or in combination with other medications.
Clonidine is also used for the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma, treatment of nicotine dependance, and opiate withdrawal.
Definition
ChEBI: A clonidine that is 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-amine in which one of the amino hydrogens is replaced by a 2,6-dichlorophenyl group.
brand name
Catapres (Boehringer Ingelheim).
Pharmacokinetics
Clonidine functions through agonism of alpha-2 adrenoceptors which have effects such as lowering blood pressure, sedation, and hyperpolarization of nerves. It has a long duration of action as it is given twice daily and the therapeutic window is between 0.1mg and 2.4mg daily.
Pharmacokinetics
Clonidine is lipid soluble and rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with a peak plasma concentration occurring in 60–90min. O ral, intravenous and intramuscular routes may be used for sedation or analgesia. I n addition, epidural and intrathecal clonidine is used to augment regional anaesthesia, but perineural administration is of limited or no effect. The elimination halflife is 9–13h and is prolonged in renal failure. Fifty percent of an administered dose is excreted unchanged by the kidneys, and 50% is metabolised in the liver to inactive metabolites.
Clinical Use
Clonidine is an α2-adrenergic agonist and is primarily used in the cardiovascular field for blood pressure reduction . The compound induces analgesia via central α2-receptor interaction and can be used orally, parenterally or epidurally for pain treatment, often in combination with opioids or local anesthetics . Epidural clonidine – opioid combinations are preferentially used for neuropathically maintained cancer pain. The compound is additionally used for migraine prophylaxis and to reduce opioid and alcohol withdrawal symptoms . Clonidine frequently induces side effects like hypotension, sedation, drowsiness, dry mouth, and constipation. The compound is well absorbed orally.
Physiological effects
Clonidine has some effects at α1-receptors (α2/ α1 > 200 : 1). Clonidine reduces the MA C of inhalational anaesthetic agents by up to 50%. I t has a synergistic analgesic effect with opioids which may be partly pharmacokinetic because the elimination half-life of opioids is also increased.
Physiological effects
CNS effects
Clonidine produces sedation, anxiolysis and analgesia. I t also has a MA Csparing
effect, but there is a ceiling to the reduction because of the potential
for activity at α1 receptors when used at higher doses.
CVS effects
The cardiovascular effects of clonidine probably involve α1 receptors and
imidazoline receptors as with dexmedetomidine. Clonidine lowers the set
point around which arterial pressure is regulated.
Respiratory effects
Clonidine has minor respiratory effects, causing only a small reduction in
minute ventilation.
Metabolic pathway
Clonidine is well absorbed orally, with peak plasma concentrations after 60–90min. I t is highly lipid soluble, and approximately 50% is metabolised in the liver to inactive metabolites; the rest is excreted unchanged via the kidneys, with an elimination half-life of 9–12h.
Metabolism
The metabolism of clonidine is poorly understood. The main reaction in clonidine metabolism is the 4-hydroxylation of clonidine by CYP2D6, CYP1A2, CYP3A4, CYP1A1, and CYP3A5.
Clonidine is <50% metabolized in the liver to inactive metabolites.
Properties of CLONIDINE
| Melting point: | 141-142℃ |
| Boiling point: | 369.21°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3946 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6300 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO:100.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);434.61(Max Conc. mM) |
| pka | 8.10±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 4205-90-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1H-Imidazol-2-amine, N-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro- (4205-90-7) |
Safety information for CLONIDINE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for CLONIDINE
CLONIDINE manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 4205-90-7 Clonidine 2,6-Dichloro-N-(imidazolidin-2-ylidene)aniline 96%View Details
4205-90-7 Clonidine 2,6-Dichloro-N-(imidazolidin-2-ylidene)aniline 96%View Details
4205-90-7 -
 4205-90-7 98%View Details
4205-90-7 98%View Details
4205-90-7 -
 Clonidine CAS 4205-90-7View Details
Clonidine CAS 4205-90-7View Details
4205-90-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1