Clomifene
- CAS NO.:911-45-5
- Empirical Formula: C26H28ClNO
- Molecular Weight: 405.96
- MDL number: MFCD00867469
- EINECS: 213-008-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-25 23:32:35
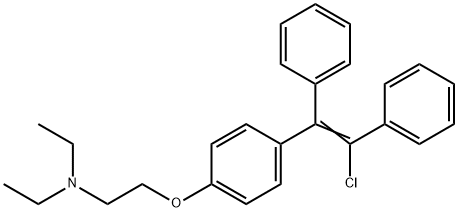
What is Clomifene?
Absorption
Based on early studies with 14 C-labeled clomifene, the drug was shown to be readily absorbed orally in humans.
Toxicity
The acute oral LD50 of clomifene is 1700 mg/kg in mice and 5750 mg/kg in rats. The toxic dose in humans is not known. Toxic effects accompanying acute overdosage of clomifene have not been reported. Signs and symptoms of overdosage as a result of the use of more than the recommended dose during clomifene therapy include nausea, vomiting, vasomotor flushes, visual blurring, spots or flashes, scotomata, ovarian enlargement with pelvic or abdominal pain.
Originator
Clomid,Lepetit,Italy,1966
The Uses of Clomifene
Clomifene is used for infertility in order to increase reproductive properties of oligoovulatory women who have three or four ovulatory cycles per year, leading to normal monthly ovulation.
The Uses of Clomifene
Antiestrogen.
Indications
Used mainly in female infertility due to anovulation (e.g. due to polycystic ovary syndrome) to induce ovulation.
Background
A triphenyl ethylene stilbene derivative which is an estrogen agonist or antagonist depending on the target tissue.
Indications
Clomifene acts by enhancing follicular growth caused by ovulation. The primary indication for using clomifene is induction of ovulation in non-ovulating women who still have some estrogen production.
Definition
ChEBI: Zuclomifene is a stilbenoid.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 20 g of 1-[p-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]-1,2-diphenylethanol
in 200 cc of ethanol containing an excess of hydrogen chloride was refluxed 3
hours. The solvent and excess hydrogen chloride were removed under
vacuum, and the residue was dissolved in a mixture of ethyl acetate and
methylene chloride. 1-[p-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]-1,2-diphenylethylene
hydrochloride was obtained, melting at 148° to 157°C. This hydrochloride salt
was treated with N-chlorosuccinimide in dry chloroform under reflux. The
product then obtained was converted to the free base and treated with citric
acid. The dihydrogen citrate salt of 1-[p-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]-1,2-
diphenylchloroethylene was obtained, melting at 116.5° to 118°C.
The intermediate 1-[p-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)phenyl]-1,2-diphenylethanol was
obtained by treating 4-(β-diethylaminoethoxy)benzophenone with
benzylmagnesium chloride. It melted at 95° to 96°C.
brand name
Clomid (Sanofi Aventis); Serophene (Serono).
Therapeutic Function
Antiestrogen
Pharmacokinetics
Clomifene (previously clomiphene) is an orally administered, non steroidal, ovulatory stimulant that acts as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). Clomifene can lead to multiple ovulation, and hence increase the risk of conceiving twins. In comparison to purified FSH, the rate of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome is low. There may be an increased risk of ovarian cancer and weight gain. Clomifene is capable of interacting with estrogen-receptor-containing tissues, including the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovary, endometrium, vagina, and cervix. It may compete with estrogen for estrogen-receptor-binding sites and may delay replenishment of intracellular estrogen receptors. Clomifene initiates a series of endocrine events culminating in a preovulatory gonadotropin surge and subsequent follicular rupture. The first endocrine event, in response to a course of clomifene therapy, is an increase in the release of pituitary gonadotropins. This initiates steroidogenesis and folliculogenesis resulting in growth of the ovarian follicle and an increase in the circulating level of estradiol. Following ovulation, plasma progesterone and estradiol rise and fall as they would in a normal ovulatory cycle.
Synthesis
Clomifene, 2-[p-(2-chloro-1,2-diphenylvinyl)phenoxy]triethylamine (28.2.4), is synthesized from 4-hydroxybenzophenone by reacting it with 2-diethylaminoethylchloride in the presence of an alkali, which gives 4-(2-diethylaminoethoxy)benzophenone (28.2.1). This is reacted with benzylmagnesium chloride in a Grignard reaction, forming as a result the corresponding carbinol (28.2.2). Dehydrating this with hydrogen chloride gives 2-[p-(1,2-diphenylvinyl) phenoxy]triethylamine (28.2.4), the vinylic hydrogen atom of which is replaced with a chlorine atom using N-chlorosuccinimide, giving clomifene (28.2.4) .

Metabolism
Hepatic
Properties of Clomifene
| Melting point: | 117.25°C |
| Boiling point: | 509.0±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.0166 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5790 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Amber Vial, -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 9.54±0.25(Predicted) |
| color | White to Pale Yellow |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C26H28ClNO/c1-3-28(4-2)19-20-29-24-17-15-22(16-18-24)25(21-11-7-5-8-12-21)26(27)23-13-9-6-10-14-23/h5-18H,3-4,19-20H2,1-2H3 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Clomiphene(911-45-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Clomiphene (911-45-5) |
Safety information for Clomifene
Computed Descriptors for Clomifene
| InChIKey | GKIRPKYJQBWNGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(N(CC)CC)COC1=CC=C(C(C2=CC=CC=C2)=C(Cl)C2=CC=CC=C2)C=C1 |
Clomifene manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Clomiphene API POWDERView Details
Clomiphene API POWDERView Details
50-41-9 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
