CLOBAZAM
Synonym(s):7-Chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4-(3H,5H)-dione
- CAS NO.:22316-47-8
- Empirical Formula: C16H13ClN2O2
- Molecular Weight: 300.74
- MDL number: MFCD00079069
- EINECS: 244-908-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
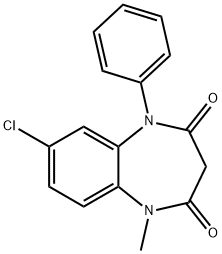
What is CLOBAZAM?
Absorption
The peak plasma levels (Cmax) and the area under the curve (AUC) of clobazam are dose-proportional over the dose range of 10-80 mg following single- or multiple-dose administration of ONFI. Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, the pharmacokinetics of clobazam are linear from 5-160 mg/day.
Clobazam is rapidly and extensively absorbed following oral administration. The time to peak concentrations (Tmax) of clobazam tablets under fasted conditions ranged from 0.5 to 4 hours after single- or multiple-dose administrations. The relative bioavailability of clobazam tablets compared to an oral solution is approximately 100%. After single-dose administration of the oral suspension under fasted conditions, the Tmax ranged from 0.5 to 2 hours. Based on exposure (Cmax and AUC) of clobazam, clobazam tablets and suspension were shown to have similar bioavailability under fasted conditions. The administration of clobazam tablets with food or when crushed in applesauce does not affect absorption. Although not studied, the oral bioavailability of the oral suspension is unlikely to be affected under fed conditions.
Chemical properties
N/AWhite Solid
Originator
Urbanyl,Diamant,France,1975
The Uses of CLOBAZAM
Benzodiazepine psychotherapeutic agent. Clobazam (CLB) has proven efficacy against multiple seizure types. Controlled substance (depressant).
Background
Clobazam belongs to the 1,5-benzodiazepine class of drugs and is marketed under different names, Onfi, Frisium, Urbanyl, and others.. Clobazam was first synthesized in 1966 and first published in 1969, following the incidental synthesis and discovery of the first benzodiazepine chlordiazepoxide in the 1950s. Unlike older 1,4-benzodiazepines, clobazam has a better side-effects profile, particularly less sedative and amnesic effects. This is likely because of clobazam's higher affinity to the α2 subunit of the GABAA receptor, which mediates anxiolytic effects, than the α1 subunit, which mediates sedative effect. Additionally, clobazam is believed to be a partial agonist to the GABAA receptor rather than non-selective full receptor agonists like 1,4-benzodiazepines, thus potentially explaining the decreased incidence of sedative effects.
Clobazam has been marketed as an anxiolytic since 1975 and an anticonvulsant since 1984. In October 21, 2011, the FDA approved clobazam as an adjunctive treatment for seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in adults and children aged two years and older. In 2005, clobazam also received approval from Health Canada as an add-on therapy for generalized tonic-clonic, myoclonic, and focal impaired awareness seizures.
Indications
Clobazam is indicated for the adjunctive treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS) in patients 2 years of age or older.
Definition
ChEBI: 7-Chloro-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4(3H,5H)-dione in which the hydrogen attached to the nitrogen at position 1 is substituted by a methyl group, whilst that attached to the other nitrogen is substitute by a phenyl group. It is used for the short-term management of acute anxiety and as an adjunct in the treatment of epilepsy in association with other antiepileptics.
Manufacturing Process
1.65 g of N-phenyl-N-(2-amino-5-chlorophenyl)-malonic acid ethyl ester
amide of MP 108° to 109°C are added to a sodium ethoxide solution, prepared
from 20 ml of absolute alcohol and 150 mg of sodium. The solution is allowed
to rest for 5 hours at room temperature. Then 1 ml of methyl iodide is added
and the reaction mixture is refluxed for 7 hours. After evaporation of the
solution in vacuo it is mixed with water and the solution is shaken with
methylene chloride. The methylene chloride phase is dried and evaporated. By
treatment of the residue with ethyl acetate/charcoal are isolated 500 mg of 7-
chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4-(3H,5H)-dione of MP
180° to 182°C. The yield amounts to 34% of theory
brand name
Urbanyl (Hoechst- Roussel).
Therapeutic Function
Tranquilizer
Pharmacokinetics
Clobazam belongs to the benzodiazepine class of drugs. Clobazam acts on the GABAA receptor to increase GABAnergic transmission, particularly chloride conductance in neurons. This causes neuronal hyperpolarization, resulting in an increase in the action potential threshold and reducing neuron firing frequency. Consequently, the general neuronal activity of the central nervous system is depressed; therefore, clobazam can be used to treat diseases caused by excessive excitatory action potentials.
The effect of clobazam 20 mg and 80 mg administered twice daily on QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, evaluator-blinded, placebo-, and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) parallel thorough QT study in 280 healthy subjects. In a study with demonstrated ability to detect small effects, the upper bound of the one-sided 95% confidence interval for the largest placebo-adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc based on the Fridericia correction method was below 10 ms, the threshold for regulatory concern.
Thus, at a dose two times the maximum recommended dose, clobazam did not prolong the QTc interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Clinical Use
Benzodiazepine:
Anticonvulsant
Anxiolytic
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. Human systemic effects by ingestion: wakefulness, withdrawal, nausea and vomiting. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. A tranquhzer. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and Cl-. See also DIAZEPAM.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: metabolism possibly increased by
rifampicin.
Antipsychotics: increased sedative effects; serious
adverse events reported with clozapine and
benzodiazepines.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Disulfiram: metabolism of clobazam inhibited;
increased sedative effects.
Sodium oxybate: enhanced effects of sodium oxybate
- avoid.
Metabolism
Clobazam is extensively metabolized in the liver via N-demethylation and hydroxylation to form two major metabolites, N-desmethylclobazam (norclobazam) and 4'-hydroxyclobazam, respectively, with approximately 2% of the dose recovered in urine and 1% in feces as an unchanged drug. The N-demethylation reaction is catalyzed primarily by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C19 and CYP2B6. N-desmethylclobazam, an active metabolite, is the major circulating metabolite in humans, and at therapeutic doses, plasma concentrations are 3-5 times higher than those of the parent compound. Based on animal and in vitro receptor binding data, estimates of the relative potency of N-desmethylclobazam compared to the parent compound range from 1/5 to equal potency. N-desmethylclobazam is extensively hydroxylated, mainly by CYP2C19. N-desmethylclobazam and its metabolites comprise ~94% of the total drug-related components in urine.. The formation of 4'-hydroxyclobazam is facilitated by CYP2C18 and CYP2C19.
The polymorphic CYP2C19 is the major contributor to the metabolism of the pharmacologically active N-desmethylclobazam. In CYP2C19 poor metabolizers, levels of N-desmethylclobazam were 5-fold higher in plasma and 2- to 3-fold higher in the urine than in CYP2C19 extensive metabolizers.
Metabolism
Clobazam is metabolised in the liver by demethylation
and hydroxylation; the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme
CYP2C19 plays a role in its metabolism. Unlike the
1,4-benzodiazepines such as diazepam, clobazam, a
1,5-benzodiazepine, is hydroxylated at the 4-position
rather than the 3-position.
Clobazam is excreted unchanged and as its main active
metabolite, N-desmethylclobazam, mainly in the urine.
Properties of CLOBAZAM
| Melting point: | 162-164°C |
| Boiling point: | 211°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2682 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in methylene chloride, sparingly soluble in alcohol. |
| pka | 8.59±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 22316-47-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1H-1,5-Benzodiazepine-2,4(3H,5H)-dione, 7-chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl- (22316-47-8) |
Safety information for CLOBAZAM
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for CLOBAZAM
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
1-methylindoline-2,3-dione 98%View Details
2058-74-4 -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
