Cilostazol
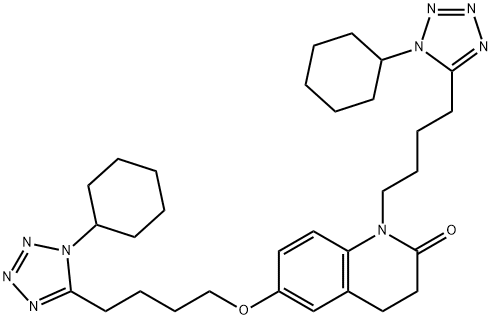
Synonym(s):6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-2(1H)-quinolinone;Cilostazol;OPC 13013;OPC 21;Pletaal
- CAS NO.:73963-72-1
- Empirical Formula: C20H27N5O2
- Molecular Weight: 369.46
- MDL number: MFCD00866780
- EINECS: 689-122-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
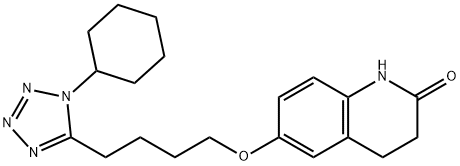
What is Cilostazol?
Absorption
Cilostazol is absorbed after oral administration. A high fat meal increases absorption, with an approximately 90% increase in Cmax and a 25% increase in AUC. Absolute bioavailability is not known.
Toxicity
Information on acute overdosage with cilostazol in humans is limited. The signs and symptoms of an acute overdose can be anticipated to be those of excessive pharmacologic effect: severe headache, diarrhea, hypotension, tachycardia, and possibly cardiac arrhythmias. The oral LD50 of cilostazol is >5.0 g/kg in mice and rats and >2.0 g/kg in dogs.
Description
Cilostazol is a platelet aggregation inhibitor with cerebral vasodilating activity, indicated for use in stroke and myocardial infarction. In patients with cerebral thrombosis, transient ischemia and cerebral arteriosclerosis, cilostazol significantly inhibits ADP-, collagenand epinephrine-induced platelet aggregation. Side effects include headache and tachycardia.
Chemical properties
Colourless Needles
Originator
Otsuka (Japan)
The Uses of Cilostazol
antibacterial; LD50(iv) 280mg/kg(mouse)
The Uses of Cilostazol
A potent phosphodiesterase III A (PDE3A) inhibitor (IC50=0.2uM) and inhibitor of adenosine uptake. Has antimitogeni, antithrombotic, vasodilatory and cardiotonic properties in vivo. Also affects lipid levels in vivo
The Uses of Cilostazol
An inhibitor of phosphodiesterase III
Indications
Indicated for the alleviation of symptoms of intermittent claudication (pain in the legs that occurs with walking and disappears with rest).
Background
Cilostazol is a quinolinone derivative and antiplatelet agent with vasodilating properties that has been used in the symptomatic treatment of intermittent claudication in patients with peripheral ischaemia. It is marketed under the brand name Pletal by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co.. Cilostazol works by inhibiting both primary and secondary aggregation and reducing calcium-induced contractions.
What are the applications of Application
Cilostazol is a PDE inhibitor, antimitogenic, antithrombotic, and cardiotonic agent
Definition
ChEBI: A lactam that is 3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one in which the hydrogen at position 6 is substiuted by a 4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy group.
brand name
Pletal (Otsuka);Reta.
General Description
Cilostazol is a potent cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitor. It is mainly used as antiplatelet agent.
Biological Activity
Potent phosphodiesterase III A (PDE3A) inhibitor (IC 50 = 0.2 μ M) and inhibitor of adenosine uptake. Has antimitogenic, antithrombotic, vasodilatory and cardiotonic properties in vivo . Also affects lipid levels in vivo .
Mechanism of action
Cilostazol exhibits greater selectivity than dipyridamole as an inhibitor of PDE3A. The drug does not affect the other PDEs (PDEs 1, 2, or 4). Cilostazol reversibly inhibit platelet aggregation induced by a number of stimuli, such as thrombin, ADP, collagen, or stress from exercise. Additionally, cilostazol inhibits adenosine uptake, leading to increased activity of adenosine at A1 and A2 receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
Cilostazol reduces the symptoms of intermittent claudication, as indicated by an increased walking distance. Intermittent claudication is pain in the legs that occurs with walking and disappears with rest. The pain occurs due to reduced blood flow to the legs.
Clinical Use
Cilostazol, a quinolinone derivative, is a potent orally active antiplatelet drug approved for the treatment of intermittent claudication (a peripheral artery disease resulting from blockage of blood vessels in the limbs).
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anagrelide: avoid concomitant use. Antibacterials: concentration increased by
clarithromycin and erythromycin - consider
reducing cilostazol dose.
Antifungals: concentration possibly increased by
ketoconazole and itraconazole - consider reducing
cilostazol dose.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
boceprevir, ritonavir and telaprevir - reduce
cilostazol dose to 50 mg twice daily.
Calcium-channel blockers: concentration increased
by diltiazem - consider reducing cilostazol dose.
Ulcer-healing drugs: concentration increased by
omeprazole - consider reducing cilostazol dose.
Metabolism
Hepatic. Cilostazol is extensively metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P-450 enzymes, mainly 3A4, and, to a lesser extent, 2C19, with metabolites largely excreted in urine. Two metabolites are active, with one metabolite appearing to account for at least 50% of the pharmacologic (PDE III inhibition) activity after administration of cilostazol.
Metabolism
Cilostazol is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, particularly with a high-fat meal, which greatly increases its bioavailability to approximately 90%. It is extensively metabolized in the liver by various cytochromes. The most important cytochromes appear to be CYP3A4 and, to lesser extent, by CYP2C19, with an elimination half-life of approximately 11 to 13 hours. Among the various metabolites produced (11 metabolites are known), the two major metabolites are 3,4-dehydrocilostazol and 4′-trans-hydroxycliostazol. These two metabolites are pharmacologically active. Studies indicate that the concomitant administration of cilostazol with CYP3A inhibitors can greatly increase cilostazol blood concentrations, and a dose reduction may be required. Similar results are seen when CYP2C19 is inhibited, leading to decreased formation of 4-trans-hydroxycliostazol and significant increases in cilostazol and 3,4-dehydrocilostazol.
storage
Store at RT
References
1) Schror (2002) The pharmacology of cilostazol; Diabetes Obes. Metab., 4 S14
Properties of Cilostazol
| Melting point: | 159-160°C |
| Boiling point: | 499.57°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1832 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7600 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | DMSO: 18 mg/mL, soluble |
| form | solid |
| pka | 14.22±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | off-white |
| λmax | 257nm(MeOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,2277 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 2 months |
Safety information for Cilostazol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Cilostazol
| InChIKey | RRGUKTPIGVIEKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Cilostazol manufacturer
Fleming Laboratories Ltd
Cleargreens Pharmaceutical Private Limited
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Cilostazol 73963-72-1 98%View Details
Cilostazol 73963-72-1 98%View Details
73963-72-1 -
 Cilostazol 73963-72-1 98%View Details
Cilostazol 73963-72-1 98%View Details
73963-72-1 -
 CILOSTAZOL 95-99 %View Details
CILOSTAZOL 95-99 %View Details
73963-72-1 -
 Cilostazol CAS 73963-72-1View Details
Cilostazol CAS 73963-72-1View Details
73963-72-1 -
 73963-72-1 Cilostazol 99%View Details
73963-72-1 Cilostazol 99%View Details
73963-72-1 -
 Cilostazol 73963-72-1 98%View Details
Cilostazol 73963-72-1 98%View Details
73963-72-1 -
 Cilostazol 98% CAS 73963-72-1View Details
Cilostazol 98% CAS 73963-72-1View Details
73963-72-1 -
 Cilostazol CAS 73963-72-1View Details
Cilostazol CAS 73963-72-1View Details
73963-72-1