Chitin
Synonym(s):Poly-(1→4)-β-N-acetyl-D -glucosamine
- CAS NO.:1398-61-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H11NO4X2
- Molecular Weight: 161.16
- MDL number: MFCD00466914
- EINECS: 215-744-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:42
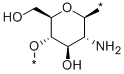
What is Chitin?
Description
Chitin is the most abundant natural amino polysaccharide. It has a similar annual yield as cellulose. Chitin is a kind of highly valuable material in biomedical applications because of its high biocompatibility, biodegradability and non-toxicity as well as its antimicrobial activity and low immunogenicity. It can be easily processed into gels, membrane, nanofibers, beads, nanoparticle, scaffold and sponges, enables its wide applications. In the tissue engineering, it can be used for manufacturing polymer scaffold to satisfy the demands of repairing, replacing, maintaining, or enhancing the function of a particular tissue or organ. In wound dressing, chitin can be used as antimicrobial reagent. In the field of drug delivery, the water-soluble carboxymethyl chitin (CMC) nanoparticle can be used as an effective carrier in drug delivery.
Description
Chitin is responsible for that crunch you hear when cracking a lobster claw at Fisherman’s Wharf in San Francisco at the ACS Fall National Meeting. This carbohydrate forms the naturally-occurring polymers that make up the hard outer shells of insects, spiders, crabs, and shrimp. Chitin extracted from crab and shrimp shells is compatible with human tissue and has been found to be useful to accelerate healing in wounds.
Chemical properties
Chitin is a colorless, crystalline or amorphous powder that is insoluble in water, organic solvents, dilute acids, and alkalis. It dissolves in concentrated mineral acids with simultaneous degradation of the polymer. Although chitosan is insoluble in water, it does dissolve in aqueous organic acids, for example, acetic and formic acids, as well as inorganic acids. Chitin and chitosan preparation can vary due to the source, with compositional differences. Similarly, the physicochemical characteristics of chitin and chitosan differ between crustacean species and preparation methods. Several studies have clearly demonstrated the specific characteristics of these products. The Mw and degree of deacetylation (DD) vary with process conditions. The physicochemical characteristics of chitin and chitosan influence their functional properties. Mw and DD vary with process conditions or different extraction methods. Chitosan's application depends on physical, biological, and chemical properties and chitosan depends on two parameters, such as DD and Mw.
The Uses of Chitin
chitin (chitine) is a moisture retainer and film-forming agent. This is a naturally occurring polysaccharide found in the shells of crustaceans, such as shrimp and crab, as well as in some fungi and algae. It is also a naturally occuring fibre found in the shells of shellfish. Used for the analysis of chitinase. lysozyme substrate.
What are the applications of Application
Chitin, a β(1,4) polymer chain of N-acetyl-D glucosamine, is used as a substrate to identify, differentiate and characterize chitinase(s) and chitin deacetylase(s). Chitin may be used as a viscosity/thickening agent or binder.
What are the applications of Application
Chitin is a long chain polymer of a glucose derivative found in cell walls
Definition
ChEBI: Chitin is a polysaccharide comprisingchains of N-acetyl-d-glucosamine,a derivative of glucose. Chitin isstructurally very similar to celluloseand serves to strengthen the supportingstructures of various invertebrates. It is the second most abundant biopolymer on earth, found especially in insects and fungi.
Agricultural Uses
Chitin is a polysaccharidec omprising chains of N-acetyl- D-glucosamine, a derivative of glucose, linked byβ-1,4 bonds and containing about 77 nitrogen atoms. It may be visualized as cellulose in which the hydroxyl groups on the second carbon are replaced by -NHCOCH3 groups Chitin is structurally very similar to cellulose and serves to strengthen various invertebrates. It offers resistance to chemicals and is present in the cell wall of some fungi as well as in the exoskeleton of insects.
References
Kumar, Majeti NV Ravi. "A review of chitin and chitosan applications." Reactive and functional polymers 46.1 (2000): 1-27.
Jayakumar, R., et al. "Biomedical applications of chitin and chitosan based nanomaterials—A short review." Carbohydrate Polymers 82.2 (2010): 227-232.
Properties of Chitin
| Melting point: | >300°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 737.18°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3744 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Room Temp |
| solubility | dilute aqueous acid (pH <6.5).: soluble |
| form | purified powder |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,2065 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chitin (1398-61-4) |
Safety information for Chitin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Chitin
Chitin manufacturer
Karandikars Orgochem Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran







You may like
-
 Chitin, purified CAS 1398-61-4View Details
Chitin, purified CAS 1398-61-4View Details
1398-61-4 -
 Chitin CAS 1398-61-4View Details
Chitin CAS 1398-61-4View Details
1398-61-4 -
 Chitin, pract CAS 1398-61-4View Details
Chitin, pract CAS 1398-61-4View Details
1398-61-4 -
 CHITIN Extra Pure (flakes) CAS 1398-61-4View Details
CHITIN Extra Pure (flakes) CAS 1398-61-4View Details
1398-61-4 -
 Chitin from shrimp shells CAS 1398-61-4View Details
Chitin from shrimp shells CAS 1398-61-4View Details
1398-61-4 -
 Chitin CAS 1398-61-4View Details
Chitin CAS 1398-61-4View Details
1398-61-4 -
 Polysaccharide type biopolymer Chitin Powder From Shrimp Shells, For Industrial Use, Packaging Size: 20kgView Details
Polysaccharide type biopolymer Chitin Powder From Shrimp Shells, For Industrial Use, Packaging Size: 20kgView Details
1398-61-4 -
 CHITINView Details
CHITINView Details
1398-61-4
