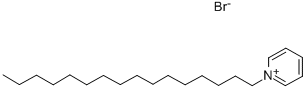
Cetylpyridinium chloride
Synonym(s):1-Hexadecylpyridinium chloride;Cetylpyridinium chloride monohydrate;Hexadecylpyridinium chloride monohydrate
- CAS NO.:123-03-5
- Empirical Formula: C21H38ClN
- Molecular Weight: 339.99
- MDL number: MFCD00011731
- EINECS: 204-593-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-06 13:21:43
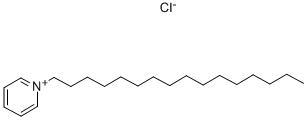
What is Cetylpyridinium chloride?
Description
Cetylpyridinium is a quaternary ammonium with broad-spectrum antiseptic activities. It is active against S. mutans, S. sanguis, E. coli, Oxford Staphylococcus, and C. albicans in media (MICs = 1.25-62.5 μg/ml) and against Oxford Staphylococcus in pooled human saliva (MICs = 7.8-15.6 μg/ml). Cetylpyridinium slows plaque formation for at least 21 days compared to a deionized water control in a rat incisor plaque model when applied topically at concentrations ranging from 0.025 to 2%. Formulations containing cetylpyridinium have been used as antiseptic agents in the treatment of gingivitis and as antimicrobial agents in raw food processing.
Description
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a quaternary ammonium salt antiseptic that is used in many over-the-counter personal-care products: mouthwashes, toothpastes, lozenges, and breath and nasal sprays, to name a few. It is also used in topical anti-infective products and as a pharmaceutical preservative.
More formally known as 1-hexadecylpyridinium chloride, CPC first appeared in the chemical literature in the 1930s. An early account1 of its disinfecting properties was written by pharmacist C. Lee Huyck at Xavier University of Louisiana (New Orleans) in 1944.
As shown in the hazard information table, CPC by itself has some dangerous properties; but its concentrations in consumer products have been considered too small to be of concern—until recently. In 2020, Brian K. Shoichet at the University of California, San Francisco; Laszlo Urban at the Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research (Cambridge, MA); and researchers at other institutions published a study showing that some supposedly inert pharmaceutical additives such as CPC have potential biological activity. But the results do not necessarily mean that the substances are toxic.
Some scientists, however, are a bit more suspicious of “quats”, as quaternary ammonium compounds are called in the industry. In the late 2000s, toxicologist Terry Hrubec at Virginia Tech and the Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine (both in Blacksburg, VA) noticed that some control mice embryos in a lab study acquired certain defects from two quat disinfectants, which were thought to be safe. Since then, she and other researchers have found more instances of quat-caused animal defects.
CPC has not been implicated in any of these studies; and no human health effects have been associated with exposure to quat-containing products. But this past March, enough evidence about defects in animals attributed to quats had been accumulated that the California Department of Public Health added these substances to its Biomonitoring California program.
1 Am. J. Pharm. 1944, 116, 50–59.
Chemical properties
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a white powder or crystals with a characteristic odor. It is slightly soapy to the touch.

Cetylpyridinium chloride is a quaternary ammonium compound and is the active chemical in some human mouthwashes on the market. It has antiseptic properties and is used in solutions or lozenges for the treatment of minor infections of the mouth and throat. The antimicrobial activity is due to an interaction of basic cetylpyridinium ions with acidic molecules on bacteria, which subsequently inhibits bacterial metabolism by forming weak ionic compounds that interfere with bacterial respiration.
The Uses of Cetylpyridinium chloride
Antibacterial in cough lozenges and syrups; emulsifier.
The Uses of Cetylpyridinium chloride
quaternary ammonium compound used as a preservative in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals; topical anti-infective and disinfectant; used on the surface of latex gloves .
Definition
ChEBI: A pyridinium salt that has N-hexadecylpyridinium as the cation and chloride as the anion. It has antiseptic properties and is used in solutions or lozenges for the treatment of minor infections of the mouth and throat.
Production Methods
Cetylpyridinium chloride is prepared from cetyl chloride by treatment with pyridine.
brand name
Ceepryn (Marion Merrell Dow); Cepacol (Marion Merrell Dow).
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Cetylpyridinium chloride is a quaternary ammonium cationic
surfactant, used in pharmaceutical and cosmetic formulations as
an antimicrobial preservative. It is used therapeutically
as an antiseptic agent; used alone or in combination with
other drugs for oral and throat care; used in nonparenteral
formulations licensed in the UK; and used in oral and inhalation
preparations at concentrations of 0.02–1.5 mg.
Mouthwashes containing cetylpyridinium chloride have been
shown to inhibit plaque formation,(1–3) although efficacy is variable
owing to limited published data.
Clinical Use
1-Hexadecylpyridinium chloride is a white powder that isvery soluble in water and alcohol. In this compound, thequaternary nitrogen atom is a member of an aromatic pyridinering.
The cetyl derivative is the most active of a series ofalkylpyridinium compounds. It is used as a general antisepticin concentrations of 1:100 to 1:1,000 for intact skin,1:1,000 for minor lacerations, and 1:2,000 to 1:10,000 forthe irrigation of mucous membranes. Cetylpyridinium chlorideis also available in the form of throat lozenges and amouthwash at a 1:20,000 dilution.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by skin contact. A skin and eye irritant. When E heated to decomposiuon it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and Cl-.
Safety
Cetylpyridinium chloride is used widely in mouthwashes as a
bactericidal antiseptic. It is generally regarded as a relatively
nontoxic material when used at a concentration of 0.05% w/v,
although minor side effects such as mild burning sensations on the
tongue have been reported.
At higher concentrations, cetylpyridinium chloride may damage
the mucous membranes in the mouth. It is harmful when ingested or
inhaled. It can cause eye irritation, and is irritant to the respiratory
system and the skin.
LD50 (rat, IP): 0.006 g/kg
LD50 (rat, IV): 0.03 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 0.2 g/kg
LD50 (rat, SC): 0.25 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.01 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 0.108 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, oral): 0.4 g/kg
LD50 (rabbit, IV): 0.036 g/kg
storage
Cetylpyridinium chloride is stable under normal conditions. It should be stored in well-closed containers.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and bases. It is also
incompatible with methylcellulose.
Magnesium stearate suspensions in cetylpyridinium chloride
have been shown to significantly reduce its antimicrobial activity.
This is due to the absorption of cetylpyridinium chloride on
magnesium stearate. The cetylpyridinium chloride ion also
interacts with gelatin, resulting in reduced bioavailability.
Regulatory Status
Included in nonparenteral formulations licensed in the UK. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database, for use in inhalation and oral preparations. Reported in the EPA TSCA Inventory. It is not approved for use in Japan. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Cetylpyridinium chloride
| Melting point: | 77°C |
| Boiling point: | 496.25°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 0.9362 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Freely soluble in water; very soluble in chloroform;
very slightly soluble in ether; insoluble in acetone, acetic acid,
and ethanol. |
| form | White Crystalline Powder |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| Odor | at 100.00?%. pyridine |
| Water Solubility | 111g/L at 20℃ |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 123-03-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cetylpyridinium chloride (123-03-5) |
Safety information for Cetylpyridinium chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Cetylpyridinium chloride
Cetylpyridinium chloride manufacturer
Suryaprabha Pharmachem
Attar Global
Colour Finders
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![2-[[(2-ethylphenyl)(2-hydroxyethyl)amino]methyl]-3,3-difluoro-Propanenitrile](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/2647-14-5.gif)

You may like
-
 123-03-5 Cetylpyridinium Chloride 99%View Details
123-03-5 Cetylpyridinium Chloride 99%View Details
123-03-5 -
 123-03-5 99%View Details
123-03-5 99%View Details
123-03-5 -
 Cetylpyridinium chloride 98%View Details
Cetylpyridinium chloride 98%View Details
123-03-5 -
 123-03-5 Cetylpyridinium chloride 98%View Details
123-03-5 Cetylpyridinium chloride 98%View Details
123-03-5 -
 123-03-5 98%View Details
123-03-5 98%View Details
123-03-5 -
 CETYL PYRIDINIUM CHLORIDE 99%View Details
CETYL PYRIDINIUM CHLORIDE 99%View Details -
 Hexadecylpyridinium chloride 97% (HPLC) CAS 123-03-5View Details
Hexadecylpyridinium chloride 97% (HPLC) CAS 123-03-5View Details
123-03-5 -
 Cetylpyridinium chloride 98% CAS 123-03-5View Details
Cetylpyridinium chloride 98% CAS 123-03-5View Details
123-03-5
