CALCIUM CARBONATE
- CAS NO.:1317-65-3
- Empirical Formula: CCaO3
- Molecular Weight: 100.09
- MDL number: MFCD00010906
- EINECS: 215-279-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-09-04 23:37:13
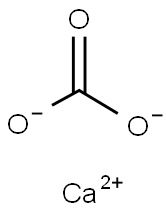
What is CALCIUM CARBONATE?
Description
Calcite is one of the most common minerals on the face of the earth, comprising about 4% by weight of the earth’s crust and is formed in many different geological environments. Calcite can form rocks of considerable mass and constitutes a significant part of all three major rock classification types. It forms oolitic, fossiliferous and massive limestones in sedimentary environments and even serves as the internal cement for many sandstones and shales.Calcite is even a major component in the igneous rock called carbonatite and forms the major portion of many hydrothermal veins. Not necessarily a variety of calcite, cave formations are certainly a unique aspect of calcite’s story.
Description
Next to quartz, calcite is the world’s most abundant mineral. Limestone and marble are both made of nearly pure calcite. Limestone is sedimentary rock made of calcite; marble is metamorphosed limestone.
Chemical properties
Calcium carbonate is a white, odorless powder, or crystalline solid.
Chemical properties
Ground limestone consists essentially of calcium carbonate. It is obtained by crushing, grinding, and classifying naturally occurring limestone benefited by flotation and/or air classification. It is pro duced as a fine, white to off-white, microcrystalline powder. It is odorless and tasteless and is stable in air. It is practically insoluble in water and in alcohol. The presence of any ammonium salt or carbon dioxide increases its solubility in water, but the presence of any alkali hydroxide reduces the solubility.
The Uses of CALCIUM CARBONATE
Source of lime; neutralizing agent, filler, and extender in rubber, plastics, paints; opacifying agent in paper; fortification of bread; putty; tooth pow- ders; antacid; whitewash; Portland cement; sulfur dioxide removal from stack gases; metallurgical flux; analytical chemistry; carbon dioxide gener- ation (laboratory).
The Uses of CALCIUM CARBONATE
Calcite is the primary mineral component in cave formations. Stalactites and stalagmites, cave veils, cave pearls, “soda straws” and the many other different cave formations that millions of visitors to underground caverns enjoy are made of calcite.
The Uses of CALCIUM CARBONATE
Manufacture of quicklime, Portland cement, and paints. United States Pharmacopeia (USP) grades are used in dentifrices, cosmetics, food, and pharmaceuticals such as antacids.
Definition
Aragonite: An
anhydrous mineral form of calcium carbonate,
CaCO3, which occurs associated
with limestone and in some metamorphic
rocks. It is also the main ingredient of
pearls. It is not as stable as calcite, into
which it may change over time.
Calcite:A mineral form of calcium
carbonate occurring in limestone,
chalk, and marble.
Charlk: A natural form of calcium carbonate
(CaCO3) formed originally by marine
organisms. (Blackboard chalk is calcium
sulfate, CaSO4.).
Preparation
The calcite present is derived mostly from the remains of organisms such as clams, brachiopods, bryozoa, crinoids and corals. These animals live on the bottom of the sea and when they die their shells accumulate into piles of shelly debris. This debris can then form beds of limestone. Some limestones may have been derived from nonbiogenic calcite formation.
General Description
Odorless, white to tan powder.
Reactivity Profile
CALCIUM CARBONATE has generally low chemical reactivity. Is non-combustible. Decomposes at high temperature (825°C) to give gaseous carbon dioxide and calcium oxide (quicklime). Incompatible with acids, alum, ammonium salts, fluorine, magnesium. Reacts with acids and acidic salts to generate gaseous carbon dioxide with effervescence (bubbling). The reaction is rapid and exothermic with concentrated solutions of acids. The efferversence can create extensive foaming. Ignites on contact with fluorine.
Hazard
A nuisance particulate dust.
Health Hazard
Calcium carbonate is considered
to be a nuisance dust.
Although no adverse effects have been
reported in the literature among workers
exposed to calcium carbonate, high concentrations
of the dust would be expected to act as a
physical irritant to the eyes and skin.1 Fourteen
British workers exposed to heavy calcium carbonate
concentrations for 12–35 years showed
no trace abnormalities due to dust or any
clinical sign of pneumoconiosis or chronic
bronchitis on X ray.2 Long exposure to high
dust concentrations of pure calcium carbonate
(quartz content less than 1.1%) did not result
in lung fibrosis.
Agricultural Uses
Limestone or dolomite, used in agriculture for liming the soil, is ground to a fineness to ensure that 50% of the particles pass through a 1.70mm Indian Standards (IS) sieve, and 50% is retained on a 150micron IS sieve.
Safety Profile
A nuisance dust. An eye and skin irritant. Igmtes on contact with F2. Incompatible with acids, ammonium salts, (Mg + H2). Calcium carbonate is a common air contaminant. See also CALCIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Calcium carbonate is used as a source of lime; neutralizing agent; manufacturing or rubber, plastics, paint and coatings; sealants, paper, dentifrices, ceramics, putty, polishes and cleaners, insecticides, inks and cosmetics; whitewash; Portland cement; antacids; analytical chemistry, and others
Incompatibilities
Calcium carbonate decomposes in high temperature forming carbon dioxide and corrosive materials
Waste Disposal
Landfills. It is the responsibility of chemical waste generators to determine if a discarded chemical is classified as a hazardous waste. See 40 CFR Parts 261.3 for United States Environmental Protection Agency guidelines for the classification determination. In addition, in order to ensure complete and accurate classification, waste generators must consult state and local hazardous waste regulations.
Properties of CALCIUM CARBONATE
| Melting point: | 825 °C |
| Boiling point: | 2850 °C |
| Density | 2.93 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| solubility | 5 M HCl: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | random crystals |
| color | Gray |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 8.47 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1317-65-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Limestone (1317-65-3) |
Safety information for CALCIUM CARBONATE
Computed Descriptors for CALCIUM CARBONATE
Abamectin manufacturer
Tara Minerals and Chemicals Pvt Ltd
Niki Chemical Industries
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Calcite 99%View Details
Calcite 99%View Details -
 Limestone 98%View Details
Limestone 98%View Details
1317-65-3 -
 1317-65-3 98%View Details
1317-65-3 98%View Details
1317-65-3 -
 Limestone 1317-65-3 98%View Details
Limestone 1317-65-3 98%View Details
1317-65-3 -
 1317-65-3 98%View Details
1317-65-3 98%View Details
1317-65-3 -
 Limestone 98%View Details
Limestone 98%View Details
1317-65-3 -
 1317-65-3 Limestone 99%View Details
1317-65-3 Limestone 99%View Details
1317-65-3 -
 Limestone 1317-65-3 99%View Details
Limestone 1317-65-3 99%View Details
1317-65-3