CALCIUM BORIDE
- CAS NO.:12007-99-7
- Empirical Formula: B6Ca
- Molecular Weight: 104.94
- MDL number: MFCD00148904
- EINECS: 234-525-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-01-16 17:26:51
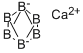
What is CALCIUM BORIDE?
Description
Typical samples of CaB6 are nonstoichiometric, i.e. the ratio of boron to calcium is not exactly 6:1, for example the ultra-fine powders of CaB6 produced by some researchers had B:Ca ratio of 5.91:1. It is an important material due to its high electrical conductivity, hardness, chemical stability, and melting point.
Chemical properties
black cub; -200 mesh 99.5% pure; refractory material [KIR78] [CER91] [CRC10]
Physical properties
Calcium boride is a black, lustrous, chemically inert powder with a low density. Calcium hexaboride is insoluble in H2O, MeOH (methanol), and EtOH (ethanol) and dissolves slowly in acids. It has the cubic structure typical for metal hexaborides, with octahedral units of six boron atoms combined with calcium atoms.
The Uses of CALCIUM BORIDE
Calcium boride is used as an electrode (cathode) material and n-type thermoelectric materials. It is used to make boron- alloyed steel, as a deoxidation agent in the production of oxygen-free copper. It is further used as an antioxidant in carbon bonded refractories. It acts as a new material which is used in the nuclear-industry for neutron- preventing, high-purity metal borid (TiB2,ZrB2,HfB2) and high-purity boron alloy(Ni-B, Co-B, Cu-b).
The Uses of CALCIUM BORIDE
Carbon hexaboride is used in the manufacturing of boron-alloyed steel. Also, calcium hexaboride is used as a deoxidation agent in production of oxygen-free copper, which results in higher conductivity than conventionally phosphorus-deoxidized copper owing to the low solubility of boron in copper. Also, it can serve as a high temperature material, surface protection, abrasives, tools, and wear-resistant material.
Preparation
Calcium boride can be formed directly from the
elements. Ca melts at 842°C and boron melts at
2076°C. Therefore, if a vapor of Ca metal at >850°C
(red-heat) is passed over crystals of boron, a gas–solid
reaction forms the desired boride. However, to obtain
stoichiometric compositions, it is better to heat the
well-mixed powders of Ca and B to obtain specific
compounds:
Ca+ 6B→CaB6
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Properties of CALCIUM BORIDE
| Melting point: | 2235°C |
| Density | 2.3 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 2.3 |
| color | refractory solid |
| Resistivity | 222 (ρ/μΩ.cm) |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. Dissolves slowly in acids |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic a = 413.77 pm D2 , cP7, Pm3m 1 CaB type (Z = 1) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 12007-99-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium boride (CaB6), (OC-6-11)- (12007-99-7) |
Safety information for CALCIUM BORIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for CALCIUM BORIDE
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7 -
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7 -
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7 -
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7 -
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7 -
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7 -
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7 -
 Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
Calcium boride CAS 12007-99-7View Details
12007-99-7