Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
Synonym(s):Butamben;Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
- CAS NO.:94-25-7
- Empirical Formula: C11H15NO2
- Molecular Weight: 193.24
- MDL number: MFCD00017112
- EINECS: 202-317-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
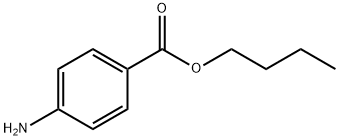
What is Butyl 4-aminobenzoate?
Absorption
When butamben is administered epidurally in a suspension form, the physical characteristics of butamben allow a very slow release. When administered topically, butamben is also reported to have a very low systemic absorption which allows for a longer duration of action.
Toxicity
In studies, the most common effect was related to the generation of a prolonged effect. It was also shown in preclinical trials to produce tissue necrosis and neuritis. The LD50 of butamben is registered to be of 67 mg/kg.
Chemical properties
It is a solid at room temperature, with a melting point of 58°C and a boiling point of 173.4°C (at 8mmHg). Butyl p-aminobenzoate is insoluble in water.
The Uses of Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
n-Butyl 4-aminobenzoate is used as pharmaceutical intermediate.
The Uses of Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
antibacterial
Background
Butamben is a local anesthetic in the form of n-butyl-p-aminobenzoate. Its structure corresponds to the standard molecule of a hydrophilic and hydrophobic domain separated by an intermediate ester found in most of the local anesthetics. Due to its very low water solubility, butamben is considered to be suitable only for topical anesthesia. The FDA removed all parenteral butamben products from the market, possibly due to the poor solubility of this drug.
Indications
Butamben was indicated for the treatment of chronic pain due to its long-duration effect. It is also indicated as a surface anesthetic for skin a mucous membrane and for the relief of pain and pruritus associated with anorectal disorders.
Definition
ChEBI: An amino acid ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-aminobenzoic acid with the hydroxy group of butan-1-ol. Its local anaesthetic properties have been used for surface anaesthesia of the skin and mucous membranes, and for r lief of pain and itching associated with some anorectal disorders.
Production Methods
Butyl p-aminobenzoate is manufactured via esterification of p-nitrobenzoic acid with n-butyl alcohol, followed by the reduction of the nitro group to an amino group.
brand name
Butesin (Abbott).
General Description
Yellow powder. Insoluble in water.
Air & Water Reactions
May be sensitive to light and air. Insoluble in water. Slowly hydrolyzed when boiled in water. Also will hydrolyze under high and low pH conditions .
Reactivity Profile
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate is an aminophenyl ester derivative. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Butyl 4-aminobenzoate are not available. Butyl 4-aminobenzoate is probably combustible.
Pharmacokinetics
Butamben has been shown to selectively inhibit dorsal root pain signal transmission for periods of months when administered as epidural suspensions. The effect of butamben is not related to any significant loss of motor function which indicates that it targets specifically the pain-sensing C fibers of the dorsal root. When administered topically, butamben produced anesthesia by accumulating in the nerve cell membrane causing it to expand and lose its ability to depolarize and blocking the impulse transmission.
Metabolism
The metabolic pathway of butamben follows the same pattern of other local anesthetics and it is driven mainly by the hydrolysis via cholinesterase for the formation of inert metabolites.
Purification Methods
Crystallise Butamben from EtOH. [Beilstein 14 IV 1130.]
Properties of Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
| Melting point: | 57-58 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 174 °C8 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.0945 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5480 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 5.38 (Uncertain) |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Very slightly soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,1512 |
| BRN | 1211465 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 94-25-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Butamben(94-25-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Butyl p-aminobenzoate (94-25-7) |
Safety information for Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Butyl 4-aminobenzoate
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Butyl 4-Aminobenzoate CAS 94-25-7View Details
Butyl 4-Aminobenzoate CAS 94-25-7View Details
94-25-7 -
 Butamben CAS 94-25-7View Details
Butamben CAS 94-25-7View Details
94-25-7 -
 Butyl 4-Aminobenzoate 98.00% CAS 94-25-7View Details
Butyl 4-Aminobenzoate 98.00% CAS 94-25-7View Details
94-25-7 -
 Butyl 4-Aminobenzoate 95.00% CAS 94-25-7View Details
Butyl 4-Aminobenzoate 95.00% CAS 94-25-7View Details
94-25-7 -
 Butyl 4-aminobenzoate 98% CAS 94-25-7View Details
Butyl 4-aminobenzoate 98% CAS 94-25-7View Details
94-25-7 -
 94-25-7 Butamben 99%View Details
94-25-7 Butamben 99%View Details
94-25-7 -
 366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 -
 Carvedilol 98%View Details
Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-3
