Butenafine hydrochloride
Synonym(s):Butenafine hydrochloride;Mentax;N-(p-tert-butylbenzyl)-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethylamine hydrochloride;N-[[4-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)phenyl]methyl]-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethanamine hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:101827-46-7
- Empirical Formula: C23H27N.ClH
- Molecular Weight: 353.93
- MDL number: MFCD00917064
- EINECS: 642-354-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
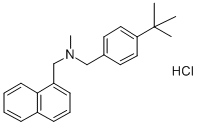
What is Butenafine hydrochloride?
Description
Butenafine hydrochloride is a new benzylamine antifungal which appears to block the squalene epoxidation step of sterol synthesis in fungi. Active against a broad spectrum of fungi, butenafine hydrochloride is more effective in a guinea-pig model of tinea pedis than clotrimazole, naftifine and tolnaftate. Its efficacy is partially attributed to its long retention time in the skin.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Kaken (Japan)
The Uses of Butenafine hydrochloride
Butenafine hydrochloride has been used as a standard in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method to determine butenafine hydrochloride in butenafine-loaded nanosponges.
The Uses of Butenafine hydrochloride
An antifungal, used to control dermal fungal infections such as athletes foot and ring worm.
The Uses of Butenafine hydrochloride
Butenafine HCl is a synthetic benzylamine antifungal, works by inhibiting the synthesis of sterols by inhibiting squalene epoxidase.
What are the applications of Application
Butenafine Hydrochloride is a compound with antifungal properties
Definition
ChEBI: The hydrochloride salt of butenafine. An inhibitor of squalene epoxidase, an enzyme responsible for the creation of sterols needed in fungal cell membranes, it is used for treatment of dermatological fungal infections.
Manufacturing Process
N-Methyl-1-naphtylmethylamine hydrochloride (2.1 g, 0.01 mole) was dissolved in 50 ml of dry dimethylformamide, and 3.71 g (0.035 mole) of anhydrous sodium carbonate was added, then 2.49 g (0.011 mole) of p-tbutylbenzyl bromide was added by stirring and the mixture was reacted at 30° to 40°C for 5 hours. Ice water was added, and the mixture was extracted with toluene. The organic layer was washed with water, and toluene was evaporated. The residue was chromatographed on silica gel column, and eluated with 5% ethyl acetate/n-hexane. The eluate was concentrated to give 2.98 g (yield 94%) of an oily substance. Hydrochloric acid/ethanol was added to 1 g of this oily product, and the mixture was concentrated. The residue was recrystallized from methanol/acetic acid to give 0.95 g of desired 1- naphthalenemethanamine, N-((4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenyl)methyl)-Nmethyl-, hydrochloride having melting point 200° to 202°C.
brand name
Lotrimin (Schering); Mentax (Mylan Bertek);Volley.
Therapeutic Function
Antifungal
General Description
Butenafine hydrochloride is chemically known as N-4-tertbutylbenzyl-N-methyl-1-naphthalenemethylamine hydrochloride. Butenafine, a benzylamine derivative, is a new generation antimycotic compound. It is easily soluble in methanol, ethanol, dichloromethane, and chloroform, but not in water. The allyl radical in butenafine hydrochloride is substituted by a butylbenzyl group.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Butenafine exhibits fungicidal and antimycotic activity. This fungal squalene epoxidase inhibitor serves as an effective fungicide against T. rubrum, T. mentagrophytes, Microsporum canis, Aspergillus fumigatus, Sporothrix schenckii, Candida parapsilosis, and C. albicans. It is considered more effective and rapid than other antifungal drugs at curing dermatophytosis and preventing recurrences. In humans, it is used topically to treat tinea conditions and superficial candidiasis. Butenafine is considered a promising antimycotic compound to treat tinea pedis due to its efficiency, safety profile, relapse rates, and cost-effectiveness.
Side Effects
Side Effects:
Blistering, burning, crusting, dryness, or flaking of the skin where the medicine is applied.
itching, scaling, severe redness, soreness, or swelling of the skin where the medicine is applied.
Properties of Butenafine hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 210-214°C |
| storage temp. | room temp |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥10mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | white to off-white |
| Merck | 14,1518 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C23H27N.ClH/c1-23(2,3)21-14-12-18(13-15-21)16-24(4)17-20-10-7-9-19-8-5-6-11-22(19)20;/h5-15H,16-17H2,1-4H3;1H |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101827-46-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Butenafine hydrochloride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H312:Acute toxicity,dermal |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Butenafine hydrochloride
| InChIKey | LJBSAUIFGPSHCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C12C=CC=CC=1C=CC=C2CN(C)CC1=CC=C(C(C)(C)C)C=C1.Cl |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 101827-46-7 Butenafine hydrochloride 98%View Details
101827-46-7 Butenafine hydrochloride 98%View Details
101827-46-7 -
 101827-46-7 98%View Details
101827-46-7 98%View Details
101827-46-7 -
 Butenafine hydrochloride 98%View Details
Butenafine hydrochloride 98%View Details
101827-46-7 -
 Butenafine Hydrochloride CAS 101827-46-7View Details
Butenafine Hydrochloride CAS 101827-46-7View Details
101827-46-7 -
 Butenafine hydrochloride 98.00% CAS 101827-46-7View Details
Butenafine hydrochloride 98.00% CAS 101827-46-7View Details
101827-46-7 -
 Butenafine hydrochloride CAS 101827-46-7View Details
Butenafine hydrochloride CAS 101827-46-7View Details
101827-46-7 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
