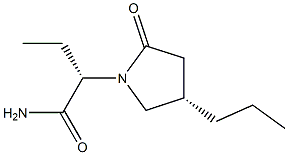
Brivaracetam
- CAS NO.:357336-20-0
- Empirical Formula: C11H20N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 212.29
- MDL number: MFCD13152385
- EINECS: 801-184-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-31 20:14:24

What is Brivaracetam?
Absorption
Nearly 100% oral bioavailability .
Toxicity
No carcinogenesis or fertility impairment found. Overdose is associated with somnolence and dizziness .
Description
Brivaracetam, a novel oral antiepileptic drug with a high affinity for synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A), was approved in Europe and the US as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalization in patients aged 16 or older.42 Brivaracetam is very closely related to levetiracetam, an antiepileptic treatment whose immediate release formulation has been available in the United States as a generic drug since 2008, but whose extended release formulation is under patent protection until 2028. The two drugs, which were both developed by UCB Pharma, are structurally similar with brivaracetam having an n-propyl group at the C-4 position of the pyrrolidinone ring and levetiracetam having a hydrogen at this same position. A systematic investigation of the various substitutions of levetiracetam resulted in the identification of more potent and selective SV2A ligands and ultimately culminated in the discovery of brivaracetam, which has greater affinity for SV2A, improved selectivity, more rapid brain penetration, and faster onset of action against seizures than levetiracetam.
The Uses of Brivaracetam
Brivaracetam, is a 4-n-propyl analog of levetiracetam (L331500), and a racetam derivative with anticonvulsant properties.
The Uses of Brivaracetam
Treatment ofTreatment of epilepsy, neuropathic pain and essential tremor.
Background
Brivaracetam is a racetam derivative of levetiracetam used in the treatment of partial-onset seizures. Brivaracetam binds SV2A with 20 times higher affinity than levetiracetam . It is available under the brand name Briviact made by UCB. Briviact received FDA approval on February 19, 2016 .
Indications
Used as adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures in patients 16 years of age or older.
Definition
ChEBI: A non-proteinogenic amino acid derivative that is butanamide in which the pro-S hydrogen at position 2 is replaced by a (4R)-2-oxo-4-propylpyrrolidin-1-yl. Used for treatment of partial onset seizures related to epilepsy.
Pharmacokinetics
Brivaracetam binds SV2A with high affinity . SV2A is known to play a role in epileptogenesis through modulation of synaptic GABA release . It is thought that brivaracetam exerts its anti-epileptogenic effects through its binding to SV2A. Brivaracetam is also known to inhibit Na+ channels which may also contribute to its anti-epileptogenic action .
Clinical Use
Antiepileptic agent
Side Effects
Common side effects of brivaracetam include: constipation, nausea, vomiting, extreme tiredness or low energy. Serious side effects that may be caused include: swelling of the face, throat, tongue, lips, and eyes; difficulty swallowing or breathing; hoarseness, hallucinations (seeing things or hearing sounds that are not there), and delusions (strange thoughts or beliefs that have no basis in reality). An overdose may cause: drowsiness, extreme tiredness, dizziness, difficulty maintaining balance, blurred or double vision, slowed heartbeat, nausea, and feeling anxious.
Synthesis
Two enantioselective routes have been reported, one employing
an enzymatic resolution and the other utilizing (R)-
(-)-epichlorohydrin as a chiral starting material. The route involves an enzymatic resolution,
is the only kilogram-scale route disclosed in the literature to
date and reportedly permits the production of brivaracetam
within the required commercial quality specifications. However,
the authors note that the development of this route for
commercial purposes has been stopped. Commercial
dimethyl n-propylmalonate 108 was first alkylated with tertbutyl-
2-bromoacetate. The resulting product underwent
Krapcho decarboxylation to afford racemic succinate derivative
109 in 94% yield over the two steps. Optimized conditions
for the key enzymatic resolution employed protease C from
Bacillus subtilis type 2 at 30 ??C for 18 h to resolve ester 109 and
provide the acid enantiomer 110. This biocatalytic process
allowed for residual unreacted diester 109 to be washed away
with cyclohexane at pH 9 (adjusted with 0.5 M NaOH), and
the desired acid 110 could be isolated upon lowering the pH
(??1) and extracting with isopropyl acetate (42% yield, 97% ee).
The transformation of acid 110 into propyllactone 111
proceeded in nearly quantitative yield by a three-step sequence:
activation of the acid with ethyl chloroformate, reduction to the
alcohol with sodium borohydride, and cyclization upon acidic
workup with TFA. Exposure of 111 to HBr in acetic acid
followed by esterification of the resulting acid-generated
bromoester 112. Finally, TBAI-catalyzed alkylation of 112
with commercial (S)-2-aminobutanamide (113) in refluxing
isopropyl acetate introduced the n-butylamide moiety while
facilitating lactamization. Addition of MTBE followed by filtration and recrystallization from isopropyl acetate afforded
brivaracetam (IX) in 32% yield and 96% ee.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration reduced by rifampicin.
Antidepressants: antagonism of anticonvulsant effect
(convulsive threshold lowered).
Antimalarials: mefloquine antagonises
anticonvulsant effect.
Antipsychotics: antagonism of anticonvulsant effect
(convulsive threshold lowered).
Orlistat: possibly increased risk of convulsions.
Metabolism
Primarily metabolized by hydrolysis of the acetamide moeity to form a carboxylic acid metabolite . Another metabolite is created via oxidation of the propyl side chain by CYP2C8 as well as CYP3A4, CYP2C19, and CYP2B6. Some conjugation with glucuronic acid and taurine account for a small amount of metabolism.
Metabolism
Brivaracetam is mainly metabolised by hydrolysis of the amide moiety to form the corresponding carboxylic acid (approximately 60% the elimination), and secondarily by hydroxylation on the propyl side chain (approximately 30% the elimination). The hydrolysis of the amide moiety leading to the carboxylic acid metabolite (34% of the dose in urine) is supported by hepatic and extra-hepatic amidase. The metabolites are inactive. Greater than 95% of the dose is excreted in the urine as brivaracetam and its metabolites.
Storage
Store at -20°C
Properties of Brivaracetam
| Melting point: | 76.38° |
| Boiling point: | 409.3±28.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D25 -60.57° (c = 1 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.062 |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 15.74±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| InChI | InChI=1/C11H20N2O2/c1-3-5-8-6-10(14)13(7-8)9(4-2)11(12)15/h8-9H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H2,12,15)/t8-,9+/s3 |
Safety information for Brivaracetam
Computed Descriptors for Brivaracetam
| InChIKey | MSYKRHVOOPPJKU-MASDURLHNA-N |
| SMILES | [C@H](N1C(C[C@@H](CCC)C1)=O)(CC)C(=O)N |&1:0,4,r| |
Brivaracetam manufacturer
SRINI PHARMACEUTICALS PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Brivaracetam 99%View Details
Brivaracetam 99%View Details -
 Brivaracetam 98%View Details
Brivaracetam 98%View Details -
 Brivaracetam 357336-20-0 98%View Details
Brivaracetam 357336-20-0 98%View Details
357336-20-0 -
 357336-20-0 98%View Details
357336-20-0 98%View Details
357336-20-0 -
 Brivaracetam 98%View Details
Brivaracetam 98%View Details -
 357336-20-0 Brivaracetam 98%View Details
357336-20-0 Brivaracetam 98%View Details
357336-20-0 -
 Brivaracetam 98%View Details
Brivaracetam 98%View Details -
 Brivaracetam CAS 357336-20-0View Details
Brivaracetam CAS 357336-20-0View Details
357336-20-0
