Benzo[k]fluoranthene
Synonym(s):11,12-Benzofluoranthene;2,3,1′,8′-Binaphthylene;8,9-Benzfluoranthene;Benzo[k]fluoranthene solution
- CAS NO.:207-08-9
- Empirical Formula: C20H12
- Molecular Weight: 252.31
- MDL number: MFCD00046287
- EINECS: 205-916-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 13:37:16
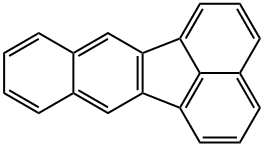
![Benzo[k]fluoranthene Structural](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/207-08-9.gif)
What is Benzo[k]fluoranthene?
Chemical properties
yellow crystals
The Uses of Benzo[k]fluoranthene
Benzo[k]fluoranthene is used as an optical sensor for nitro-aromatic compounds due to fluorescence quenching of the molecule. It is also a carcinogen and mutagen.
What are the applications of Application
Benzo[k]fluoranthene is an optical sensor for nitro-aromatic compounds, chosen due to fluorescence quenching of the molecule.
Definition
ChEBI: Benzo[k]fluoranthene is a member of naphthalenes.
General Description
Pale yellow needles or yellow crystalline solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
BENZO[K]FLUORANTHENE can react with strong oxidizing agents. May react with electrophiles, peroxides, nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides
Hazard
Possible carcinogen.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition BENZO(K)FLUORANTHENE emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Health Hazard
Benzo[k]fluoranthene caused lungs and skincancers in animals. It produced tumors atthe site of application. Its carcinogenicity inhumans is not known.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for BENZO(K)FLUORANTHENE are not available; however, BENZO(K)FLUORANTHENE is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen withexperimental tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported.When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke andirritating fumes.
Carcinogenicity
Benzo[k]fluoranthene wastested for carcinogenicity by dermal application in mice in one study, intraperitoneal injection into newborn mice in one study, and intrapulmonary implantation into rats in one study. Benzo[k]fluoranthene exhibited a significant carcinogenic activity in the dermal and intrapulmonary assays.
Source
Benzo[b]fluoranthene and benzo[k]fluoranthene were detected in 8 diesel fuels at
concentrations ranging from 0.0027 to 3.1 mg/L with a mean value of 0.266 mg/L (Westerholm
and Li, 1994). Also present in gasoline (9 μg/L), bitumen (34–1,140 μg/L), crude oil (<1 ppm)
(quoted, Verschueren, 1983), and coal (32.5 g/kg) (Lao et al., 1975).
Based on laboratory analysis of 7 coal tar samples, benzo[k]fluoranthene concentrations ranged
from 350 to 3,000 ppm (EPRI, 1990). Identified in high-temperature coal tar pitches used in
roofing operations at concentrations ranging from 1,670 to 4,500 mg/kg (Malaiyandi et al., 1982).
Nine commercially available creosote samples contained benzo[k]fluoranthene at concentrations
ranging from 2 to 67 mg/kg (Kohler et al., 2000).
Schauer et al. (2001) measured organic compound emission rates for volatile organic
compounds, gas-phase semi-volatile organic compounds, and particle phase organic compounds
from the residential (fireplace) combustion of pine, oak, and eucalyptus. The particle-phase
emission rates of benzo[k]fluoranthene were 0.671 mg/kg of pine burned, 0.303 mg/kg of oak
burned, and 0.286 mg/kg of eucalyptus burned.
California Phase II reformulated gasoline contained benzo[k]fluoranthene at a concentration of
280 μg/kg. Particle-phase tailpipe emission rate from a noncatalyst-equipped gasoline-powered
automobile was 32.7 μg/km (Schauer et al., 2002).
Under atmospheric conditions, a low rank coal (0.5–1 mm particle size) from Spain was burned
in a fluidized bed reactor at seven different temperatures (50 °C increments) beginning at 650 °C.
The combustion experiment was also conducted at different amounts of excess oxygen (5 to 40%) and different flow rates (700 to 1,100 L/h). At 20% excess oxygen and a flow rate of 860 L/h, the
amount of benzo[k]fluoranthene emitted ranged from 0 ng/kg at three temperatures (650, 750, and
950 °C) to 180.5 ng/kg at 850 °C. The greatest amount of PAHs emitted were observed at 750 °C
(Mastral et al., 1999).
Environmental Fate
Soil. Based on aerobic soil die-away test data, the half-life in soil ranged from 910 d to 5.86 yr
(Bossert et al., 1984).
Photolytic. The atmospheric half-life was estimated to range from 1.1 to 11 h (Atkinson, 1987).
Chemical/Physical. Benzo[k]fluoranthene will not hydrolyze because it has no hydrolyzable
functional group (Kollig, 1995).
Properties of Benzo[k]fluoranthene
| Melting point: | 215-217 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 480 °C |
| Density | 1.286 |
| vapor pressure | 9.59 x 10-11 mmHg at 25 °C (extrapolated from vapor pressures determined at higher temperatures, Puppet al., 1974) |
| refractive index | 1.8390 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 95% ethanol: <1mg/mL at 20°C |
| form | neat |
| pka | >15 (Christensen et al., 1975) |
| color | Pale yellow needles |
| Water Solubility | 1.09 μg/L at 25 °C (de Maagd et al., 1998) |
| BRN | 1873745 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.17, 4.24, 10.56, 13.62, 19.54, and 39.77 at 10.0, 20.0, 35.0, 40.1, 45.0, and 55.0 °C, respectively
(wetted-wall column, ten Hulscher et al., 1992) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 207-08-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 92) 2010 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzo[k]fluoranthene (207-08-9) |
Safety information for Benzo[k]fluoranthene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H350:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Benzo[k]fluoranthene
Benzo[k]fluoranthene manufacturer
GRK RESEARCH LABORATORIES PVT LTD
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![BENZO[CDE]RUBICENE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure21/GIF/CB6843052.gif)
![NAPHTHO[2,3-K]FLUORANTHENE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/207-18-1.gif)
![9-FLUOROBENZO[K]FLUORANTHENE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/113600-15-0.gif)
You may like
-
 207-08-9 98%View Details
207-08-9 98%View Details
207-08-9 -
 207-08-9 98%+View Details
207-08-9 98%+View Details
207-08-9 -
![Benzo[k]fluoranthene CAS 207-08-9](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) Benzo[k]fluoranthene CAS 207-08-9View Details
Benzo[k]fluoranthene CAS 207-08-9View Details
207-08-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1