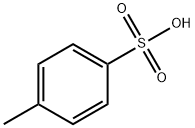
Benzenesulfonic acid
Synonym(s):Benzenesulfonic acid;Phenylsulfonic acid
- CAS NO.:98-11-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H6O3S
- Molecular Weight: 158.18
- MDL number: MFCD00011689
- EINECS: 202-638-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
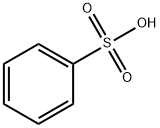
What is Benzenesulfonic acid?
Description
Benzene sulfonic acid is an organo sulfur compound with the formula C6H5SO3H. It is the simplest aromatic sulfonic acid. It forms colorless deliquescent sheet crystals or a white waxy solid that is soluble in water and ethanol, slightly soluble in benzene and insoluble in carbon disulfide and diethyl ether. It is often stored in the form of alkali metal salts. Its aqueous solution is strongly acidic.
Description
Benzenesulfonic acid is the simplest aromatic sulfonic acid. It is highly water-soluble and a strong acid with a pKa of –2.8. It has been known since at least the 1880s; its synthesis, which goes back to 1916, is via the reaction of benzene with hot concentrated sulfuric acid.
Benzenesulfonic acid is used to produce phenol by fusing it with sodium hydroxide or hydrolyzing one of its salts, usually sodium. Other uses include surfactants made with its metal or amine salts and as a counterion for cationic pharmaceuticals.
For additional information on benzenesulfonic acid’s properties and uses, see articles curated by ScienceDirect.
Chemical properties
green solid
History
Benzenesulfonic acid was first obtained, together with diphenyl sulfone, by E. M ITSCHERLICH in 1834 by heating benzene with fuming sulfuric acid. The industrially important reaction of benzenesulfonic acid with alkali hydroxide to form phenol (alkali fusion) was developed by A. WURTZ and A. KEKULé in 1867 and by P. O. D EGENER in 1878. Until the early 1960s benzenesulfonic acid was used chiefly in the manufacture of phenol. Other phenol syntheses are preferred now.
The Uses of Benzenesulfonic acid
Benzenesulfonic acid is mainly consumed by conversion to other specialty chemicals. A variety of pharmaceutical drugs are prepared as salts of benzenesulfonic acid and are known as besylates or besilates. The alkali metal salt of benzenesulfonic acid was once widely used in the production of phenol. It acts as an acid catalyst for direct esterification of amino acids and peptides.
The Uses of Benzenesulfonic acid
Benzenesulfonic acid is an aryl sulfonic acid that can be used to form an organic salt with 5,7-dimethyl-1,8-naphthyridine-2-amine, that can be a synthon for developing supramolecular structures. It can also act as a dopant for the polymerization of pyrrole to form poly(pyrrole), a conducting polymer useful in the development of flexible capacitors.
Definition
ChEBI: The simplest member of the class of a benzenesulfonic acids that consists of a benzene carrying a single sulfo group.
Definition
A white crystalline acid made by sulfonation of benzene. Any further substitution onto the benzene ring is directed into the 3 position.
Definition
benzenesulphonic acid: A colourlessdeliquescent solid, C6H5SO2OH,m.p. 43–44°C, usually found as anoily liquid. It is made by treating benzenewith concentrated sulphuricacid. Its alkyl derivatives are used asdetergents.
What are the applications of Application
The alkali metal salt of benzene sulfonic acid was once widely used in the production of phenol :
C6H5SO3Na + 2 NaOH → C6H5ONa + Na2SO3
C6H5ONa + HCl → C6H5OH + NaCl
The process has been largely displaced by the Hock process, which generates less waste. Benzene sulfonic acid is mainly consumed by conversion to other specialty chemicals. A variety of pharmaceutical drugs are prepared as salts of benzene sulfonic acid and are known as besylates or besilates.
Preparation
Benzene sulfonic acid is prepared from the sulfonation of benzene using concentrated sulfuric acid :
This conversion illustrates aromatic sulfonation, which has been called "one of the most important reactions in industrial organic chemistry.".
What are the applications of Application
Benzenesulfonic acids are used chiefly as intermediates. They are employed in the manufacture of sulfonic acid amides, hydrazides, and esters; of sulfinic acids, sulfones, phenols, and thiophenols; and of other compounds. Sulfonic acids that are substituted with OH and/or NH 2 groups serve as intermediates in the manufacture of finishing agents, optical brighteners, pickling agents, dyes, tanning agents, water-soluble resins, insecticides, ion-exchange resins, wetting agents, pharmaceuticals, polymeric thickeners, plasticizers, etc. Benzenesulfonic acids are also used as such as acidic catalysts and standardizing agents in dye manufacture.
Reactions
Benzene sulfonic acid exhibits the reactions typical of other aromatic sulfonic acids, forming sulfonamides , sulfonyl chloride, and esters. The sulfonation is reversed above 220 °C. Dehydration with phosphorus pentoxide gives benzene sulfonic acid anhydride ((C6H5SO2)2O). Conversion to the corresponding benzene sulfonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) is effected with phosphorus penta chloride. It is a strong acid, being dissociated in water.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 61, p. 1530, 1996 DOI: 10.1021/jo9520710
Tetrahedron Letters, 19, p. 1211, 1978 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)94501-0
General Description
Deliquescent needles or large plates.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Benzenesulfonic acid reacts with bases and many organic compounds. Benzenesulfonic acid has the characteristic reactions of a strong aromatic sulfonic acid. Acid hydrolysis at 175 ℃ splits it into benzene and sulfuricacid. Additional sulfonation with fuming sulfuric acid gives 1,3-benzenedisulfonic acid, which reacts further to 1,3,5-benzenetrisulfonic acid, and also diphenyl sulfone disulfonic acid.
Benzenesulfonic acid reacts with benzene to form diphenyl sulfone according to a Friedel – Crafts-type reaction.
Benzenesulfonic acid reacts with alkali metal hydroxide at 320 – 350 ℃ to form sodium phe- nolate. This reaction was used in the first industrial synthesis of phenol.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Benzenesulfonic acid are not available, however Benzenesulfonic acid is probably combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, sbn contact, and probably inhalation. A severe skin and eye irritant. See also SULFATES and SULFONATES.
Purification Methods
Purify benzenesulfonic acid by dissolving it in a small volume of distilled H2O and stirring with slightly less than the theoretical amount of BaCO3. When effervescence is complete and the solution is still acidic, filter off the insoluble barium benzenesulfonate. The salt is collected and dried to constant weight in vacuo, then suspended in H2O and stirred with a little less than the equivalent (half mol.) of sulfuric acid. The insoluble BaSO4 (containing a little barium benzenesulfonate) is filtered off and the filtrate containing the free acid is evaporated in a high vacuum. The oily residue will eventually crystallise when completely anhydrous. A 32% commercial acid is allowed to fractionally crystallise at room temperature over P2O5 in a vacuum desiccator giving finally colourless deliquescent plates m 52.5o. The anhydrous crystalline acid is deliquescent and should be stored over anhydrous Na2SO4 in the dark and should be used in subdued sunlight as it darkens under sunlight. The main impurity is Fe which readily separates as the Fe salt in the early fractions [Taylor & Vincent J Chem Soc 3218 1952]. The S-benzylisothiuronium salt has m 148o (from EtOH/H2O). It is an IRRITANT to the skin and eyes. [See Adams & Marvel Org Synth Coll Vol I 84 1941, Michael & Adair Chem Ber 10 585 1877, Beilstein 11 IV 27.]
Waste Disposal
Benzenesulfonic acid is biologically degradable. If the desired benzenesulfonic acid can be precipitated from sulfuric acid solution without salt being added, the spent acid can be upgraded in a sulfuric acid recovery plant. If the wastewater contains salts and nondegradable sulfonic acids, low-pressure wet oxidation is a possible method of treatment that subsequently allows effective degradation in wastewater treatment works.
Properties of Benzenesulfonic acid
| Melting point: | 30-60 °C |
| Boiling point: | 137℃ |
| Density | 1.32 |
| vapor pressure | 69.8Pa at 20℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5151 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble0.1g/10 mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Damp Crystalline Solid or Fused Mass |
| appearance | deliquescent white crystals or waxy solid |
| pka | 0.7(at 25℃) |
| color | Yellow to light brown |
| PH | 2 (H2O, 20℃)(saturated solution) |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1070 |
| BRN | 742513 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, bases, many organic compounds. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 98-11-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenesulfonic acid(98-11-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzenesulfonic acid (98-11-3) |
Safety information for Benzenesulfonic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Benzenesulfonic acid
| InChIKey | SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Benzenesulfonic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Ultra Pure Lab Chem Industries LLP
Jaiswal S Cyber Shop
Stratechem (India) Private Limited
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Benzenesulfonic Acid 98%View Details
Benzenesulfonic Acid 98%View Details -
 BENZENE SULPHONIC ACID 99%View Details
BENZENE SULPHONIC ACID 99%View Details -
 Benzenesulfonic acid CAS 98-11-3View Details
Benzenesulfonic acid CAS 98-11-3View Details
98-11-3 -
 Benzene Sulphonic AcidView Details
Benzene Sulphonic AcidView Details
98-11-3 -
 Off White To Grey Solid Or Semisolid Benzene Sulfonic Acid, 50kgView Details
Off White To Grey Solid Or Semisolid Benzene Sulfonic Acid, 50kgView Details
98-11-3 -
 LUMPS OR CRYSTAL Benzene Sulphonic Acid, 98% MinView Details
LUMPS OR CRYSTAL Benzene Sulphonic Acid, 98% MinView Details
98-11-3 -
 Benzene Sulphonic Acid, Purity: 90%, CAS Number: 98-11-3View Details
Benzene Sulphonic Acid, Purity: 90%, CAS Number: 98-11-3View Details
98-11-3 -
 JCSSUPER 98-11-3 Benzene Sulphonic Acid Extrapure 500 Gm.View Details
JCSSUPER 98-11-3 Benzene Sulphonic Acid Extrapure 500 Gm.View Details
98-11-3
