Bentonite
Synonym(s):K-Catalyst;Montmorillinite clay, bentonite;Montmorillonite;Nanomer clay;Nanomer PGV
- CAS NO.:1302-78-9
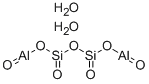
- Empirical Formula: Al2O3.4(SiO2).H2O
- Molecular Weight: 360.31
- MDL number: MFCD00130611
- EINECS: 215-108-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
What is Bentonite?
Description
Bentonite is a light yellow, creamy, palebrown or gray to black powder or granules. These chemicals contain 1- 24% crystalline silica (O2Si). Specificgravity (H2O:1)=2.5. Hazard Identification (based onNFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 1,Reactivity 0. Insoluble in water
Chemical properties
Bentonite is a light yellow, creamy, pale brown or gray to black powder or granules.
Chemical properties
Bentonite is a crystalline, claylike mineral, and is available as an odorless, pale buff, or cream to grayish-colored fine powder, which is free from grit. It consists of particles about 50–150 mm in size along with numerous particles about 1–2μm. Microscopic examination of samples stained with alcoholic methylene blue solution reveals strongly stained blue particles. Bentonite may have a slight earthy taste.
The Uses of Bentonite
bentonite (bentonite clay) is used to regulate the viscosity and suspension properties of a cosmetic formulation. It also acts as an overall formula stabilizer. Bentonite’s water-absorption capabilities allow it to form a gelatinous mass. Considered a noncomedogenic raw material, bentonite is a colloidal aluminum silicate clay.
The Uses of Bentonite
filler in cosmetics and other products, gel, or solid if dry
The Uses of Bentonite
As of Fuller's earth; as emulsifier for oils; as a base for plasters. Pharmaceutic aid (suspending agent).
The Uses of Bentonite
Bentonite is a general purpose additive that is used as a pigment and colorant and to clarify and stabilize wine.
What are the applications of Application
Bentonite is a suspending agent
Production Methods
Bentonite is a native, colloidal, hydrated aluminum silicate, found in regions of Canada and the USA. The mined ore is processed to remove grit and nonswelling materials so that it is suitable for pharmaceutical applications.
Definition
A type of clay that is used as an adsorbent in making paper. The gelatinous suspension it forms with water is used to bind together the sand for making iron castings. Chemically bentonite is an aluminosilicate of variable composition.
General Description
Bentonite is comprised primarily of the smectite group (montmorillonite) of clay minerals. It is widely used in various industrial applications such as clarification of edible and mineral oils, paints, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. It is also used as an adsorbent for the elimination of pollutants from wastewater.
The swelling property of bentonite is used to produce viscous water suspensions for bonding, plasticizing, and suspending applications. The presence of a large surface area of bentonite is due to the colloidal dispersion of the particles is the main reason for its application as an insecticide carrier, an emulsifier, and an emulsion stabilizer.
Agricultural Uses
Bentonite, also known as montmorillonite, volcanic
clay, soap clay and amargosite, is a soft, plastic, lightcolored,
porous rock consisting largely of colloidal
silica. Composed essentially of clay minerals, it swells
extensively when wet. Bentonite belongs chiefly to the
montmorillonite group and has two varieties: (a) sodium
bentonite, with a high swelling capacity in water, and
(b) calcium bentonite, with negligible swelling capacity.
Bentonite is used variously as a suspending aid, a
gelatinous slurry to extinguish fire, a paint thickener, and
as a sealant for earthen pots. Bentonite is also widely used
in metallurgy, soap manufacture, and in petroleum
refining because of its high decolorizing power and
strong adsorbing capacity.
Agricultural Uses
Clays exist in many forms, of which montmorillonite is
one form. Kaolinite and montmorillonite, which are clay
minerals, have different layer structures with differing
abilities to absorb and retain water, and to adsorb and
exchange cations.
Montmorillonites have an expanding structure (2: 1)
and have high cation exchange capacity (80 to 120 mg per
100 g). They have abundant black clay soils. Other
minerals in this group are biedellite and nontronite.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Bentonite is a naturally occurring hydrated aluminum silicate used
primarily in the formulation of suspensions, gels, and sols, for
topical pharmaceutical applications. It is also used to suspend
powders in aqueous preparations and to prepare cream bases
containing oil-in-water emulsifying agents.
Bentonite may also be used in oral pharmaceutical preparations,
cosmetics, and food products. In oral preparations,
bentonite, and other similar silicate clays, can be used to adsorb
cationic drugs and so retard their release. Adsorbents are also
used to mask the taste of certain drugs.
Bentonite has been investigated as a diagnostic agent for
magnetic resonance imaging.
Therapeutically, bentonite has been investigated as an adsorbent
for lithium poisoning.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route causing blood clotting. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data.
Safety
Bentonite is mainly used in topical pharmaceutical formulations but
has also been used in oral pharmaceutical preparations, food
products, and cosmetics.
Following oral administration, bentonite is not absorbed from
the gastrointestinal tract. Bentonite is generally regarded as a
nontoxic and nonirritant material.
LD50 (rat, IV): 0.035 g/kg
Potential Exposure
This material is used as Fuller’s earth; as a mineral, natural, or synthetic fiber; as an emulsifier for oils; as a base for plasters; in cosmetics, in polishes and abrasives; as a food additive and others. Bentonites are aluminate silicate and can contain crystalline silica. The content varies widely from less than 1% to about 24% .
First aid
Inhalatio Move person to fresh air. Seek medical attention if necessary. Skin: Wash with water. Eyes:Wash with water as needed. Seek medical attention if necesvsary.
Metabolism
Not Available
storage
Bentonite is hygroscopic, and sorption of atmospheric water should
be avoided.
Aqueous bentonite suspensions may be sterilized by autoclaving.
The solid material may be sterilized by maintaining it at 1708℃ for 1
hour after drying at 1008℃.
Bentonite should be stored in an airtight container in a cool, dry
place.
Shipping
Bentonite is not cited in the DOT Performance- Oriented Packaging Standards.
Incompatibilities
Substance is a weak acid in water; avoid contact with strong alkaline material. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Incompatibilities
Aqueous bentonite suspensions retain their viscosity above pH 6,
but are precipitated by acids. Acid-washed bentonite does not have
suspending properties. The addition of alkaline materials, such as
magnesium oxide, increases gel formation.
Addition of significant amounts of alcohol to aqueous preparations
will precipitate bentonite, primarily by dehydration of the
lattice structure.
Bentonite particles are negatively charged and flocculation
occurs when electrolytes or positively charged suspensions are
added. Bentonite is thus said to be incompatible with strong
electrolytes, although this effect is sometimes used beneficially to
clarify turbid liquids.
The antimicrobial efficacy of cationic preservatives may be
reduced in aqueous bentonite suspensions, but nonionic and anionic
preservatives are unaffected.
Bentonite is incompatible with acriflavine hydrochloride.
Waste Disposal
Land fill disposal.
Regulatory Status
Accepted in Europe as a food additive in certain applications. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral capsules, tablets and suspensions, topical suspensions, controlled release transdermal films and vaginal suppositories). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Bentonite
| Density | 2~3g/cm3 |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water and in aqueous solutions. It swells with a little water forming a malleable mass. |
| form | powder |
| color | Light yellow or green, cream,pink, gray to black solid |
| Odor | odorless, sl. earthy taste |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water and forms a colloidal solution. |
| Merck | 14,1055 |
| Dielectric constant | 8.1(Ambient) |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1302-78-9 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Bentonite (1302-78-9) |
Safety information for Bentonite
Computed Descriptors for Bentonite
Bentonite manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Neelam Aqua and Speciality Chem. P Ltd.
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
Shivam Minerals & Allied Industries Pvt. Ltd.
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 Bentonite 99%View Details
Bentonite 99%View Details -
 BENTONITE 98%View Details
BENTONITE 98%View Details -
 Bentonite pure CAS 1302-78-9View Details
Bentonite pure CAS 1302-78-9View Details
1302-78-9 -
 BENTONITE 99%View Details
BENTONITE 99%View Details -
 montmorillonite clay 98%View Details
montmorillonite clay 98%View Details -
 Bentonite 99%View Details
Bentonite 99%View Details -
 Bentonite CAS 1302-78-9View Details
Bentonite CAS 1302-78-9View Details
1302-78-9 -
 Bentonite Powder CAS 1302-78-9View Details
Bentonite Powder CAS 1302-78-9View Details
1302-78-9
