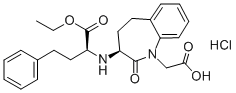
Benazepril
- CAS NO.:86541-75-5
- Empirical Formula: C24H28N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 424.49
- MDL number: MFCD00864466
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-07-02 08:55:11

What is Benazepril?
Absorption
Bioavailability of oral dosing is 3% to 4% in horses. In humans at least 37% of oral benazepril is absorbed and reaches peak plasma concentration in 0.5 hours to 1 hour. Other studies have shown a peak plasma concentration at a median of 1.5 hours.
Toxicity
The most common adverse effects include headache, dizziness, fatigue, somnolence, postural dizziness, nausea, and cough.
The most likely symptom of overdosage is severe hypotension.
Originator
Lotensin,Novartis
The Uses of Benazepril
Benazepril Free base is a non-sulfhydryl ACE inhibitor.
What are the applications of Application
Benazepril Free base is a non-sulfhydryl ACE inhibitor
Background
Benazepril, brand name Lotensin, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), congestive heart failure, and chronic renal failure. Upon cleavage of its ester group by the liver, benazepril is converted into its active form benazeprilat, a non-sulfhydryl angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor.
Indications
Benazepril is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with thiazide diuretics.
Definition
ChEBI: A benzazepine that is benazeprilat in which the carboxy group of the 2-amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid moiety has been converted to the corresponding ethyl ester. It is used (generally as its hydrochloride salt) as a prodrug for the angiotensin-converting enzy e inhibitor benazeprilat in the treatment of hypertension and heart failure.
Manufacturing Process
The synthesis of benzazepril based on a benzazepinone. It started by chlorination of lactam - 1,2,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-2-one to the dichloro derivative 3,3-dichloro-1,2,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-2-one. Catalytic reduction removed one of the gem chloro substituents to give 3- chloro-1,2,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-2-one; the halogen was then displaced with sodium azide to give 3-azido-1,3,4,5- tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-2-one. Alkylation of the amide with ethyl bromoacetate in the presence of base yielded the ester (3-azido-2-oxo- 2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-1-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester. Hydrogenation then converted the azide to an amino group to give 3-amino-2-oxo-2,3,4,5- tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-1-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester. It was then resolved by classical salt formation and crystallization. Saponification of the S enantiomer - S-(3-amino-2-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-1-yl)acetic acid ethyl ester with sodium hydroxide afforded (3-amino-2-oxo-2,3,4,5- tetrahydrobenzo[b]azepin-1-yl)acetic acid. Reductive alkylation of it with 2- oxo-4-phenylbutyric acid ethyl ester and sodium cyanoborohydride gave the desired product as 70:30 mixture of diastereoisomers. The isolation of the predominant isomer gave benazepril. The epimerization occurred thermally and therefore required a sufficiently high temperature. The high temperature condition can be achieved by either using a high boiling-point solvent such as xylene or by heating the reaction mixture under pressure to increase its boiling-point temperature. Good results can be achieved in both polar and non-polar solvent systems. For example, both p-xylene and ethylene glycolwater systems are found suitable to conduct this process. The crude product acid 3-[(1-ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenyl-(1S)-propylamino]-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-2- oxo-1H-1-benzazepine-1-acetic acid was heated to reflux temperature for 30 hours in p-xylene. The mixture was cooled down to room temperature. Solvent removal resulted in a solid, which was then dried at reduced pressure to give a 98:2 diasteriomeric mixture as determined by HPLC, MP: 287°- 290°C. IR and 1H-NMR spectrum analysis. was confirmed the structure of product.
Therapeutic Function
Antihypertensive
Pharmacokinetics
Benazepril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, is a prodrug which, when hydrolyzed by esterases to its active Benazeprilat, is used to treat hypertension and heart failure, to reduce proteinuria and renal disease in patients with nephropathies, and to prevent stroke, myocardial infarction, and cardiac death in high-risk patients. Benazepril and Benazeprilat inhibit angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) in human subjects and animals. ACE is a peptidyl dipeptidase that catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin I to the vasoconstrictor substance, angiotensin II. Angiotensin II also stimulates aldosterone secretion by the adrenal cortex.
Enzyme inhibitor
This ACE-directed pro-drug (FWfree-acid = 424.50 g/mol; CAS 86541-75-5), also known as 3-((1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl)amino)-2,3,4,5- tetrahydro-2-oxo-(S-(R*,R*))-1H-1-benzazepine-1-acetic acid, Lotensin and CGS 14824A, is rapidly metabolized to its diacid benazeprilat (CGS 14831; FWfree-diacid = 396.44 g/mol), the latter a potent, long-acting inhibitor of peptidyl-dipeptidase A, or angiotensin I-converting enzyme, IC50 = 1.7 nM. Lotensin is used to treat hypertension, congestive heart failure, and chronic renal failure. The antihypertensive effects of benazepril begin as early as 30 min after a single dose, and those effects during consecutive dosing are also sustained for 24 h with a lesser diurnal variation in blood pressure
Metabolism
Cleavage of the ester group (primarily in the liver) converts benazepril to its active metabolite, benazeprilat. Benazepril and benazeprilat are conjugated to glucuronic acid prior to urinary excretion.
Properties of Benazepril
| Melting point: | 148-149° |
| Boiling point: | 691.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D -159° (c = 1.2 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1.26±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| pka | 3.73±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 86541-75-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Benazepril
Computed Descriptors for Benazepril
Benazepril manufacturer
Alfa Omega Pharma
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 86541-75-5 Benazepril 98%View Details
86541-75-5 Benazepril 98%View Details
86541-75-5 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1