BAUXITE
- CAS NO.:1318-16-7
- Empirical Formula: Al2H2O4
- Molecular Weight: 119.98
- MDL number: MFCD01741757
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
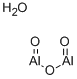
What is BAUXITE?
Description
Bauxite is the major source of aluminum sesquioxide (alumina, Al2O3) worldwide. Bauxite is
a soft and red clay, rich in alumina. From a geological point of view bauxite is defined as a residual
sedimentary rock in the laterite family that results from in situ superficial weathering in moist tropical climates of clays, clayey limestones, or high-alumina-content silicoaluminous
igneous and metamorphic rocks containing feldspars and micas.
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock, so it has neither a precise
definition nor chemical formula. From a mineralogical point of view, bauxite is mainly composed of hydrated alumina minerals such as gibbsite [Al(OH)3 or Al2O3.3H2O, monoclinic] in
recent tropical and equatorial bauxite deposits, while boehmite [AlO(OH) or Al2O3.H2O, orthorhombic] and, to a lesser extent, diaspore [AlO(OH) or Al2O3
.H2O, orthorhombic] are the
major minerals in subtropical and temperate bauxite old deposits. The average chemical
composition of bauxite is 45 to 60 wt.% Al2O3
and 10 to 30 wt.% Fe2O3, the remainder consisting of silica, calcia, titanium dioxide, and water.
Chemical properties
solid
Chemical properties
Bauxite consists mainly of gibbsite, Al(OH)3, and varying amounts of kaolinite, and iron and titania impurities. Because the loss on ignition is high, bauxite must be calcined to high temperatures before use. During calcination, it is converted to a dense grain consisting mainly of corundum, Al2O3, and mullite.
The Uses of BAUXITE
Absorbent catalysts
The Uses of BAUXITE
Ore for production of alumina; adsorbent in oil refining
Definition
A natural aggregate of aluminumbearing minerals, more or less impure, in which the aluminum occurs largely as hydrated oxides. It is usually formed by prolonged weathering of aluminous rocks. Contains 30–75% Al2O 3 , 9–31% H2O, 3–25% Fe2O 3 , 2–9%, SiO2, 1–3% Ti O 2 .
Definition
A mineral hydrated form of aluminum hydroxide; the principal ore of aluminum.
What are the applications of Application
Bauxite is the best raw material for the production of alumina and aluminium. More than 95 per cent of the world's alumina is extracted from bauxite using the Bayer process. Therefore, it is mainly used for the production of primary aluminium metal. The following diagram shows the flow chart for aluminium production:
Health Hazard
Bauxite can be considered to be
a nuisance particulate; long experience with
mining and refining of bauxite has not revealed
significant adverse health effects.
Nuisance particulates have little adverse
effect on lungs and do not produce significant organic disease or toxic effect when exposures
are kept under reasonable control.
Safety Profile
A nuisance dust. Human systemiceffects by inhalation: fibrosis, focal (pneumoconiosis).
Properties of BAUXITE
| Density | 2.275 |
| form | Dust (red, brown, or yellow) |
| color | Buff to orange solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Dielectric constant | 2.5(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1318-16-7 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Bauxite (1318-16-7) |
Safety information for BAUXITE
Computed Descriptors for BAUXITE
BAUXITE manufacturer
Krishnaraj Chemicals Pvt Ltd
Shivam Minerals & Allied Industries Pvt. Ltd.
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Bauxite 99%View Details
Bauxite 99%View Details -
 1318-16-7 99%View Details
1318-16-7 99%View Details
1318-16-7 -
 Bauxite 98%View Details
Bauxite 98%View Details
1318-16-7 -
 Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
1318-16-7 -
 Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
1318-16-7 -
 Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
1318-16-7 -
 Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
Bauxite CAS 1318-16-7View Details
1318-16-7 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0