Azathioprine
Synonym(s):6-(1-Methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thiopurine;6-[(1-Methyl-4-nitro-1H imidazol-5yl) sulfanyl]-7H-purine
- CAS NO.:446-86-6
- Empirical Formula: C9H7N7O2S
- Molecular Weight: 277.26
- MDL number: MFCD00069203
- EINECS: 207-175-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
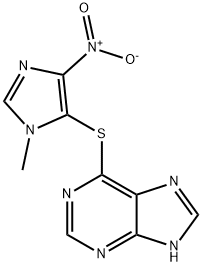
What is Azathioprine?
Absorption
Oral azathioprine is well absorbed, with a Tmax of 1-2h. Further data regarding the absorption of azathioprine is not readily available.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in mice is 2500mg/kg and in rats is 400mg/kg.
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with bone marrow hypoplasia, bleeding, and infection, which may progress to death. Patients should be treated with supportive and symptomatic treatments. 8 hour hemodialysis may remove 45% of a dose from serum.
Chemical properties
Yellow Solid
Chemical properties
Azathioprine is a complex heterocyclic compound which forms pale yellow crystals.
Originator
Imuran,Wellcome,UK,1964
The Uses of Azathioprine
An immunosuppressive antimetabolite. Also active as disease modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD). Azathioprine is a purine analog with immunosuppressive effects.
The Uses of Azathioprine
immunosuppressant, antineoplastic, antirheumatic
The Uses of Azathioprine
Azathioprine is an immunosuppressive purine antimetabolite. The mechanism of action of azathioprine is as a nucleic acid synthesis inhibitor. It has shown promise in treatment of alopecia areata (autoimmune hair loss), with no difference in effectiveness between genders.
Background
Azathioprine is a prodrug of 6-mercaptopurine, first synthesized in 1956 by Gertrude Elion, William Lange, and George Hitchings in an attempt to produce a derivative of 6-mercaptopurine with a better therapeutic index. Azathioprine is used to treat inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and as an immunosuppressant in the prevention of renal transplant rejection.
Azathiprine was granted FDA approval on 20 March 1968.
Indications
Azathioprine is indicated to treat rheumatoid arthritis and prevent renal transplant rejection.
Definition
ChEBI: A thiopurine that is 6-mercaptopurine in which the mercapto hydrogen is replaced by a 1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl group. It is a prodrug for mercaptopurine and is used as an immunosuppressant, prescribed for the treatment of inflammatory conditions and a ter organ transplantation and also for treatment of Crohn's didease and MS.
Indications
Azathioprine (Imuran) is a cytotoxic agent that preferentially destroys any rapidly dividing cell. Since immunologically competent cells are generally rapidly dividing cells, azathioprine is very effective as an immunosuppressive drug. Unfortunately, any cell that is replicating is a target for this action. This lack of specificity leads to serious side effects. Azathioprine, in combination with corticosteroids, has historically been used more widely than any other drug in immunosuppressive therapy. It is classified as a purine antimetabolite and is a derivative of 6-mercaptopurine.
Manufacturing Process
N,N'-Dimethyloxaldiamide is reacted with PCl5, to give 4-chloro-1-methyl
imidazole. This is nitrated with HNO3 to give 5-nitro-1-methyl-4-
chloroimidazole. Then, a mixture of 4.6 grams of anhydrous 6-
mercaptopurine, 5 grams of 1-methyl-4-chloro-5-nitroimidazole and 2.5 grams
of anhydrous sodium acetate in 100 ml of dry dimethyl sulfoxide was heated
at 100°C for 7 hours.
After standing overnight at room temperature, the mixture was poured into
200 ml of cold water and the yellow precipitate of 6-(1'-methyl-4'-nitro-5'-
imidazolyl)mercaptopurine (7.0 grams) collected. After recrystallization from
50% aqueous acetone, the product melted at 243-244°C, dec., and had an UV
spectrum with λ maximum = 280 nm at pH 1 and λ max. = 285 nm at pH 11.
brand name
Imuran (Promethus).
Therapeutic Function
Immunosuppressive
General Description
Pale yellow crystals or yellowish powder. Decomposes at 243-244°C. Used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A known carcinogen.
Air & Water Reactions
Sensitive to oxidation in the air. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Azathioprine may react exothermically with acids. Incompatible with isocyanates, peroxides, phenols, epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Hydrolyzed by strongly basic solutions . May react with strong reducing agents to generate flammable gaseous hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide.
Hazard
Confirmed carcinogen.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Azathioprine are not available. Azathioprine is probably combustible.
Contact allergens
This immunosuppressive and antineoplastic drug is derived from 6-mercaptopurine. It caused allergic contact dermatitis in a mother crushing tablets for her leukemic son, and occupational dermatitis in a pharmaceutical reconditioner of old tablet packaging machines, and in a production mechanic working in packaging for a pharmaceutical company.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Has shown promise in treatment of alopecia areata (autoimmune hair loss), with no difference in effectiveness between genders.
Mechanism of action
Azathioprine is a phase-specific drug that is toxic to
cells during nucleic acid synthesis. Phase-specific drugs
are toxic during a specific phase of the mitotic cycle,
usually the S-phase, when DNA synthesis is occurring,
as opposed to cycle-specific drugs that kill both cycling
and intermitotic cells.
Azathioprine is converted in vivo to thioinosinic
acid, which competitively inhibits the synthesis of inosinic
acid, the precursor to adenylic acid and guanylic
acid. In this way, azathioprine inhibits DNA synthesis
and therefore suppresses lymphocyte proliferation.This
effectively inhibits both humoral and cell-mediated immune
responses.
Pharmacokinetics
Azathioprine is an immunosuppressive agent which functions through modulation of rac1 to induce T cell apoptosis, as well as other unknown immunosuppressive functions. It has a long duration of action as it is given daily, and has a narrow therapeutic index. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of malignancies of the skin and lymphomas.
Pharmacology
Azathioprine is well absorbed following oral administration, with peak blood levels occurring within 1 to 2 hours. It is rapidly and extensively metabolized to 6- mercaptopurine, which is further converted in the liver and erythrocytes to a variety of metabolites, including 6- thiouric acid. Metabolites are excreted in the urine.The half-life of azathioprine and its metabolites in the blood is about 5 hours.
Clinical Use
Azathioprine is a relatively powerful antiinflammatory
agent. Although its beneficial effect in various conditions
is principally attributable to its direct immunosuppressive
action, the antiinflammatory properties of the
drug play an important role in its overall therapeutic effectiveness.
Azathioprine has been used widely in combination
with corticosteroids to inhibit rejection of organ transplants,
particularly kidney and liver allografts. However,
it is usually reserved for patients who do not respond to
cyclosporine plus corticosteroids alone.
Azathioprine also has applications in certain disorders
with autoimmune components, most commonly
rheumatoid arthritis. It is as effective as cyclophosphamide
in the treatment of Wegener’s granulomatosis.
It has largely been replaced by cyclosporine in immunosuppressive
therapy. Relative to other cytotoxic
agents, the better oral absorption of azathioprine is the
reason for its more widespread clinical use.
Side Effects
The therapeutic use of azathioprine has been limited by the number and severity of adverse effects associated with its administration. Bone marrow suppression resulting in leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or both may occur. GI toxicity may be a problem. It is also mildly hepatotoxic. Because of its immunosuppressive activity, azathioprine therapy can lead to serious infections. It has been shown to be mutagenic in animals and humans and carcinogenic in animals.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen producing bladder tumors and leukemia. Poison by subcutaneous, intradermal, and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Human systemic effects: liver changes, hypermotility, diarrhea, nausea or vomiting, increased body temperature, BP lowering, decreased urine volume or anuria, normocytic anemia, bone marrow changes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NO,xand SOx. An immunosuppressant.
Synthesis
Azathioprine, 6-[(1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol-5-yl)thio]purine (31.2.1), is synthesized by heteroarylation of the sulfhydrile group of 6-mercaptopurine (30.1.2.9) with 5-chloro-1-methyl-4-nitroimidazol in the presence of sodium acetate as a weak base.

Potential Exposure
Azathioprine is an immunosuppressive agent, generally used in combination with a corticosteroid to prevent rejection following renal homotransplantations. It also is used following transplantation of other organs. Other uses of azathioprine include the treatment of a variety of presumed autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; systemic lupus erythematosus; dermatonyositis, periarteritis nodosa, scleroderma, refractory thombocytopenic purpura; autoimmune hemolytic anemia; chronic active liver disease; regional enteritis; ulcerative colitis; various autoimmune diseases of the eye; acute and chronic glomerulonephritis; the nephritic syndrome; Wegener’s granulomatosis; and multiple sclerosis.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In veterinary medicine, azathioprine is used primarily as an immunosuppressive
agent in the treatment of immune-mediated
diseases in dogs. See Doses below for more information. For autoagglutinizing
immune mediated hemolytic anemia, azathioprine is
generally recommended to start at the time of diagnosis. When used
in combination with cyclosporine, azathioprine has been used to
prevent rejection of MHC-matched renal allografts in dogs.
Although the drug can be very toxic to bone marrow in cats, it is
sometimes used to treat feline autoimmune
skin diseases.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Allopurinol: enhances effect with increased
toxicity. Reduce azathioprine dose by 50-75% if
administered concomitantly - ideally avoid.
Antibacterials: increased risk of haematological
toxicity with co-trimoxazole.
Anticoagulants: possibly reduced anticoagulant effect
of coumarins.
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine.
Antivirals: myelosuppressive effects enhanced by
ribavirin.
Ciclosporin: decreased ciclosporin absorption and
bioavailability.
Cytotoxics may be additive or synergistic in
producing toxicity, particularly on the bone marrow.
Febuxostat: avoid concomitant use.
Vaccines: risk of generalised infections with live
vaccines - avoid.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate with water or normalsaline immediately for at least 20°30 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts the skin, removecontaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap andwater. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemicalhas been inhaled, remove from exposure, begin rescuebreathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR if heart actionhas stopped. Transfer promptly to a medical facility. Whenthis chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention.Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do notmake an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
Azathioprine is known to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans.
Metabolism
Azathioprine is converted to 6-mercaptopurine nonenzymatically. 6-mercaptopurine is then metabolized to 6-methylmercaptopurine by thiopurine methyltransferase, 6-thiouric acid by xanthine oxidase, or 6-thiosine-5'-monophosphate by hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. 6-thiosine-5'-monophosphate is metabolized to 6-methylthiosine-5'-monophosphate by thiopurine methyltransferase or 6-thioxanthylic acid by inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase. 6-thioxanthylic acid is metabolized by guanosine monophosphate synthetase to 6-thioguanine monophosphate, the first of the 6-thioguanine nucleotides. 6-thioguanine monophosphate is phosphorylated to produce the remaining 6-thioguanine nucleotides, 6-thioguanine diphosphate and 6-thioguanine triphosphate.
Metabolism
Azathioprine is extensively metabolised to its active moiety mercaptopurine, which in turn is activated intracellularly by conversion to nucleotide derivatives. Mercaptopurine is rapidly and extensively metabolised in the liver, by methylation, oxidation and by the formation of inorganic sulfates. Thiol methylation is catalysed by the enzyme thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT). TPMT activity is highly variable in patients because of a genetic polymorphism in the TPMT gene. About 10% of a dose of azathioprine is reported to be split between the sulfur and the purine ring to give 1-methyl-4-nitro-5-thioimidazole. The proportion of different metabolites is reported to vary between patients. Metabolites and small amounts of unchanged azathioprine and mercaptopurine are eliminated in the urine.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store ina secure poison location. Prior to working with this chemicalyou should be trained on its proper handling and storage.Store in a refrigerator under an inert atmosphere. A regulated, marked area should be established where this chemicalis handled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHAStandard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with reducing agents, such as hydrides (may cause the release of explosive gases), oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong acids (violent exothermic reaction), strong bases.
Properties of Azathioprine
| Melting point: | 243-244°C |
| Boiling point: | 521.0±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.5379 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in Dichloromethane and dimethyl sulfoxide. |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 8.2(at 25℃) |
| color | Pale-yellow crystals from Me2CO (aq) |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
| Merck | 14,902 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 446-86-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 1 (Vol. 26, Sup 7, 100A) 2012 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Azathioprine (446-86-6) |
Safety information for Azathioprine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Azathioprine
| InChIKey | LMEKQMALGUDUQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Azathioprine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Azathioprine 446-86-6 98%View Details
Azathioprine 446-86-6 98%View Details
446-86-6 -
 446-86-6 98%View Details
446-86-6 98%View Details
446-86-6 -
 Azathioprine 98%View Details
Azathioprine 98%View Details
446-86-6 -
 Azathioprine 446-86-6 99%View Details
Azathioprine 446-86-6 99%View Details
446-86-6 -
 Azathioprine 98%View Details
Azathioprine 98%View Details
446-86-6 -
 Azathioprine 98.00% CAS 446-86-6View Details
Azathioprine 98.00% CAS 446-86-6View Details
446-86-6 -
 Azathioprine CAS 446-86-6View Details
Azathioprine CAS 446-86-6View Details
446-86-6 -
 Azathioprine CAS 446-86-6View Details
Azathioprine CAS 446-86-6View Details
446-86-6
