Azadirachtin
- CAS NO.:11141-17-6
- Empirical Formula: C35H44O16
- Molecular Weight: 720.71
- MDL number: MFCD00210582
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
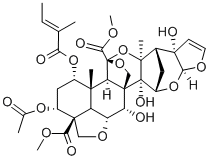
What is Azadirachtin?
Description
Kernel extracts from the Indian neem tree (Azadirachta indica) have insecticidal and insect-repellent properties. The key active ingredient is azadirachtin, a nortriterpenoid that exhibits insect growth regulator effects but no adulticidal activity.
Description
Azadirachtin is an impressive molecule. It contains eight rings (five of which incorporate oxygen atoms), 16 chiral centers, and three quaternary carbon atoms. Its functionalities include a hydroxyl group, an enol ether, an acetal, two hemiacetals, an epoxide, and four carboxylic acid esters.
Synthetic organic chemists had a tough time synthesizing azadirachtin, but it came naturally to the neem tree (Azadirachta indica), a member of the mahogany family that grows in India, Iran, and parts of Africa. Azadirachtin, along with many related compounds, is found in neem seeds, leaves, and bark. Its biosynthetic pathway has not been completely elucidated.
For centuries, the seeds and leaves of A. indica have been known to repel harmful insects from agricultural crops. In the 1960s, chemists began to study neem seed extracts to determine the active ingredients. J. H. Butterworth and E. D. Morgan at the University of Keele (UK) identified azadirachtin as the key molecule in 1968. Stephen V. Ley and four co-workers at the University of Cambridge (UK) completed its prodigious total synthesis in 2007.
Azadirachtin is a white microcrystalline solid with a strong garlicky or sulfurous odor, which is a bit strange because it contains no sulfur. Perhaps the odor is what repels insects. In any case, neem oil (extracted from the seeds) is used in many commercial pesticides and growth regulators. Although azadirachtin has some toxic properties (see hazard information table), it is harmless to mammals in the amounts normally used. As the table also shows, however, it brings some environmental concerns.
Azadirachtin has another, perhaps unexpected, use. Much of the Indian population chews neem twigs or uses them as brushes to clean their teeth. Taking things further, neem bark, leaves, and oil are used in many “natural” toothpastes. You can purchase all of these products in health food stores or online.
Chemical properties
Off-white, yellowish powder or dark brown emulsifiable concentrate.
The Uses of Azadirachtin
Azadirachtin is a tetranortriterpinoid isolated from the seeds of the neem tree. Highly active insect feeding deterrent and growth regulator.It is used experimentally as insect control agent.
The Uses of Azadirachtin
Azadiractin is extracted from the neem tree (Azadirachta indica). It is the principal active ingredient of extracts of neem. Neem extracts and pure azadirachtin are used to control whitefly, leaf miners and other pests including pear psylla.
What are the applications of Application
Azadirachtin is a highly oxidized tetranortriterpenoid
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the family of azadirachtins that is isolated from the neem tree (Azadirachta indica).
Agricultural Uses
Insecticides, Nematicide: Azadirachtin is an extract of fruit from the Neem tree, which is largely grown in India. It is used as a commercial insect growth regulator that controls the metamorphosis process as the insect passes from the larva stage to the pupa stage. The Neem tree also yields extracts from its bark, leaves and wood that are used in medicine and cosmetics.
Trade name
ALIGN®; AZATIN EC®; AZATIN®-XL PLUS; AZATROL EC®; AMAZIN® ECOZIN® EI- 783®; MARGOSAN-O®; NEEM®; NEEMAZAL®; ORNAZIN® SALANNIN®; SUPERNEEM®; TURPLEX®
Biochem/physiol Actions
Triterpenoid found in need tree seeds, azadiractin suppresses feeding by many insect species and disrupts growth of most insect and other arthropod species, while having very low mammalian toxicity. Promising as a natural pesticide.
Potential Exposure
Biological tetranortriterpinoid insecticide; insect growth regulator. A natural product extracted from seeds of the Neem tree (Azadirachta indica).
Metabolic pathway
The natural insecticide azadirachtin is most stable in mildly acidic solutions between pH 4 and 6 at room temperature and unstable in alkaline and strong acidic conditions. While azadirachtin is relatively stable to heating in the seeds or as a pure solid, it is rapidly destroyed or altered by heating in aqueous solution and methanol. In methanol at 90°C, it is quantitatively converted to 3-acetyl-1-tigloylazadirachtinin.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
After 90 hours exposure to UV radiation, very little azadirachtin (l)its 3-
acetyl derivative and 22,23-dihydroazadirachtin remained intact. However,
these compounds retained biological activity, and at least 200 hours
irradiation was necessary to reduce the biological activity of 1. It is suggested
that the effect of ultraviolet radiation is confined to the tigloyl
residue which is common to these three compounds and which may
undergo cis-trans isomerisation, rearrangement, etc. without significant
effect on the biological activity of the molecule, because reduction or
removal of the tigloyl residue causes only limited reduction in biological
activity of the parent (Barnby ef al., 1989).
Azadirachtin was hydrolysed readily in several buffers (pH 4.1-8.1)
and natural waters (pH 6.2,7.3,8.0 and 8.1) at 35 °C and its disappearance
followed pseudo-first-order kinetics (Szeto and Wan, 1996). Rates of
disappearance of the parent were faster in basic than in acidic solution
(DT50 was 12 hours at pH 8 and 206 hours at pH 6) and the compound is
not expected to be persistent in water.
Mode of action
Azadirachtin acts on insect gustatory receptors to inhibit feeding, and also interferes with development by inhibiting synthesis of the neuropeptide that triggers ecdysone release. The molecular targets mediating these effects are not known.
Toxicity evaluation
Azadirachtin is practically non-toxic to mammals, birds and plants. It is moderately toxic to aquatic invertebrates, but exposure is negligible due to low application rates and rapid degradation. Since it is only active by ingestion of treated foliage, exposure of non-target insects and honeybees is minimal.
Incompatibilities
Powder or liquid may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, reducing agents and metals, acid chlorides, alkalis, alkali metals, high heat, including sunlight.
Waste Disposal
Waste product may be disposed of onsite (open dumping may be prohibited) or at an approved waste disposal facility. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of Azadirachtin
| Melting point: | 159°C |
| Boiling point: | 792.4±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D -53° (c = 0.5 in CHCl3) |
| Density | 1.51 |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Sparingly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| appearance | white microcrystalline solid |
| pka | 9.78±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to Pale Yellow |
| Merck | 13,896 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 11141-17-6 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Azadirachtin A (11141-17-6) |
Safety information for Azadirachtin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Azadirachtin
| InChIKey | TWGPOIQWWGNBKW-POEZYEDVSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Azadirachtin 11141-17-6View Details
Azadirachtin 11141-17-6View Details -
 Azadirachtin 98%View Details
Azadirachtin 98%View Details
11141-17-6 -
 11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6 99%View Details
11141-17-6 -
 Azadirachtin 98%View Details
Azadirachtin 98%View Details
11141-17-6 -
 Azadirachtin, 95% CAS 11141-17-6View Details
Azadirachtin, 95% CAS 11141-17-6View Details
11141-17-6 -
 Azadirachtin CAS 11141-17-6View Details
Azadirachtin CAS 11141-17-6View Details
11141-17-6 -
 Azadirachtin CAS 11141-17-6View Details
Azadirachtin CAS 11141-17-6View Details
11141-17-6 -
 Azadirachtin Technical PowderView Details
Azadirachtin Technical PowderView Details
11141-17-6
