ANILAZINE
Synonym(s):6-(2-Chloroanilino)-2,4-dichloro-1,3,5-triazine
- CAS NO.:101-05-3
- Empirical Formula: C9H5Cl3N4
- Molecular Weight: 275.52
- MDL number: MFCD00041815
- EINECS: 202-910-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
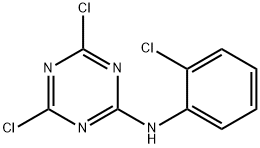
What is ANILAZINE?
Chemical properties
white to light brown crystals or powder
The Uses of ANILAZINE
Pesticide used to control fungus diseases in lawns and turf.
The Uses of ANILAZINE
Fungicide.
The Uses of ANILAZINE
Nonsystemic, foliar fungicide used in potatoes, tomatoes, wheat, barley and ornamentals.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of triazenes that is dichlorotriazene in which the hydrogen is replaced by an o-chloroanilino group. A fungicide formerly used to control leaf spots and downy mildew, it is no longer approved for use within the European U ion.
General Description
White to tan crystals or white powder. Moderately soluble in organic solvents. Insoluble in water. Melting point 159°C.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water. Stable in neutral and slightly acidic aqueous media but hydrolyzes on heating with alkali.
Reactivity Profile
ANILAZINE is incompatible with oils and alkalis. ANILAZINE is slightly corrosive to metals.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for ANILAZINE are not available; however, ANILAZINE is probably combustible.
Environmental Fate
Soil. Anilazine is readily degraded by soil bacteria (Harris et al., 1968). The reported
half-life of anilazine in soil is approximately 12 hours (Hartley and Kidd, 1987)
Plant. In plants, one or both of the chlorine atoms on the triazine ring may be replaced
by thio or amino groups (Hartley and Kidd, 1987)
Chemical/Physical. Anilazine is subject to hydrolysis (Windholz et al., 1983) releasing
chlorine gas (Hartley and Kidd, 1987)
Properties of ANILAZINE
| Melting point: | 159-160℃ |
| Boiling point: | 425.99°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.611 |
| refractive index | 1.6000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| form | neat |
| pka | 0.43±0.10(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 10mg/L(temperature not stated) |
| Merck | 13,659 |
| BRN | 223133 |
| Exposure limits | The German Research Society’s recommended Maximum Allowable
Concentration is 0.2 mg/m3. |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with oils and alkalies. May corrode some types of metal and alloy. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101-05-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Anilazine (101-05-3) |
Safety information for ANILAZINE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for ANILAZINE
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


![1,1'-[(6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diyl)diimino]bisanthraquinone](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/4118-16-5.gif)
You may like
-
 Anilazine CAS 101-05-3View Details
Anilazine CAS 101-05-3View Details
101-05-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8