Ammonia
- CAS NO.:7664-41-7
- Empirical Formula: H3N
- Molecular Weight: 17.03
- MDL number: MFCD00011418
- EINECS: 231-635-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
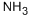
What is Ammonia?
Absorption
Ammonia can be absorbed via oral or inhalation route. Inhales ammonia is temporarily dissolved in the mucus of the upper respiratory tract, however the majority of the gas is released back into the air via expiration . In healthy male subjects under exposure to 500 ppm ammonia for 10-27 minutes, about 70-80% of total inspired ammonia was expired . In extrahepatic tissues such as the intestine, ammonia is incorporated into nontoxic glutamine and released into blood, where it is transported to the liver for ureagenesis .
Toxicity
LC50 via inhalation in rat is 7338 ppm/1h . High exposure to ammonia can cause pulmonary edema, which may be life-threatening. Exposure can cause headache, loss of sense of smell, nausea, and vomiting. While mammals has various mechanisms to detoxify and excrete ammonia from the body, death has been reported after an exposure to 10,000 ppm for an unknown duration. Bradycardia was seen at 2,500 ppm, and hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias leading to cardiovascular collapse followed acute exposures to concentrations exceeding 5,000 ppm .
Description
Ammonia is a colorless, pungent-smelling gas that is one of the most important industrial inorganic chemicals. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and as a feedstock to produce numerous other chemicals. Ammonia ranks as one of the top 10 chemicals produced annually.
Chemical properties
At standard temperature and pressure, NH3 is a colorless gas with a penetrating, pungent-sharp odor in small concentrations which, in heavy concentrations, produces a smothering sensation when inhaled. Formula weight is 17.03, and sp gr 0.817 (at ?79 °C) and 0.617 (at 15 °C). Ammonia is very soluble in water, a saturated solution containing approximately 45% NH3 (weight) at the freezing temperature of the solution and about 30% (weight) at standard conditions. Ammonia dissolved in water forms a strongly alkaline solution of ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH. The univalent radical many respects like K+ and Na+ in vigorously reacting with acids to form salts. Ammonia is an excellent nonaqueous electrolytic solvent, its ionizing power approaching that of water. Ammonia burns with a greenish-yellow flame.
Physical properties
Colorless gas with a penetrating, pungent, suffocating odor. An experimentally determined odor threshold concentration of 45.8 ppmv was reported by Leonardos et al. (1969). A detection odor threshold concentration of 11.6 mg/m3 (16.7 ppmv) was experimentally determined by Nishida et al. (1974).
History
During the Middle Ages ammonia was produced by the distillation of animal dung, hooves, and horn. Its preparation from horn gave it another name: spirit of hartshorn. Joseph Priestley (1733–1804) isolated ammonia in 1774 and called the compound alkaline air. The modern name ammonia was given to the compound in 1782 by the Swedish chemist Torbern Bergman (1735–1784). The exact chemical composition was determined by Claude-Louis Berthollet (1748–1822) in 1785. During the 19th century ammonia was obtained from the distillation of coal tar. The importance of nitrogen fertilizers in agriculture was established during the mid-1800s, and this coupled with the growth of the chemical industry provided incentive to find a method for fixing nitrogen.
Synthesis
To a solution of the SM (1.0 g, 6.4 mmol) in DMF (5.0 mL) at 0 C was added EDC-HCl (1.2 g, 7.7 mmol), NH4Cl (1.4 g, 26.9 mmol), and HOBt (1.1 g, 8.3 mmol). The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 12 h, after which time ice-cold H2O was added and the mixture was extracted with EtOAc. The org layer was dried (Na2SO4) and concentrated in vacuo to provide the product as an orange/red solid. [600 mg, 61%]
The Uses of Ammonia
Ammonia is a large-tonnage industrial product and finds its major use in the manufacture of nitric acid and fertilizers. It is the most commonly used refrigerant, particularly for large industrial installations.
The Uses of Ammonia
Ammonia is a major feedstock for fertilizer, explosives, plastics, and other chemicals. The primary use of ammonia is in the production of fertilizers, with approximately 70% of ammonia being used for this purpose. Major fertilizers produced include ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, and urea.
The Uses of Ammonia
NH3 (ammonia) is produced in the so-called Haber Bosch process. This industrial process uses finely
divided iron as catalyst and a reaction temperature of around 450 °C at a pressure of 50 atm. Ammonia is used
to produce fertilisers, nitric acid, nylon and many more products important to our modern life style.
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Indications
Indicated for use as a smelling salt to treat or prevent fainting. (when radiolabelled) Indicated for diagnostic PET imaging of the myocardium under rest or pharmacologic stress conditions to evaluate myocardial perfusion in patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease . Reduce drug development failure ratesBuild, train, & validate machine-learning modelswith evidence-based and structured datasets.See how Build, train, & validate predictive machine-learning models with structured datasets.See how
Background
Ammonia is a naturally-occurring compound with a chemical formula NH3 and structure of trigonal pyramidal geometry. It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell, and become NH4, or ammonium ion, when in water. Although ammonia is used as a food additive in the anhydrous form and serves as a starting material in pharmaceutical and commercial products, it is caustic and hazardous when concentrated. Ammonia gas has been used in the clinical setting as a respiratory stimulant to prevent fainting. The radiolabelled form of ammonia, ammonia N 13, is intravenously administered as a radioactive diagnostic agent for Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the myocardium to evaluate myocardial perfusion. Ammonia is a natural byproduct of biological and chemical reactions, including decomposition of organic matter, including plants, animals, and animal wastes. It is present in normally present in all tissues constituting a metabolic pool, where it is mostly taken up by glutamic acid and take part in transamination and other reactions, including the synthesis of protein by the Krebs-Hanseleit cycle in the liver . It is proposed that human adults produce about 1000 mmol of ammonia daily, most of which undergoes excretion in the urine.
Production Methods
Ammonia is obtained commercially chiefly by synthesis from its constituent elements, nitrogen and hydrogen, which are combined under high pressure and temperature in the presence of a catalyst. Ammonia solution is produced by dissolving ammonia gas in water.
Production Methods
The Haber process for the synthesis of ammonia is based on the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen: N2(g) + 3H2(g) ? 2NH3(g). Nitrogen in the reaction is obtained by separating nitrogen from air through liquefaction, and hydrogen is obtained from natural gas by steam reforming: CH4(g) + H2O(g) → H2(g) + CO(g) According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the production of ammonia is favored by a high pressure and a low temperature. The Haber process is typically carried out at pressures between 200 and 400 atmospheres and temperatures of 500°C. In the commercial production of ammonia, NH3 is continually removed as it is produced.
Definition
ChEBI: An azane that consists of a single nitrogen atom covelently bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
General Description
The product is a 0.4 M solution of ammonia in dioxane. Ammonia is a colorless gas with a characteristic strong odor. It is highly soluble in water, alcohol, chloroform and ether. It is extensively sold in the form of solution.1 Ammonia molecule is pyramidal in shape with nitrogen in the center and the three hydrogen atoms along the three vertices and the lone pair of electrons on the fourth vertex. Ammonia solution is commonly used as a base.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water with evolution of heat. The amount of heat generated may be large.
Reactivity Profile
AMMONIA is a base. Reacts exothermically with all acids. Violent reactions are possible. Readily combines with silver oxide or mercury to form compounds that explode on contact with halogens. When in contact with chlorates Ammonia forms explosive ammonium chlorate [Kirk-Othmer, 3rd ed., Vol. 2, 1978, p. 470]. Reacts violently or produces explosive products with fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine and some of the interhalogen compounds (bromine pentafluoride, chlorine trifluoride). Mixing of bleaching powder (hypochlorite solution) with ammonia solutions produces toxic/explosive ammonia trichloride vapors. Undergoes potentially violent or explosive reactions on contact with 1,2-dichloroethane (with liquid ammonia), boron halides, ethylene oxide (polymerization), perchlorates or strong oxidants (chromyl chloride, chromium trioxide, chromic acid, nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide, chlorates, fluorine, nitrogen oxide, liquid oxygen). Reacts with silver chloride, silver oxide, silver nitrate or silver azide to form the explosive silver nitride. May react with some heavy metal compounds (mercury, gold(III) chloride) to produce materials that may explode when dry. [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 1553].
Hazard
Inhalation of concentrated fumes may be fatal. Moderate fire risk, explosive limits in air 16– 25%. Forms explosive compounds in contact with silver or mercury. Eye damage and upper respiratory tract irritant.
Health Hazard
Ammonia is intensely irritating to the eyes,nose, and respiratory tract. Toxic effectsinclude lachrymation, respiratory distress,chest pain, and pulmonary edema. A concentration of 10 ppm may be detected by odor;irritation of eyes and nose is perceptible atabout 200 ppm. A few minutes of exposureto 3000 ppm can be intolerable, causing seri ous blistering of the skin, lung edema, andasphyxia, leading to death. It is corrosive toskin because it reacts with moisture to formcaustic ammonium hydroxide. Long expo sure may result in destruction of tissues
LC50 value, inhalation (mice): 4200 ppm/hr.
Fire Hazard
Mixing of ammonia with several chemicals can cause severe fire hazards and/or explosions. Ammonia in container may explode in heat of fire. Incompatible with many materials including silver and gold salts, halogens, alkali metals, nitrogen trichloride, potassium chlorate, chromyl chloride, oxygen halides, acid vapors, azides, ethylene oxide, picric acid and many other chemicals. Mixing with other chemicals and water. Hazardous polymerization may not occur.
Flammability and Explosibility
Ammonia vapor is slightly flammable (NFPA rating = 1) and ignites only with difficulty. Ammonia forms explosive mixtures with air in the range 16 to 25%. Water, carbon dioxide, or dry chemical extinguishers should be used for ammonia fires.
Agricultural Uses
Anhydrous ammonia is an ammonium fertilizer made by
the Haber-Bosch process, by reacting hydrogen with
nitrogen in the ratio of 3: 1 at high temperatures (450 to
500'C) and pressure (about 500 atm) in the presence of an
iron catalyst promoted by potassium and alumina. The
nitrogen derived from air and the hydrogen obtained
from (a) synthesis gas, (b) steam reforming of naptha,
coal or coke (c) lignite, or (d) electrolysis of water, are
purified by standard procedures before use. The
anhydrous ammonia thus produced can be directly used
as a fertilizer. It can also be converted to ammonium salts
which are important fertilizers, by reacting ammonia
with nitric, sulphuric and phosphoric acids. Anhydrous
ammonia is also reacted with carbon dioxide to get urea
which is another important source of nitrogen.
Anhydrous ammonia is an important fluid fertilizer
and is the cheapest nitrogen source, having the highest
nitrogen content (about 82 %) among nitrogenous
fertilizers. However, because of safety and
environmental considerations, many dealers and users
are now switching over to other sources of nitrogen.
Anhydrous liquid ammonia can cause dehydration of
tissue and severe damage to the skin, lungs and eyes by
its freezing and caustic action. Because of the low vapor
pressure (6 bar at lO℃, 9 bar at 20℃ and 12 bar at
3O℃), anhydrous ammonia must be stored and
transported in pressure vessels.
Due to the volatile nature of anhydrous ammonia it
has to be injected with an applicator 15 to 30 cm below
the soil surface to be effective and to reduce ammonia
loss. Ammonia loss depends on the soil type,
its moisture content, and the depth to which the
applicator is injected.
Ammonia applicators range in size from small 5-row
rigs to large rigs that have a swath width of upto 20 m (65
feet) and are pulled by high-powered tractors.
Anhydrous ammonia is usually metered by a variable
orifice-type meter or by a piston pump.
Physical properties of anhydrous ammonia are
somewhat similar to other liquids under pressure like
butane or propane gas. Because of the difficulties in
handling anhydrous ammonia, water solutions of
ammonia, urea, ammonium phosphate or other soluble
solid nitrogen materials are used widely. Anhydrous
ammonia is also used in the preparation of protein feeds
for cattle and sheep, and as a defoliant to hasten the
shedding of cotton leaves to facilitate mechanical
harvesting.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Ammonia solution is typically not used undiluted in pharmaceutical
applications. Generally, it is used as a buffering agent or to adjust
the pH of solutions. Most commonly, ammonia solution (the
concentrated form) is used to produce more dilute ammonia
solutions.
Therapeutically, dilute ammonia solution is used as a reflex
stimulant in ‘smelling salts’, as a rubefacient, and as a counterirritant
to neutralize insect bites or stings.
Industrial uses
Ammonia (NH3) is an alkaline gas with a sharp, penetrating odor. Reacting nitrogen and hydrogen under pressure, in the presence of a catalyst, produces ammonia. Gaseous ammonia is flammable in air at concentrations of 15–28% by volume. Anhydrous liquid ammonia is a colorless liquid with a strong odor. Ammonia, because of its unique chemical properties to metal ions, is primarily used in hydrometallurgical processing. In the mineral processing industry, ammonia is rarely used as a pH regulator. There was only one operating plant in the world that used ammonia as a pH regulator in treatment of a copper/zinc ore.
Pharmacokinetics
As a gas, ammonia is a natural byproduct and respiratory stimulant. Its renal metabolism plays a role in whole body acid-base balance.
Materials Uses
Most common metals are not affected by dry
ammonia. However, when combined with water
vapor, ammonia will attack copper, zinc, or
alloys containing copper as a major alloying
element. Therefore, these materials should not
be used in contact with ammonia. Certain hightensile-
strength steel have developed stresscorrosion
cracking in ammonia service, but such
cracking can be prevented by the use of 0.2 percent
water by weight in the ammonia as an inhibitor.
Ammonia storage tanks and their valves
and fittings are usually made of steel.
Safety
Ingestion of strong solutions of ammonia is very harmful and causes
severe pain in the mouth, throat, and gastrointestinal tract as well as
severe local edema with cough, vomiting, and shock. Burns to the
esophagus and stomach may result in perforation. Inhalation of the
vapor causes sneezing, coughing, and, in high concentration,
pulmonary edema. Asphyxia has been reported. The vapor is
irritant to the eyes. Strong solutions are harmful when applied to the
conjunctiva and mucous membranes. Topical application of even
dilute ammonia solutions, used to treat insect bites, has caused
burns, particularly when used with a subsequent dressing.
When used as an excipient, ammonia solution is generally
present in a formulation in a highly diluted form.
Potential Exposure
Ammonia is used as a nitrogen source for many nitrogen-containing compounds. It is used in the production of ammonium sulfate and ammonium nitrate for fertilizers; and in the manufacture of nitric acid, soda; synthetic urea, synthetic fibers; dyes; and plastics. It is also utilized as a refrigerant and in the petroleum refining and chemical industries. It is used in the production of many drugs and pesticides. Other sources of occupational exposure include the silvering of mirrors, gluemaking, tanning of leather; and around nitriding furnaces. Ammonia is produced as a by-product in coal distillation and by the action of steam on calcium cyanamide, and from the decomposition of nitrogenous materials.
Physiological effects
Persons having chronic respiratory disease or
persons who have shown evidence of undue
sensitivity to ammonia should not be employed
where they will be exposed to ammonia.
Ammonia is not a cumulative metabolic poison;
ammonium ions are actually important constituents
of living systems. However, ammonia
in the ambient atmosphere has an intense irritating
effect on the mucous membranes of the
eyes, nose, throat, and lungs. High levels of
ammonia can produce corrosive effects on tissues
and can cause laryngeal and bronchial
spasm and edema so as to obstruct breathing.
The pungent odor of ammonia affords a protective
warning, and as long as people are conscious
they can avoid breathing significantly
contaminated air.
Source
Ammonia is released as a combustion product of coal, fuel oil, natural gas, wood, butane,
and propane (quoted, Verschueren, 1983).
Ammonia naturally occurs in soybean (8,600 ppm), evening-primrose seeds (2,300–2,455 ppm),
lambsquarter, and tobacco leaves (Duke, 1992).
Environmental Fate
Chemical/Physical. Reacts violently with acetaldehyde, ethylene oxide, ethylene dichloride
(Patnaik, 1992).
Reacts with acids forming water soluble ammonium salts.
Metabolism
Healthy hepatocytes detoxify ammonia where hepatic glutaminase, glutamine synthetase and the urea cycle enzymes act as major enzymes for ammonia metabolism. Ammonia is converted to urea in the liver and other tissues. Glutaminase and glutamine synthetase catalyze the condensation of ammonia with glutamate to glutamine, which is a common nontoxic carrier of ammonia . In case of hepatic dysfunction or impairment, detoxification capacity decreases and may cause severe pathologies from hyperammonemia, such as hepatic encephalopathy .
storage
On exposure to the air, ammonia solution rapidly loses ammonia. Ammonia solution should be stored in a well-closed container, protected from the air, in a cool, dry place. The storage temperature should not exceed 208℃.
Shipping
Shipped in tank cars, tank trucks, barges, and steel cylinders. Labeling and restrictions vary with concentration: NA1005 Ammonia, anhydrous, Hazard Class: 2.2; Labels: 2.2-Nonflammable compressed gas, Domestic (U.S.), Inhalation Hazard (Special Provision 13). UN1005 Ammonia, anhydrous, Hazard Class: 2.3; Labels: 2.3-Poison Gas, 8-Corrosive material International, Inhalation Hazard Zone D. UN2672 Ammonia solutions, relative density between 0.880 and 0.957 @ 15 C in water, with .10 % but NOT . 35 % ammonia, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN2073 Ammonia solution, relative density less than 0.880 @ 15 C in water, with . 35% but NOT . 50% ammonia, Hazard Class: 2.2; Labels: 2.2-Nonflammable compressed gas. Note: Also used for Ammonium hydroxide, CAS1336-21-6, Record A:0110.
Purification Methods
Dry the liquid, and store it, with sodium in a steel cylinder, then distil and condense it by means of liquid air, the non-condensable gases being pumped off. In order to obtain liquid NH3 from a cylinder, turn the cylinder upside-down (i.e. with the valve at the bottom, use a metal stand to secure it in this position) and lead a plastic tube from the tap to a measuring cylinder placed in an efficient fume cupboard which is kept running. Turn the tap on and allow the ammonia to be released. At first, gas and liquid will splatter out (make sure that the plastic tube is secure), but soon the liquid will drip into the measuring cylinder. The high latent heat of evaporation will cool the ammonia so that the liquid will remain cool and not boil vigorously. If the ammonia is required dry, the necessary precautions should be taken, i.e. the gas is allowed to flow through tubes packed with coarse CaO pellets. AMMONIA (gas, liquid or aqueous solution) is very irritating and should not be inhaled in any quantity as it can lead to olfactory paralysis (temporary or permanent).
Toxicity evaluation
With a vapor pressure of 8611 hPa at 20 °C, ammonia is a gas under normal environmental conditions. In the atmosphere, ammonia is estimated to have a half-life of several days. The primary fate process is the reaction of ammonia with acid air pollutants and removal of the resulting ammonium(NH4+ ) compounds by dry or wet deposition. Rain washout and reaction with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals also contribute to the atmospheric fate of vapor–phase ammonia. In water, ammonia acting as a weak base (pKa=9.25) will exist in equilibrium with the ammonium ion. Ammonia will volatilize to the atmosphere due to its high vapor pressure in water (2878 hPa at 25°C) while the ammonium ion will be removed via uptake by aquatic plants, adsorption to sediments, and microbial transformation to nitrites(NO2-)and nitrates (NO3-). In soil, the same general processes will occur.As a result, ammonia does not readily leach through soil. However, nitrate can leach through soil due to its high water solubility and if present at a high enough concentration may cause methemoglobinemia in infants. Due to the multiple physical and biological transformation processes that exist in nature, ammonia is not expected to accumulate in the environment or living organisms.
Incompatibilities
Ammonia solution reacts vigorously with sulfuric acid or other strong mineral acids and the reaction generates considerable heat; the mixture boils.
Waste Disposal
Dilute with water, neutralize with HCl and discharge to sewer. Recovery is an option to disposal which should be considered for paper manufacture, textile treating, fertilizer manufacture and chemical process wastes.
Regulatory Status
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral suspensions, topical preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
GRADES AVAILABLE
No commodity grade specifications for ammonia have been published as standard for the industry.
Properties of Ammonia
| Melting point: | −78 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 60 °C |
| Density | 1.023 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor density | 0.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 8.75 atm ( 21 °C) |
| FEMA | 4494 | AMMONIA (ALSO INCLUDES AMMONIUM CHLORIDE) |
| Flash point: | 52 °F |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Miscible with ethanol (95%) and water. |
| appearance | colorless gas |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 38(at 25℃) |
| color | Colorless |
| Odor | Intense pungent odor detectable at 17 ppm |
| explosive limit | 25% |
| Odor Threshold | 1.5ppm |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,492 |
| BRN | 3587154 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.31 at 0 °C, 2.92 at 20 °C (droplet train apparatus, Shi et al., 1999) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 25 ppm (~18 mg/m3) (ACGIH
and MSHA), 50 ppm (OSHA); STEL
35 ppm; IDLH 500 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Dielectric constant | 25.0(-59℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Hygroscopic. Flammable. Incompatible with acids, strong oxidizing agents. May react violently with acids, aldehydes, alkylene oxides, amides, boron, boron halides, calcium, chlorine azide, chloric acid, chlorine monoxide, chlorites, halogens, heavy metals and many other materials - check the complete data sheet before use! |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7664-41-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ammonia(7664-41-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ammonia (7664-41-7) |
Safety information for Ammonia
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Gas Cylinder Compressed Gases GHS04  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H280:Gases under pressure H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonia
Ammonia manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
SKS FINE CHEM PVT LTD
SSD Gases Pvt Ltd.
Maharashtra Gas Co
Gujarat Narmada Valley Fertilizers Chemicals Ltd
Vijay Group of Industries
Global Calcium Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Ammonia sol 2.0M in Diethyl Ether 99%View Details
Ammonia sol 2.0M in Diethyl Ether 99%View Details -
 Methanolic Ammonia 99%View Details
Methanolic Ammonia 99%View Details -
 Ammonia CAS 7664-41-7View Details
Ammonia CAS 7664-41-7View Details
7664-41-7 -
 AMMONIA (15-20% SOLUTION IN MEOD) CAS 7664-41-7View Details
AMMONIA (15-20% SOLUTION IN MEOD) CAS 7664-41-7View Details
7664-41-7 -
 Ammonia 2 M in etoh CAS 7664-41-7View Details
Ammonia 2 M in etoh CAS 7664-41-7View Details
7664-41-7 -
 Ammonia in methanol 98%View Details
Ammonia in methanol 98%View Details -
 Ammonia anhydrous CAS 7664-41-7View Details
Ammonia anhydrous CAS 7664-41-7View Details
7664-41-7 -
 Ammonia solution 2.0 M in isopropanol CAS 7664-41-7View Details
Ammonia solution 2.0 M in isopropanol CAS 7664-41-7View Details
7664-41-7