Amitraz
Synonym(s):N′-(2,4-Dimethylphenyl)-N-{[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)imino]methyl}-N-methylmethanimidamide;NSC 324552
- CAS NO.:33089-61-1
- Empirical Formula: C19H23N3
- Molecular Weight: 293.41
- MDL number: MFCD00069396
- EINECS: 251-375-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
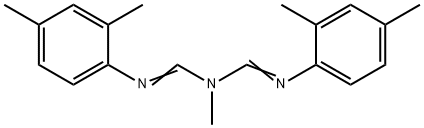
What is Amitraz?
Chemical properties
Beige to Pale Yellow Solid
Chemical properties
Amitraz forms colorless needle-like crystals. Liquid formulations may contain flammable organic solvents.
Originator
Aludex,Hoechst Roussel Vet Ltd.
The Uses of Amitraz
Amitraz is an antiparasitic used to control red spider mites, leaf miners and scale insects. This compound is active by inhibiting the targets monoaminooxidase enzyme.
The Uses of Amitraz
coccidiostat, antiplatelet
The Uses of Amitraz
Acaricide; insecticide.
The Uses of Amitraz
Amitraz is used for the control of all stages of mites and insects such as aphids and whitefly, and the eggs and first instar larvae of Lepidoptera on fruit, cotton and vegetables. It is also used in honey bee hives and for the control of ticks, mites and lice on domestic and farm animals.
Definition
ChEBI: A tertiary amino compound that is 1,3,5-triazapenta-1,4-diene substituted by a methyl group at position 3 and 2,4-dimethylphenyl groups at positions 1 and 5.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 55.1 g 2,4-dimethylaniline hydrochloride, 83.7 g ptoluenesulphonyl
chloride and 150 ml N-methylformamide was stirred with
occasional cooling to maintain the temperature at 20°-35°C. When the
exothermic reaction had subsided, the mixture was stirred at room
temperature for 4 h, poured into a mixture of ice and water, and basified with
10 N sodium hydroxide solution, keeping the temperature of the mixture below 10°C. The precipitated solid was filtered, washed with water until free
from alkali, dried at room temperature, to give N-2,4-dimethylphenyl-N'-
methylformamidine, melting point 75°-76°C (recrystallized from cyclohexane).
A solution of 19.4 g N-2,4-dimethylphenyl-N'-methylformamidine and 0.3 g ptoluenesulphonic
acid in 195 ml dry xylene was refluxed under anhydrous
conditions for 48 h, causing the evolution of methylamine. The xylene was
distilled off under reduced pressure to give 1,5-di-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-3-
methyl-1,3,5-triaza-penta-1,4-diene, melting point 88°-89°C (crystallized
twice from isopropyl).
Therapeutic Function
Acaricide, Scabicide, Tickicide, Appetite stimulant
Toxicity
Amitraz poisoning is frequently encountered in dogs and cats. With dogs, poisoning is most often associated with accidental ingestion of the flea and tick collar, resulting in severe toxicity and sometimes fatal poisoning. In humans, poisoning occurs because of oral ingestion of amitraz. The major signs of acute poisoning are nausea, vomiting, coma, somnolence, miosis or mydriasis, bradycardia, hypo- or hyperthermia, polyuria, and respiratory failure.
Toxicity
Amitraz poisoning is frequently encountered in dogs and cats. With dogs, poisoning is most often associated with accidental ingestion of the flea and tick collar, resulting in severe toxicity and sometimes fatal poisoning. In humans, poisoning occurs because of oral ingestion of amitraz. The major signs of acute poisoning are nausea, vomiting, coma, somnolence, miosis or mydriasis, bradycardia, hypo- or hyperthermia, polyuria, and respiratory failure.
Toxicity
Amitraz poisoning is frequently encountered in dogs and cats. With dogs, poisoning is most often associated with accidental ingestion of the flea and tick collar, resulting in severe toxicity and sometimes fatal poisoning. In humans, poisoning occurs because of oral ingestion of amitraz. The major signs of acute poisoning are nausea, vomiting, coma, somnolence, miosis or mydriasis, bradycardia, hypo- or hyperthermia, polyuria, and respiratory failure.
General Description
White monoclinic crystals. Melting point 187-189°F (86-87°C). Insoluble in water. Used as an acaricide, insecticide and treatment of demodectic mange in dogs.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Unstable in acid.
Agricultural Uses
Insecticde, Acaricide, Veterinary medicine: Registered for control of pear psylla on pears, whitefly and mites on pears and cotton; cattle, dogs, sheep, and hog dip to control ticks, mange mites, lice and other pests. Not permitted on apples. Used to control red spider mites, leaf miners, scale insects, and aphids. Also used on cotton to control bollworms, white fly, leaf worms, and tobacco budworms. Not registered for use in EU countries
Trade name
AAZDIENO®; ACARAC®; ACADREX®; ARMY®; AZODIENO®; BAAM®; BOOTS BTS 27419®; BTS 27,419®; BUMETRAN®; COYOTE®; DANICUT®; ECTODEX®; EDRIZAN®; EDRIZAR®; GARIAL®; ISTAMBUL®; MITABAN®; MITAC®; OVASYN®; OVIDREX®; PARSEC®; ROTRAZ®; SENDER®; TAC-PLUS®; TACTIK®; TRIATIX®; TRIATOX®; TUDY®; VAPCOZIN TAKTIC®; UPJOHN U-36059®
Pharmacology
The mechanism of action of amitraz has not been completely elucidated, and, presently, a dual mode of action appearsmost likely. Firstly, the enzymemonoamine oxidase, which metabolizes neurotransmitter amines in mites and ticks, is inhibited. Secondly, octopamine receptors in the central nervous system of ectoparasites are activated by amitraz, thereby modifying tonic muscle contractions. The effect of amitraz is to induce increased neuronal activity, abnormal behavior, detachment, and death of mites and ticks.
Potential Exposure
Those engaged in the manufacture, formulation and application of this insecticide and acaricide. A rebuttable presumption against registration for amitraz was issued on April 6, 1977 by United States Environmental Protection Agency on the basis of oncogenicity. Incompatibilities: Keep away from strong oxidizers and strong acids. Acids may render this material unstable.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In dogs, amitraz solution is used topically primarily in the treatment of generalized demodicosis. A topical spot-on solution (ProMeris? for Dogs) and a collar (Preventic?) are available for treatment and prevention of flea and tick infestation. It is also used as a general insecticidal/ miticidal agent in several other species (see label information). The pharmacologic action of amitraz is not well understood, but it is a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor (in mites) and may have effects on the CNS of susceptible organisms. It apparently also possesses alpha-2 adrenergic activity and inhibits prostaglandin synthesis. Amitraz can cause a significant increase in plasma glucose levels, presumably by inhibiting insulin release via its alpha2-adrenergic activity. Yohimbine (alpha2 blocker) or atipamezole can antagonize this effect.
Metabolic pathway
14C-Amitraz is applied on lemons grown under glasshouse conditions at final harvest and the applied radioactivity is quantitatively recovered, predominantly in the peel (86%). The total residue at harvest contains amitraz, N-methyl-N'-(2,4-xylyl)formamidine, and formyl-2',4'-xylydine and conjugates of 4-amino- m-toluic acid and the conjugated metabolites which are convertible to 2,4-xylidine. Amitraz is readily hydrolyzed at low pH values, forming acid-stable formyl-2,4-xylydine which can be further hydrolyzed to 2,4-xylidine.
Metabolism
Amitraz is poorly absorbed when applied topically to animals. By contrast, orally administered amitraz is rapidly and extensively absorbed. The metabolism and excretion of amitraz are also rapid. It is hydrolyzed to N-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)-N -methyl formamidine and 2,4- dimethyl formamidine and the final product, 4-amino-3- methylbenzoic acid, is converted to non-toxic conjugates. The latter are excreted in the urine and, to a lesser extent, in bile.
Shipping
UN2763 Triazine pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Degradation
Amitraz is readily hydrolysed at acidic pH but is relatively stable under alkaline conditions. Its DT50 values at 25 °C at pH 5,7 and 9 are given as 2.1,22.1 and 25.5 hours, respectively (PM). A recent study (Pierpoint et aE., 1997) as part of the development of a vat management and waste disposal programme for animal dips describes the kinetics and mechanism of hydrolysis of amitraz in detail. Pseudo-first-order rate constants are given for six pH values between 3.24 and 9.12. The DT50 values at pH values 3.24, 5.09 and 9.12 were respectively 0.4, 8.7 and 112 hours. The reaction was mainly acid-catalysed with a small unassisted component. There was no base catalysis. One of the primary products (Scheme 1) was N-2,4 dimethylphenyl-N-methylformamidine( 2); however, at low pH this was not detected because it was rapidly hydrolysed to 2,4-dimethylphenylformamide (3). Some direct hydrolysis of amitraz to product 3 was also seen. The latter underwent slow base-catalysed hydrolysis to 2,4 dimethylaniline (4). This was a much slower reaction with a DT50 (pH 9.12) of about 300 days.
Toxicity evaluation
Amitraz displays serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) blocking activity and a2-adrenoceptor agonist activity in animals. The clinical signs associated with intoxication in dogs include sedation, bradycardia, hypotension, hyperglycaemia, hypothermia, and mydriasis. The specific antidote for animal toxicity is the a2-adrenoceptor antagonist, yohimbine. The toxicity profile of amitraz in the horse includes transient sedation and intestinal stasis that can progress to impaction colic (79). For this reason, amitraz is not approved for use in this species in any country.
Incompatibilities
Those engaged in the manufacture, formulation and application of this insecticide and acaricide. A rebuttable presumption against registration for amitraz was issued on April 6, 1977 by United States Environmental Protection Agency on the basis of oncogenicity. Incompatibilities: Keep away from strong oxidizers and strong acids. Acids may render this material unstable.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR 165 recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Amitraz
| Melting point: | 86-87°C |
| Boiling point: | 425.25°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1280 |
| vapor pressure | 3.4×10-4 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5892 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | DMF: 30 mg/ml; DMF:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:2): 0.33 mg/ml; DMSO: 20 mg/ml; Ethanol: 2 mg/ml |
| pka | 4.2 (weak base) |
| form | Powder/Solid |
| Water Solubility | 0.08 mg l-1 |
| color | White |
| λmax | 247nm(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,486 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 33089-61-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Amitraz(33089-61-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Amitraz (33089-61-1) |
Safety information for Amitraz
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for Amitraz
| InChIKey | QXAITBQSYVNQDR-ZIOPAAQOSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 33089-61-1 AmitrazView Details
33089-61-1 AmitrazView Details
33089-61-1 -
 33089-61-1 98%View Details
33089-61-1 98%View Details
33089-61-1 -
 Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
33089-61-1 -
 Amitraz 98% (HPLC) CAS 33089-61-1View Details
Amitraz 98% (HPLC) CAS 33089-61-1View Details
33089-61-1 -
 Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
33089-61-1 -
 Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
33089-61-1 -
 Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
Amitraz CAS 33089-61-1View Details
33089-61-1 -
 Amitraz API PowderView Details
Amitraz API PowderView Details
33089-61-1
