ALPHA-MSH
Synonym(s):α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone;α-Melanotropin;α-MSH;α-MSH, Melanotropin
- CAS NO.:581-05-5
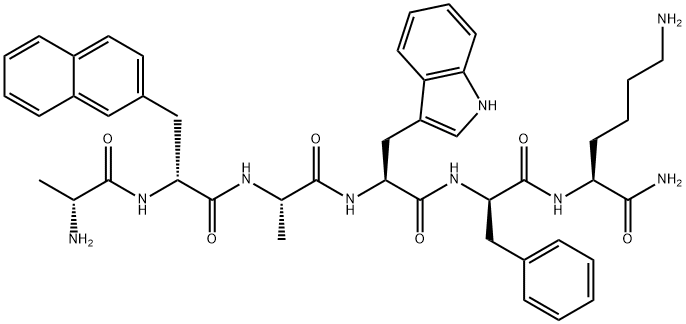
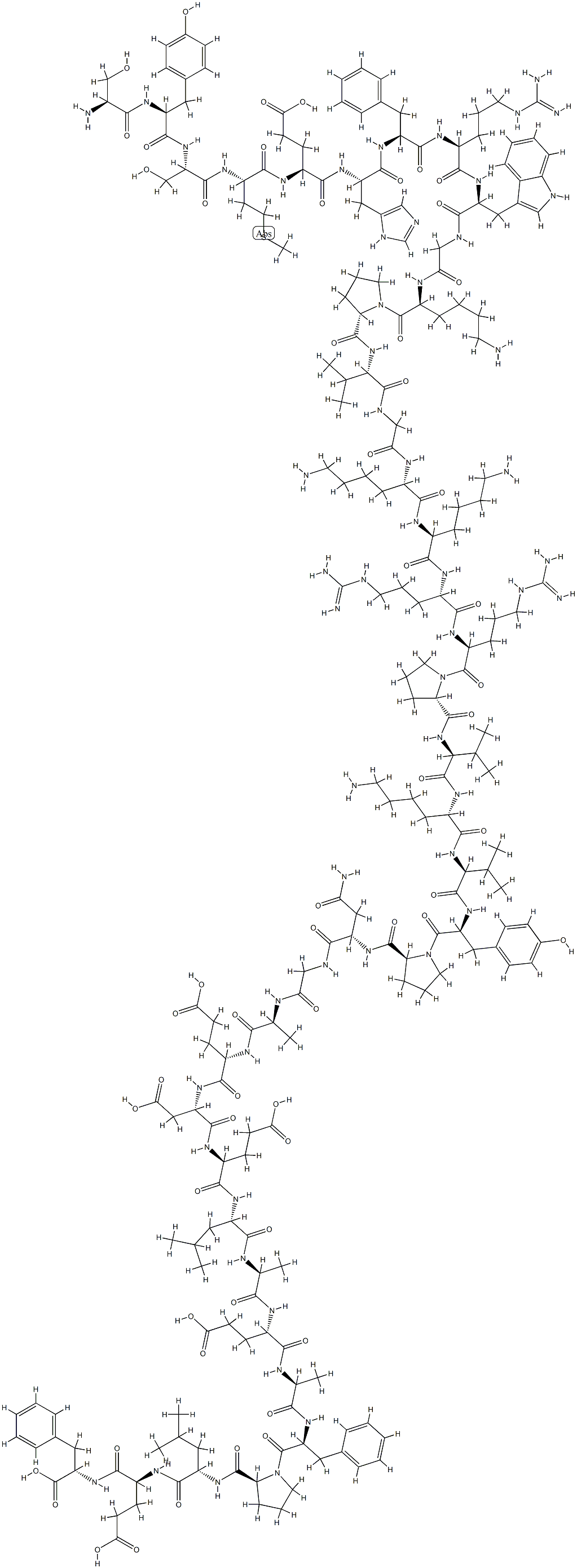
- Empirical Formula: C77H109N21O19S
- Molecular Weight: 1664.88
- MDL number: MFCD00133062
- EINECS: 232-660-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
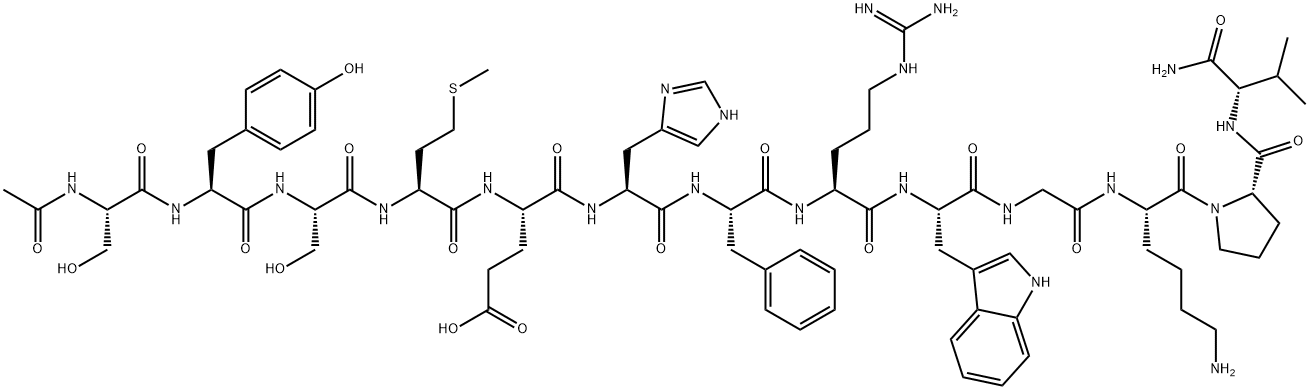
What is ALPHA-MSH?
Description
A pituitary hormone secreted from the pars intermedia, MSH was one of the first adenohypophysial hormones demonstrated to be present in vertebrates, from jawless fish to mammals, together with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). The fact that MSH is derived from a precursor protein called proopiomelanocortin (POMC) was demonstrated in 1979, using the pars intermedia from the bovine pituitary.
The Uses of ALPHA-MSH
alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone amide is an endogenous melanocortin receptor agonist (Ki values are 0.12, 31, 660 and 5700 nM for MC1, MC3, MC4 and MC5 receptors respectively). Anti-inflammatory peptide; antagonizes proinflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, IL-6 and NO and induces anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. Inhibits food intake and induces penile erections following i.c.v. administration.
What are the applications of Application
α-Melanocyte stimulating hormone is an endogenous melanocortin receptor agonist
General Description
α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) is a tridecapeptide, mostly produced by the cells in the brain, pituitary and circulation. Pro-inflammatory cytokines or UV light induced epidermal cells such as keratinocytes and melanocytes synthesize and discharge α–MSH. Poopiomelanocortin (POMC) acts as a precursor for α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) production.
Biochem/physiol Actions
α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) acts as an anti-inflammatory agent via down regulating the production and activity of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-6 expressed in various cells of the immune system. It also controls the nitric oxide production associated with inflammation. α?MSH inhibits nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-dependent gene transcription and NF-κB pathway induced by TNF and other inflammatory agents. This activity of α-MSH is mediated through the production of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and activation of protein kinase A (PKA) enzyme. α–MSH functions as a potent therapeutics for various conditions resulted through NF-κB activation including, inflammatory diseases, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) replication in AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), and septic shock. α-MSH has an essential role to play in melanin production in animals. α-MSH regulates development of several skin diseases, including cutaneous inflammation and hyper-proliferative skin diseases.
Clinical Use
The measurement of the blood concentration of MSH has not been validated for routine clinical use. MSH analogs have recently been developed for antiobesity medication, treatment of skin diseases, and prevention of actinic keratoses in organ transplant recipients. The potential use of radiolabeled α-MSH peptides in melanoma imaging and the treatment of disseminated disease has also been reported.
storage
Store at -20°C
Purification Methods
Its solubility in H2O is 1mg/mL. It is separated from the extract by ion-exchange on carboxymethyl cellulose, desalted, evaporated and lyophilised, then chromatographed on Sephadex G-25. [Lande et al. Biochemical Preparations 13 45 1971.]
Structure and conformation
Three types of MSH molecules, with different amino
acid sequences, are contained in the common precursor
POMC in mammals. α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone
(α-MSH) is composed of 13 aa residues. This peptide is generated from the N-terminal region of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and corresponds to acetylACTH(1–13)-amide. In MSH, the N-terminal Ser residue
is free, monoacetylated at the N position, or diacetylated
at the N and O positions, whereas the carboxyl terminal
is consistently in the amide form. These variations of
MSH are called desacetyl-α-MSH, α-MSH, and diacetyl-α-MSH, respectively. Of these peptides, α-MSH is a classical
α-MSH. β-MSH, which is generated from POMC via
β-lipotropin (β-LPH), is composed of 18 aa residues. Unlike
α-MSH, in β-MSH both termini are free. γ-MSH is produced
from POMC via pro-γ-MSH or N-POMC, which consists of
γ-MSH together with a joining peptide. γ-MSH (also known
as γ1-MSH) is composed of 12 aa residues in which the
N-terminus and the C-terminus are free and amide, respectively. γ3-MSH is composed of 25 aa residues in which the
N-terminal region corresponds to γ1-MSH. Each MSH segment is flanked by basic amino acid residues. Cartilaginous
fish such as sharks, rays, and ratfish possess δ-MSH in addition to the three other MSH peptides. Comparison with the
amino acid sequence and topology of POMC suggests that
δ-MSH might have evolved from β-MSH. Accordingly,
α-MSH and γ-MSH are suggested to share an antecedent.
Teleost POMC lacks γ-MSH.
Properties of ALPHA-MSH
| Density | 1.48±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | insoluble in EtOH; ≥10.44 mg/mL in H2O with ultrasonic; ≥166.5 mg/mL in DMSO with gentle warming |
| pka | 4.43±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Lyophilized |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (~1 mg/ml). |
| BRN | 741840 |
Safety information for ALPHA-MSH
Computed Descriptors for ALPHA-MSH
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
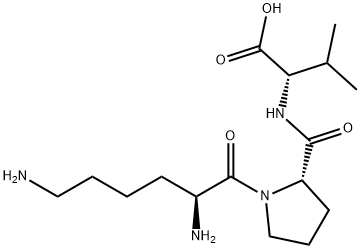
![alpha-MSH (1-13), Val(13)-,[VAL-OH13]-ALPHA-MSH,val(13)-alpha-msh(1-1](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/10466-28-1.gif)
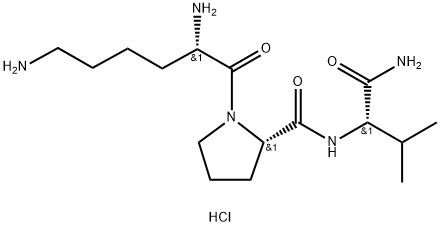
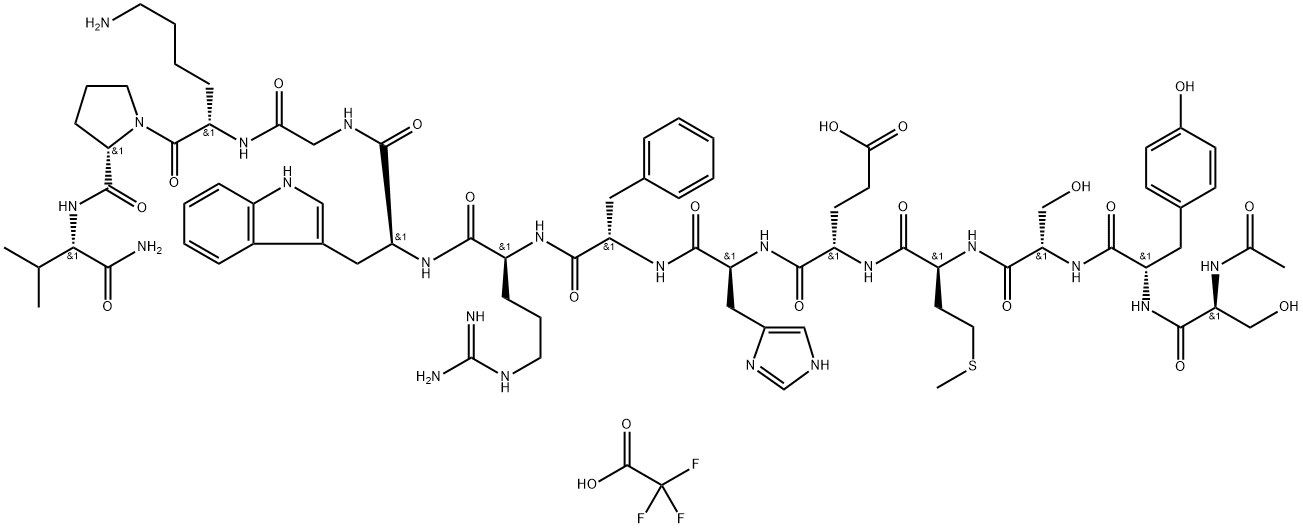
![N-ACETYL, [NLE4,DPHE7] ALPHA-MSH (4-10), AMIDE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB1760240.gif)

You may like
-
 α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone CAS 581-05-5View Details
α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone CAS 581-05-5View Details
581-05-5 -
 55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 2 2-BIS(2-HYDROXYETHOXY)-1 1-BINAPHTHYL 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5