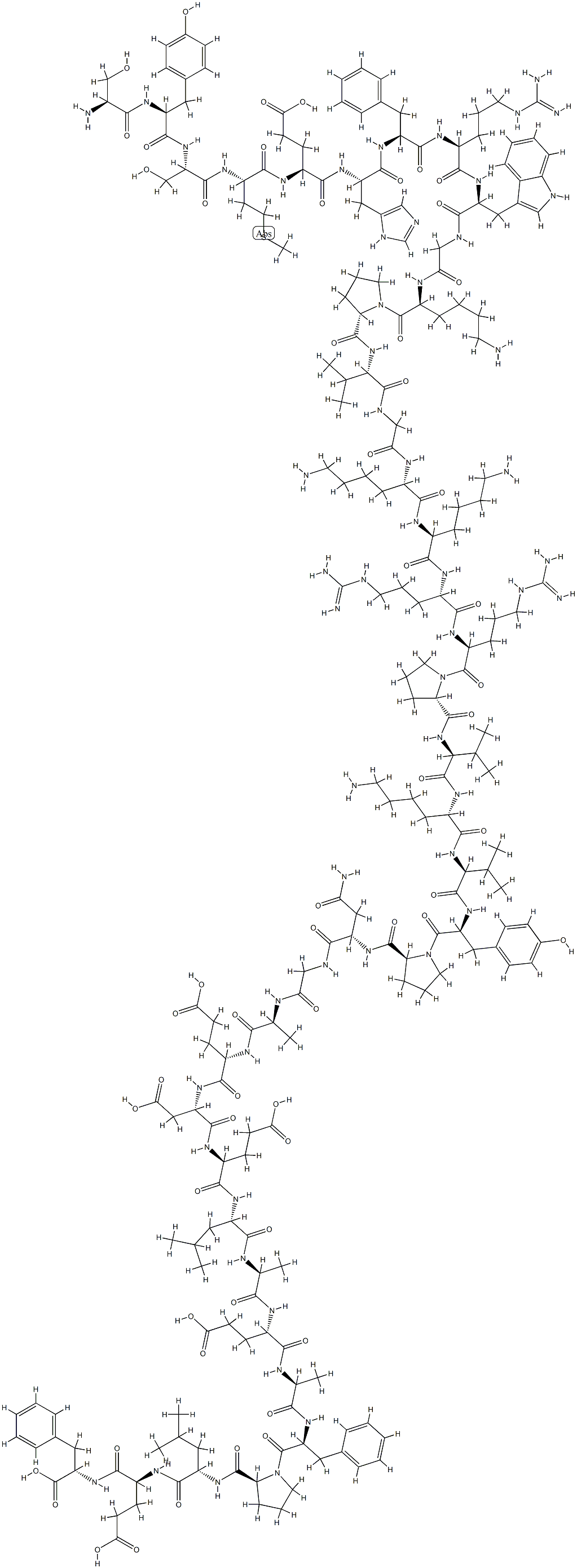
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Synonym(s):Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Fragment 1-39;Corticotropin A
- CAS NO.:9061-27-2
- Empirical Formula: C210H314N56O57S
- Molecular Weight: 4567.14616
- MDL number: MFCD00167432
- EINECS: 232-946-7
- Update Date: 2024-01-03 18:42:19
What is Adrenocorticotropic hormone ?
Indications
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), or corticotropin, a peptide of 39 amino acids, is first synthesized as a larger precursor from which ACTH is derived by proteolytic cleavage. ACTH stimulates production of glucocorticoids from the adrenal cortex. Release of ACTH depends on diurnal rhythms with serum levels highest in the early morning. Secretion of this peptide also increases under stress. It is easier and less expensive to treat patients having adrenocortical insufficiency with glucocorticoid replacement therapy than it is to use ACTH. Therefore, use of ACTH (Acthar) is restricted to diagnosis; a shorter 24–amino acid analogue (Cosyntropin) is also used. Intravenous administration of ACTH should result in peak plasma levels of glucocorticoids within 30 to 60 minutes if the adrenal gland is functional. Prolonged administration of ACTH in a repository form, however, may be necessary to stimulate steroid production, because ACTH has long-term trophic effects on adrenal cells in addition to the rapid stimulation of steroid production. If the cause of steroid deficiency is at the level of the pituitary gland, ACTH should eventually stimulate steroid production.
Biological Functions
The main function of Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is to regulate the glucocorticoid (steroid) hormone cortisol. Cortisol is released by the adrenal gland. It regulates blood pressure, blood sugar, the immune system, and the response to stress. This test can help find the causes of certain hormone problems
Health Hazard
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH;Adrenocorticotropin; corticotropic hormone): (1)Maintenance of adrenal cortex;(2)Promotes secretion of steroids, oxidative phosphorylation in adrenal cortex;(3)Mobilizes and increases oxidation of free fatty acid in adipose tissue;(4)Increases gluconeogenesis in liver; increases cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) in adrenal cortex;Decreases urea formation in liver.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Stimulates synthesis and secretion of glucocorticoids by adrenal cortex.
Producing and consuming organs
The anterior pituitary produces ACTH. It is considered a tropic hormone. Tropic hormones indirectly affect target cells by first stimulating other endocrine glands. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is released from the hypothalamus, which stimulates the anterior pituitary to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH then acts on its target organ, the adrenal cortex.
Properties of Adrenocorticotropic hormone
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| form | powder |
Safety information for Adrenocorticotropic hormone
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H312:Acute toxicity,dermal H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Adrenocorticotropic hormone
| InChIKey | XFBDTKGDXZDJAN-WODOTNDISA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
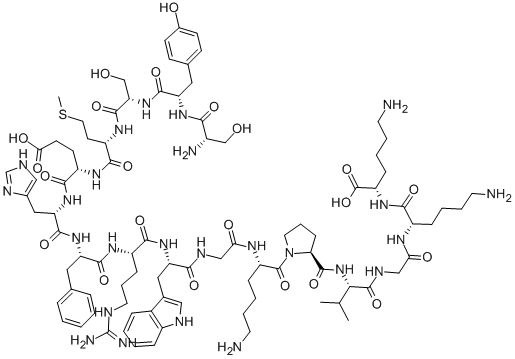


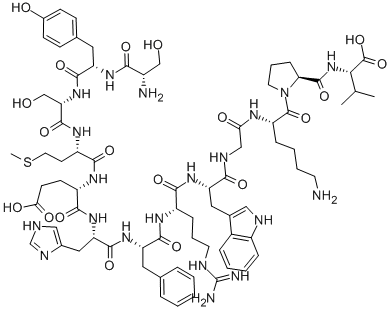

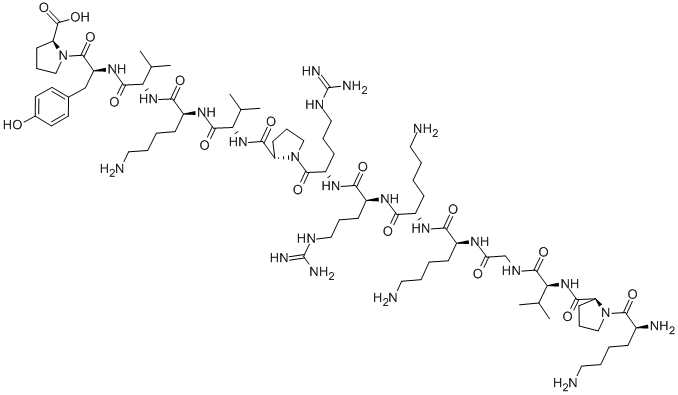
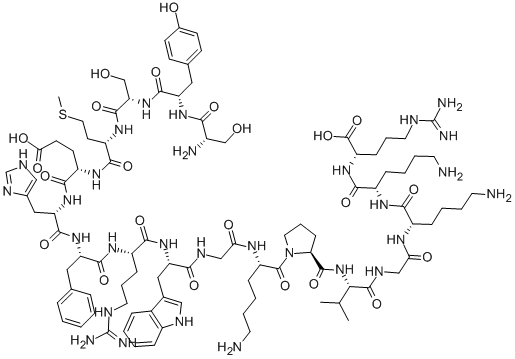
![ACTH (4-9) (Adrenocorticotropic Hormone) [Met(O2)4, D-Lys8, Phe9]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8