Allicin
- CAS NO.:539-86-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H10OS2
- Molecular Weight: 162.27
- MDL number: MFCD00468100
- EINECS: 208-727-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
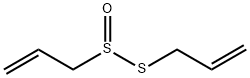
What is Allicin?
Description
Allicin is one of the major allergens in garlic (Allium sativum L.). It is responsible of the characteristical fiavour of the bulbs.
Description
When garlic is crushed or otherwise damaged, allicin is released, giving off its recognizable odor. Allicin does not naturally occur in garlic but rather is the result of the amino acid alliin combining with the enzyme alliinase. Although research has shown that it is not bioavailable, studies confirm that allicin inhibits the bacteria responsible for gastric ulcers and lowers the risk of stomach cancer.
Description
Allicin is a natural product originally isolated from A. sativum that has wide-ranging biological effects including antioxidative, anticancer, antimicrobial, and antifungal activities. It inhibits the cysteine proteases cathepsin B and L, facipain 2, and rhodesain with Ki values of 8.6 and 9.3, 1.04, and 5.31 μM, respectively. It shows antiparasitic activity against P. falciparum (IC50 = 5.2 μM) and T. b. brucei (IC50 = 13.8 μM), the parasites that cause malaria and African sleeping sickness, respectively. Allicin (5-10 μM) dose-dependently inhibits cell adhesion, invasion, and migration in various lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. It also alters the balance of tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), decreases phosphorylation of Akt, and decreases PI3K/Akt signaling.
Chemical properties
Light yellow oily liquid
Physical properties
Appearance: Light yellow powder or light yellow oily liquid, with strong irritating odor. Unstable and light, heat, and organic solvents will easily degrade it into a variety of sulfur-containing organic compounds. Solubility: Its solubility is about 2.5% in the 10?°C water. Soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, and other organic solvents. Boiling point: 80–85?°C (0.2?kPa). Relative density of d20?=?1.112; refractive index nD 20 ?=?1.561.
History
As the main active substance of garlic, garlic was separated by Cavallito and Bailey
in 1944 from crushed garlic. Cavallito firstly clarified the physical properties and
chemical structure of the scent of garlic.
Fresh garlic does not contain free allicin but only its precursor material alliin.
When the garlic undergoes physical mechanical crushing, garlic alliinase is activated and catalyzes the breakdown of alliin into allicin.
The reported preparation methods of allicin contain extraction, biosynthesis, and
chemical synthesis. Chemical synthesis starts from raw material of diallyldisulfides,
m-chloroperoxy benzoic acid to get crude allicin. According to the United States
patent report, biosynthesis preparation of allicin comes from natural sources or synthetic, after it is made into a certain concentration of aqueous solution, it is converted into allicin by reaction with alliinase. Extraction of allicin with low boiling
nonpolar solvent can acquire pure allicin, but it must be stored at ?70?°C to prevent
from decomposing.
The Uses of Allicin
Allicin is naturally formed by the action of the enzyme allicinase on alliin when the tissue of the garlic bulb is disrupted. Allicin shows antibacterial activity.
What are the applications of Application
Allicin is a compound that exhibits anticancer, antioxidative, cardioprotective, antihypertensive, anti-arrhythmic, anti-parasitic, and anti-diabetic activities activity.
Definition
An antibacterial substance extracted from garlic (allium).
Indications
This product conforms to the national standards for chemical drugs. The current clinical used forms are allicin injection, garlic instant kelp capsule, etc. It is used clinically mainly for anti-pathogenic microbial infection, anti-tumor, and anti-dilation of blood vessels. It could also be used for the treatment of periodontitis and ulcerative colitis.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 106, p. 8295, 1984 DOI: 10.1021/ja00338a049
Contact allergens
Allicin is one of the major allergens in garlic (Allium sativum L.). It is responsible for the characteristic flavor of the bulbs and has immunomodulating and antibacterial properties.
Pharmacology
Allicin has a broad spectrum of pharmacological activities, such as antibacterial,
antiviral, anticancer, decreasing the blood pressure, and inhibition of platelet
aggregation.
2. The Effect on Heart and Cerebral Vessels
Allicin exerts a protective effect on the heart and cerebral vessels through reducing plasma total cholesterol, lowering blood pressure, inhibition of platelet activity,
and reducing hematocrit and blood viscosity. Allicin increases the activity of inducible nitric oxide synthetase (iNOS) and boosts the NO level, which results in the
vasodilation. In vitro study also found that allicin’s vasodilation is related to NO,
and allicin can improve the level of iNOS and NO in platelet and placental villi as
well as choriocarcinoma. In addition, allicin administration effectively reverses
hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis, inhibits lipid peroxidation, and reduces the
level of glutathione decomposition and superoxide dismutase and peroxidase activity in high cholesterol-fed rats.
3. Anticancer
Allyl sulfide, the active ingredient of allicin, shows anticancer effect.
Epidemiological investigation and experimental studies have shown that allicin has
a significant inhibitory effect on gastric, colon, liver, and lung cancers. Experimental
results show that allicin improves the cellular immune function of cancer
patients. Alliin is the precursor of allicin, which also has significant antitumor activity. In the 1980s, it was found that the growth of S180 tumor in mice was significantly inhibited by alliin injection or garlic thionine. Meanwhile, alliin could
selectively inhibit the reduction synthesis of reduced glutathione (GSH)-dependent
prostaglandin E2?in gland cells.
Anticancer Research
For allicin, a reduction of tumoral cell proliferation was reported by Misharina et al.(2013).
Clinical Use
Allicin shows inhibitory effects on infections caused by bacteria, fungi, and virus. Clinical studies reported that allicin has cured 23 Candida albicans-infected patients . Combining allicin with surgery had cured ten patients with maxillary sinus aspergillosis. Good results for the treatment of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer, chronic colitis, and fatty liver were achieved after allicin administration. Allicin is also capable of eliminating oxygen free radical ion. In addition, allicin can reduce the nitrite- and nitrate-reducing bacteria, and taking garlic could benefit chronic symptoms in stomach, such as stomach discomfort, fullness pain, acid reflux, heating, burning and loss of appetite, and so on.
Properties of Allicin
| Melting point: | 25°C |
| Boiling point: | 259°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | d420 1.112 |
| refractive index | nD20 1.561 |
| storage temp. | 4°C, away from moisture and light |
| solubility | DMSO : 5 mg/mL (30.81 mM; Need ultrasonic)H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) |
| form | liquid |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | 24g/L(10 ºC) |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C6H10OS2/c1-3-5-8-9(7)6-4-2/h3-4H,1-2,5-6H2 |
Safety information for Allicin
Computed Descriptors for Allicin
| InChIKey | JDLKFOPOAOFWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(S(SCC=C)=O)C=C |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 539-86-6 Allicin 99%View Details
539-86-6 Allicin 99%View Details
539-86-6 -
 539-86-6 98%View Details
539-86-6 98%View Details
539-86-6 -
 Allicin CAS 539-86-6View Details
Allicin CAS 539-86-6View Details
539-86-6 -
 Allicin Cas 539 86 6View Details
Allicin Cas 539 86 6View Details
539-86-6 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4
