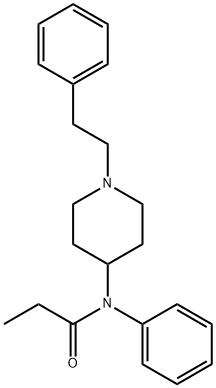
alfentanil
- CAS NO.:71195-58-9
- Empirical Formula: C21H32N6O3
- Molecular Weight: 416.52
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2022-12-21 16:56:50
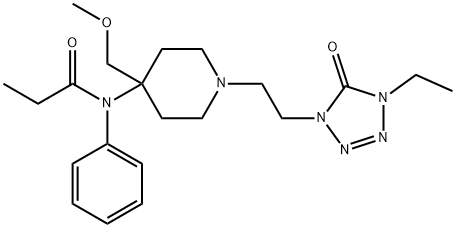
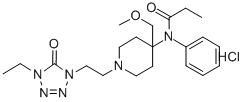
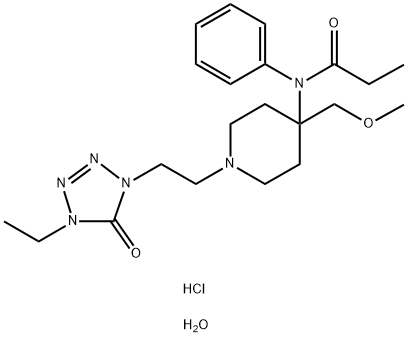
What is alfentanil?
Absorption
For intravenous injection or infusion only.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overexposure include characteristic rigidity of the skeletal muscles, cardiac and respiratory depression, and narrowing of the pupils.
The Uses of alfentanil
The low pKa of alfentanil (6.9) results in it being largely unionised at plasma pH, allowing rapid diffusion to the effect site (t1.2keo ~1min) and rapid onset of action despite it being less lipid soluble than other opioids. It does not bind strongly to opioid receptors, and the effect-site concentration also decreases rapidly as plasma concentrations decrease. Alfentanil is metabolised by the hepatic cytochrome P450 isoform CYP3A4. Genetic variability in the activity of this enzyme may result in two- to threefold variations in pharmacokinetic values when given by infusion. Low, medium or high metabolisers have been identified; this has implications for duration of action when prolonged use is contemplated.
The Uses of alfentanil
Analgesic (narcotic).
Indications
For the management of postoperative pain and the maintenance of general anesthesia.
Background
A short-acting opioid anesthetic and analgesic derivative of fentanyl. It produces an early peak analgesic effect and fast recovery of consciousness. Alfentanil is effective as an anesthetic during surgery, for supplementation of analgesia during surgical procedures, and as an analgesic for critically ill patients.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of piperidines that is piperidine having a 2-(4-ethyl-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)ethyl group at the 1-position as well as N-phenylpropanamido- and methoxymethyl groups at the 4-position.
brand name
Alfenta (Akorn).
General Description
The addition of a methoxy methyl on the 4-piperidine and thesubstitution of the phenethyl ring for an ethyl-substitutedtetrazole-one yielded a compound with about one fourth toone third the potency of fentanyl. Although lesspotent, it has a quicker onset of action, a shorter duration ofaction, and thus a better, safety profile for use as an anestheticadjunct. The piperidine amine has a pKa of 6.5 compared withfentanyl’s pKa of 8.4. This results in a higher proportion ofunionized drug for alfentanil leading to quicker penetrationthrough the blood-brain barrier and thus onset of action.Alfentanil (Alfenta) is available as an IV injection for use asan analgesic adjunct for induction of general anesthesia and tomaintain analgesia during general surgical procedures.
Pharmacokinetics
Alfentanil is a synthetic opioid analgesic. Alfentanil interacts predominately with the opioid mu-receptor. These mu-binding sites are discretely distributed in the human brain, spinal cord, and other tissues. In clinical settings, alfentanil exerts its principal pharmacologic effects on the central nervous system. Its primary actions of therapeutic value are analgesia and sedation. Alfentanil may increase the patient's tolerance for pain and decrease the perception of suffering, although the presence of the pain itself may still be recognized. In addition to analgesia, alterations in mood, euphoria and dysphoria, and drowsiness commonly occur. Alfentanil depresses the respiratory centers, depresses the cough reflex, and constricts the pupils.
Clinical Use
Opioid analgesic:
Short surgical procedures
Intensive care sedation
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: concentration increased by
erythromycin; metabolism accelerated by rifampicin.
Antidepressants: possible CNS excitation or
depression (hypertension or hypotension) in patients
also receiving MAOIs (including moclobemide)
- avoid; possibly increased sedative effects with
tricyclics.
Antifungals: metabolism inhibited by fluconazole
and ketoconazole (risk of prolonged or delayed
respiratory depression); metabolism possibly
inhibited by itraconazole; concentration increased by
voriconazole, consider reducing alfentanil dose.
Antihistamines: increased sedative effects with
sedating antihistamines.
Antipsychotics: enhanced hypotensive and sedative
effects.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with saquinavir - avoid.
Cytotoxics: use crizotinib with caution.
Dopaminergics: avoid with selegiline.
Sodium oxybate: enhanced effect of sodium oxybate
- avoid.
Metabolism
The liver is the major site of biotransformation.
Metabolism
Alfentanil is metabolised in the liver; oxidative N- and O-dealkylation by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 leads to inactive metabolites, which are excreted in the urine.
Properties of alfentanil
| Melting point: | 140.8 °C |
| Boiling point: | 511.8±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.22±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | pKa 6.5 (Uncertain) |
Safety information for alfentanil
Computed Descriptors for alfentanil
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8