ADIPAMIDE
- CAS NO.:628-94-4
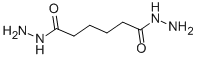
- Empirical Formula: C6H12N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 144.17
- MDL number: MFCD00008045
- EINECS: 211-062-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
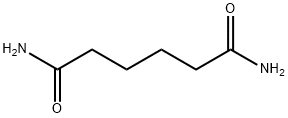
What is ADIPAMIDE?
Description
Adipamide is a chunky white powder. It is slightly soluble in water and incompatible with strong oxidising agents. Adipamide on combustion and decomposition produces hazardous products of toxic fumes of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. Exposures to adipamide by inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption cause adverse health. The symptoms include irritation of the eyes, skin, mucous membranes, and upper respiratory tract. There is no complete information about the toxicological properties of the chemical.
Chemical properties
Adipamide is white powder and chunks. It is slightly soluble in water and incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. On combustion and decomposition, adipamide produces toxic fumes of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides.
Chemical properties
Adipamide is powder in appearance and slightly soluble in water. It is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. On combustion or decomposition, adipamide releases hazardous products, toxic fumes of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen oxides.
The Uses of ADIPAMIDE
Adipamide has been used in the preparation of bisimidates.
Definition
ChEBI: Adipamide is a fatty amide.
Preparation
Adipamide has been traditionally prepared from the dimethyl ester by treatment with concentrated ammonium hydroxide or by heating the diammonium salt of adipic acid in a stream of ammonia. Other substituted amides can be prepared from amines by the usual synthetic methods.
General Description
Colorless powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Slightly soluble in water .
Reactivity Profile
ADIPAMIDE forms flammable gases with strong reducing agents. A very weak base. Mixing with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates adiponitrile. Combustion generates toxic mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Health Hazard
Exposures to adipamide by inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption cause adverse health effects. The symptoms include irritation of the eyes, skin, mucous membranes, and upper respiratory tract. There is no complete information about the toxicological properties of the chemical.
Health Hazard
Exposures to adipamide cause health disorders such as irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. No specifi c adverse health effects have been reported from human exposure to polyhexamethylene adipamide, except for mechanical irritation of the skin and eyes caused by particles. Signifi cant skin permeation and systemic toxicity after contact appears unlikely. The compound is not likely to be hazardous by skin contact, but cleansing the skin after use is advisable. If molten polymer gets on the skin, cool rapidly with cold water. Workers should not attempt to peel polymer from skin, but consult a medical unit for treatment of thermal burn.
Fire Hazard
The flash point of ADIPAMIDE has not been determined, but ADIPAMIDE is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx,.
storage
Adipamide should be kept stored in a cool, dry place, with containers tightly closed to prevent moisture absorption and contamination.
storage
Workers should avoid repeated exposures to adipamide. During use, workers should wear suitable protective clothing, self-contained breathing apparatus, chemical safety goggles, rubber boots, and heavy rubber gloves.
Precautions
During use and handling of adipamide, workers should wear self-contained breathing apparatus, rubber boots, heavy rubber gloves, and chemical safety goggles to avoid splashing of material. A full-face mask respirator provides protection from eye irritation. Workers should avoid exposure to high concentrations of dust. No specifi c intervention is indicated as the compound is not likely to be hazardous by inhalation. Consult a physician if necessary. If exposed to fumes from overheating or combustion, move to fresh air. Consult a physician if symptoms persist.
Properties of ADIPAMIDE
| Melting point: | 226-229 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 262.78°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1804 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | formic acid: soluble50mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow |
| form | powder to crystal |
| pka | 16.26±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Almost white |
| Water Solubility | 4.4g/L(12.20 ºC) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 628-94-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Adipamide (628-94-4) |
Safety information for ADIPAMIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for ADIPAMIDE
ADIPAMIDE manufacturer
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 628-94-4 Adipamide, 98% 99%View Details
628-94-4 Adipamide, 98% 99%View Details
628-94-4 -
 Adipamide 95% CAS 628-94-4View Details
Adipamide 95% CAS 628-94-4View Details
628-94-4 -
 Adipamide CAS 628-94-4View Details
Adipamide CAS 628-94-4View Details
628-94-4 -
 Adipamide CAS 628-94-4View Details
Adipamide CAS 628-94-4View Details
628-94-4 -
 Adipamide CAS 628-94-4View Details
Adipamide CAS 628-94-4View Details
628-94-4 -
 366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 -
 Carvedilol 98%View Details
Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-3 -
 73590-58-6 Omeprazole 98%View Details
73590-58-6 Omeprazole 98%View Details
73590-58-6
