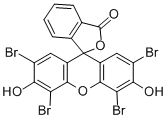
Acid Red 94
Synonym(s):Insulin-like growth factor I;Mechano growth factor;Somatomedin-C
- CAS NO.:632-69-9
- Empirical Formula: C20H5Cl4I4NaO5
- Molecular Weight: 997.66
- MDL number: MFCD00151169
- EINECS: 211-183-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32

What is Acid Red 94?
Description
Rose bengal is a xanthene dye, fluorescein derivative, and photosensitizer. It exhibits absorption/emission maxima of 548/567 nm, respectively. Rose bengal binds to S. aureus cells and decreases survival of photoirradiated S. aureus to 0.012% when used at a concentration of 1 μM. It generates singlet oxygen when exposed to photoirradiation in cell-free assays and induces potassium ion leakage from S. aureus and bovine erythrocytes in the presence of photoirradiation. Rose bengal inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP3A4/5 and the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoform UGT1A6 in human liver microsomes in a light-dependent manner, with IC50 values of 0.072 and 0.035 μM, respectively, in yellow light, 3.1 and 4.2 μM, respectively, in ambient light, and 3 and 4.2 μM, respectively, in the dark. It has been used for staining of live cells, but exhibits both intrinsic and phototoxicity.
Chemical properties
bordeaux-red to red-brown crystalline powder
The Uses of Acid Red 94
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Please refer to the attached Protocolfor details.
The Uses of Acid Red 94
Rose Bengal Sodium Salt is used in biological studies as potential for use as sensitizers in photodynamic and sonodynamic therapy by synthesizing Rose Bengal amphiphilic derivatives. This compound has neuroprotective properties.
What are the applications of Application
Rose Bengal Sodium Salt is a photosensitizer and dye
General Description
This ELISA antibody pair detects Bovine IGF-1
Safety Profile
An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-, I-, and NazO.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Rose bengal is a vital stain and stains dead epithelial cells and mucus.
Full thickness loss of the corneal epithelium is not necessary
(only dead cells need be present) to obtain rose bengal stain uptake.
It does not stain epithelial defects and does not pass into intercellular
spaces.
Rose bengal stain is most commonly employed in the detection
of the presence of viral keratitis in the cat. Because feline herpes virus
tends to infect one cell, moving then to an adjacent cell (causing
the so called dendritic tracts in the cornea) without full thickness
loss of corneal epithelium initially, rose bengal is an ideal diagnostic
agent for this infection. Rose Bengal can also be used to detect damaged
corneal epithelium on the dorsal cornea in early cases of keratoconjunctivitis
sicca. Rose bengal stain is virucidal although no
information is available relative to its use as a therapeutic agent.
in vitro
rose bengal was a quite potent membrane-permeant inhibitor of glutamate uptake into isolated synaptic vesicles. such vesicular glu uptake inhibition was achieved without affecting h1-pump atpase. it was found that various degrees of reduction elicited by rose bengal in [3h]glu in synaptic vesicles inside the synaptosome [1].
in vivo
the distribution of i.v. administered rose bengal was found to depend on its dose. at a low dose, rose bengal could be found almost solely in the liver and plasma. however, at higher doses, the amount of rose bengal found in extra-hepatic tissues gradually increased. the hepatic transfer maximum of rose bengal amounted to 146 micrograms/kg/min. by increasing the dose from 10 to 200 mg/kg, the hepatic concentration of rose bengal also approached a maximum. the storage capacity of the liver, however, did not limit the transfer maximum of rose bengal [1].
storage
Store at RT
Purification Methods
This biological stain can be purified by chromatography on silica TLC using a 35:65 mix of EtOH/acetone as eluent. [Beilstein 19 II 261, 19 III/IV 2926.]
References
[1] ogita k,hirata k,bole dg,yoshida s,tamura y,leckenby am,ueda t. inhibition of vesicular glutamate storage and exocytotic release by rose bengal. j neurochem.2001 apr;77(1):34-42.
[2] fischer e,varga f. hepatic storage and biliary excretion of rose bengal in the rat. acta physiol acad sci hung.1979;54(1):89-94.
Properties of Acid Red 94
| Melting point: | >300°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble1mg/mL |
| form | Solid |
| Colour Index | 45440 |
| pka | 3.9, 4.7(at 25℃) |
| color | Red-brown |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| λmax | 548 nm |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8262 |
| BRN | 3645857 |
| Biological Applications | Apoptosis assay; diagnosis of diseases related to amyloid accumulation; controlling plant diseases; identifying fungi; treating skin,mouth,digestive tract,urinary tract,reproductive tract,respiratory tract,circulatory system |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 632-69-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Spiro[isobenzofuran-1(3H),9'-[9H]xanthen]-3-one, 4,5,6,7-tetrachloro-3',6'-dihydroxy-2',4',5',7'-tetraiodo-, disodium salt (632-69-9) |
Safety information for Acid Red 94
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H290:Corrosive to Metals |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P234:Keep only in original container. P390:Absorb spillage to prevent material damage. |
Computed Descriptors for Acid Red 94
Acid Red 94 manufacturer
GSP Dyes and Chemicals Pvt.Ltd
Anubhav Business Corporation
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 632-69-9 2',4',5',7'-Tetraiodo-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorofluorescein disodium salt 98%View Details
632-69-9 2',4',5',7'-Tetraiodo-3,4,5,6-tetrachlorofluorescein disodium salt 98%View Details
632-69-9 -
 Rose Bengal CAS 632-69-9View Details
Rose Bengal CAS 632-69-9View Details
632-69-9 -
 Rose Bengal CAS 632-69-9View Details
Rose Bengal CAS 632-69-9View Details
632-69-9 -
 Rose bengal 91% CAS 632-69-9View Details
Rose bengal 91% CAS 632-69-9View Details
632-69-9 -
 Rose bengal 90% CAS 632-69-9View Details
Rose bengal 90% CAS 632-69-9View Details
632-69-9 -
 Rose bengal, dye content, 95 % CAS 632-69-9View Details
Rose bengal, dye content, 95 % CAS 632-69-9View Details
632-69-9 -
 Rose Bengal 90% (HPLC) CAS 632-69-9View Details
Rose Bengal 90% (HPLC) CAS 632-69-9View Details
632-69-9 -
 Rose Bengal CAS 632-69-9View Details
Rose Bengal CAS 632-69-9View Details
632-69-9