ACETALDEHYDE AMMONIA
- CAS NO.:75-39-8
- Empirical Formula: C2H7NO
- Molecular Weight: 61.08
- MDL number: MFCD00008058
- EINECS: 200-868-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-11-16 17:07:08
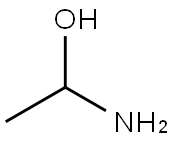
What is ACETALDEHYDE AMMONIA?
Description
Acetaldehyde ammonia is a white crystalline solid and very soluble in water. It is used to make other chemicals and vulcanise rubber. On long exposure to air, acetaldehyde ammonia oxidises, hardens, and turns yellow or brown in colour and reacts exothermically with water to evolve gaseous ammonia. Acetaldehyde ammonia reacts with strong oxidising agents and halogens, and when heated, it readily decomposes into acetaldehyde and ammonia. It attacks copper, aluminium, zinc, and their alloys and reacts with mercury and silver oxides to form shock-sensitive compounds.
The Uses of ACETALDEHYDE AMMONIA
For preparing pure acetaldehyde; in organic syntheses.
General Description
A white crystalline solid. Melting point 97°C. Boiling point 110°C (with some decomposition). An addition product between acetaldehyde and ammonia. Presents moderate fire and explosion hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Moderately toxic by ingestion and inhalation and a strong irritant. Used to make other chemicals, vulcanize rubber.
Air & Water Reactions
Resinifies (oxidizes, hardens and turns yellow or brown) on long exposure to air. Very soluble in water [Hawley]. Reacts exothermically with water to evolve gaseous ammonia.
Reactivity Profile
ACETALDEHYDE AMMONIA reacts with strong oxidizing agents and halogens. Attacks copper, aluminum, zinc and their alloys. Reacts with mercury and silver oxides to form shock-sensitive compounds [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 139]. Readily decomposes into acetaldehyde and ammonia when heated, causing the hazards of those substances [Lewis].
Health Hazard
Inhalation of material may be harmful. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Inhalation of Asbestos dust may have a damaging effect on the lungs. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Some liquids produce vapors that may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Some may burn but none ignite readily. Containers may explode when heated. Some may be transported hot.
Safety Profile
It readily decomposes into acetaldehyde and ammonia when heated, causing the hazards of these substances. Moderate fire and explosion hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Can react with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NH3 and NOx
Properties of ACETALDEHYDE AMMONIA
| Melting point: | 95-97°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 109-111°C |
| Density | 0.9610 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.4521 (estimate) |
| pka | 14.09±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White, crystalline solid |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-39-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1-Aminoethanol (75-39-8) |
Safety information for ACETALDEHYDE AMMONIA
Computed Descriptors for ACETALDEHYDE AMMONIA
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![bis[2-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]ethanolato][2-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]ethanolato-O](propan-2-olato)titanate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180808/GIF/65380-84-9.gif)
![2-[(5-Nitro-2-pyridyl)amino]ethanol](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/25948-12-3.gif)
![Cuprate(2-), [29H,31H-phthalocyaninedisulfonato(4-)-N29,N30,N31,N32]-, compds. with 2-(methylamino)ethanol](https://img.chemicalbook.in/)
![Formaldehyde, polymer with 2-(dimethylamino)ethanol and 4,4'-(1-methylethylidene)bis[phenol]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20211123/GIF/51877-21-5.gif)
You may like
-
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 98%View Details
88491-46-7 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4