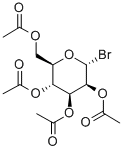
6-bromohexyl acetate
Synonym(s):Mineral Spirits;Stoddard Solvent
- CAS NO.:8052-41-3
- Empirical Formula: C8H15BrO2
- Molecular Weight: 223.109
- MDL number: MFCD00132767
- EINECS: 232-489-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02

What is 6-bromohexyl acetate?
Description
Stoddard solvent is a refined petroleumdistillate derived fromthe naphtha and kerosene carbon ranges (C7–C12) in crude oil. It is a type of ‘white spirit,’ characterized as a clear solvent absent of objectionable odors (hydrodesulfurized to remove hydrogen sulfide and mercaptans). Stoddard solvent typically contains paraffinic alkanes (saturated branched and linear), cycloalkanes (also known as cycloparaffins), and aromatic hydrocarbons. Paraffins (30–50%) and cycloparaffins (30–40%) tend to predominate, with a remaining 10–20%comprised of aromatics. The exact composition of Stoddard solvent can vary due to variations in crude oils and the refining processes. The boiling range of Stoddard solvent is approximately 148.8–204.4 °C.
Chemical properties
colourless liquid with a kerosene-like odour (odour threshold typically
Chemical properties
Stoddard solvent is a refined petroleum solvent containing .65% C10 or higher hydrocarbons (mineral spirits, 85% nonane & 15% trimethylbenzene). Stoddard solvent is a colorless liquid. Kerosene-like odor
The Uses of 6-bromohexyl acetate
Dry cleaning, spot and stain removal.
The Uses of 6-bromohexyl acetate
Stoddard solvent is used widely in dry cleaning processes, and as a general cleaning and universal solvent.
The Uses of 6-bromohexyl acetate
Dry cleaning; degreasing; paint thinner.
Definition
6-bromohexyl acetate is a colorless, refined petroleum distillate that is free from rancid or objectionable odors and that boils in the range of approximately 149.degree.C to 204.5.degree.C (300.degree.F to 400.degree.F).
General Description
A clear colorless mixture with a strong odor. Insoluble in water and about the same density as water. Flash point over 100°F. Avoid exposure. Used as a solvent and to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
NAPHTHA: NEO-CLEAR(R) XYLENE SUBSTITUTE is incompatible with the following: Strong oxidizers .
Hazard
Fire risk. Toxic by ingestion. Eye, skin and kidney damage; nausea; central nervous system impairment.
Health Hazard
High concentration of vapors may cause intoxication. If liquid is swallowed, it may get into lungs by aspiration; not very irritating to skin or eyes.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Safety Profile
Mildly toxic by inhalation. A human eye irritant. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat, sparks, or flame. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid fumes and may explode; can react with oxidzing materials. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. See also n-NONANE.
Potential Exposure
Stoddard solvent is used as a diluent in paints, coatings, and waxes; as a paint thinner; as a drycleaning agent; as a degreaser for metal parts; as a herbicide
Carcinogenicity
Stodddard solvent was not genotoxic in a variety of assays including Salmonella typhimurium, a mouse lymphoma mutation assay, rodent bone marrow cytogenic tests, and rodent dominant lethal tests.
Environmental Fate
The hydrocarbons in Stoddard solvent vary in volatility and water solubility. Spills of Stoddard solvent would be expected to partition to soil, groundwater, and air. Smaller alkanes and aromatics will likely volatilize to the air where photooxidation can occur. Biodegradation in soil and/or water may be more likely for the larger aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, although Stoddard solvent is unlikely to be readily biodegradable. Although the larger hydrocarbons in Stoddard solvent are expected to have slower elimination from biological tissues than the smaller constituents, Stoddard solvent overall would not be expected to bioaccumulate.
Shipping
UN1993 Flammable liquids, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, Technical Name Required. UN1268 Petroleum distillates, n.o.s. or Petroleum products, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Toxicity evaluation
Stoddard solvent, as with a number of petroleum hydrocarbons,
can produce kidney effects in male rats due to accumulation
of a-2m-globulin. Effects observed microscopically
include hyaline droplet accumulation, granular casts within
medullary tubules, corticotubular basophilia, and degeneration
with regeneration of tubular epithelium. These lesions,
characterized as hyaline droplet nephropathy, are attributed to
accumulation of a-2m-globulin, a carrier protein produced in
substantial quantities in male rat livers but in negligible
amounts in female rats and humans. The a-2m-globulin
protein, which transports endogenous pheromones into the kidneys of male rats, also has an affinity for petroleum
hydrocarbon. This mechanism is specific to male rats and is
considered irrelevant to human health risk assessment.
The lipophilic nature of Stoddard solvent can cause defatting
of the skin. Longer or repeated exposure can increase the
severity of the effects.
High exposures can produce neurological symptoms such
as dizziness and lack of coordination. The specific mechanism
of toxicity for this is unknown but could be similar to other
short- to medium-length hydrocarbons that also produce
neurotoxicity at high exposures.
The low viscosity of Stoddard solvent poses a risk of aspiration
into the lungs if it is ingested, which can induce pneumonia
that may be fatal.
Incompatibilities
May form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Properties of 6-bromohexyl acetate
| Melting point: | 40°C |
| Boiling point: | 149-213°C/760mmHg |
| Density | 0.75 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | 5.341hPa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | n20/D 1.417 |
| Flash point: | 98 °C |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| form | Solvent |
| color | Clear |
| Water Solubility | 100μg/L at 25℃ |
| Stability: | Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Store and handle in accord with Petroleum Act. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 8052-41-3 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Stoddard solvent (8052-41-3) |
Safety information for 6-bromohexyl acetate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H226:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for 6-bromohexyl acetate
6-bromohexyl acetate manufacturer
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![3-(ACETYLOXY)-6-BROMO-5-HYDROXY-10,13-DIMETHYLPERHYDROCYCLOPENTA[A]PHENANTHREN-17-YL BENZOATE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB5253751.gif)

You may like
-
 8052-41-3 Solvent C-9 98%View Details
8052-41-3 Solvent C-9 98%View Details
8052-41-3 -
 Xylene Substitute CASView Details
Xylene Substitute CASView Details -
 Xylene Substitute CASView Details
Xylene Substitute CASView Details -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1