2,6-Dinitrotoluene
- CAS NO.:606-20-2
- Empirical Formula: C7H6N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 182.13
- MDL number: MFCD00007158
- EINECS: 210-106-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
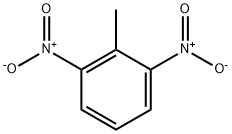
What is 2,6-Dinitrotoluene?
Chemical properties
2,6-Dinitrotoluene is one of the six dinitrotoluene isomers. Dinitrotoluene (DNT) or Dinitro is an explosive with the formula C6H3(CH3)(NO2)2. At room temperature it is a pale yellow to orange crystalline solid. It is a high explosive and one of the precursors for trinitrotoluene (TNT), which is synthesized through three separate nitrations of toluene. The first product is mononitrotoluene, DNT is the second, and TNT is the third and final product.
Physical properties
Pale yellow, orange, brown or reddish rhombic crystals. Odor threshold concentration in water is 100 ppb (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992).
The Uses of 2,6-Dinitrotoluene
2,6-Dinitrotoluene is used primarily, along with the other isomers, in producing toluene diisocyanate; production of the diisocyanate ranges from 100 million to almost a billion pounds each year.
The Uses of 2,6-Dinitrotoluene
Organic synthesis; propellant additive; manufacture of explosives; intermediate in the manufacture of polyurethanes.
What are the applications of Application
2,6-Dinitrotoluene is a biochemical used in the production of toluene diisocyanate
Definition
ChEBI: 2,6-dinitrotoluene is a dinitrotoluene carrying nitro substituents at positions 2 and 6. It has a role as a genotoxin.
Preparation
2,6-Dinitrotoluene is synthesized from o-nitrotoluene by nitration with mixed acid.
General Description
Yellow to red solid or heated liquid with a slight odor. Solidifies in cool water. Solid and liquid sink in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Mixes slowly with water. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
2,6-Dinitrotoluene is sensitive to heat. 2,6-Dinitrotoluene may explode when exposed to heat or flame. 2,6-Dinitrotoluene can be detonated only by a very strong initiator. 2,6-Dinitrotoluene is incompatible with strong oxidizers. 2,6-Dinitrotoluene is also incompatible with caustics and metals such as tin and zinc. 2,6-Dinitrotoluene may react with reducing agents. 2,6-Dinitrotoluene will attack some forms of plastics, rubber and coatings.
Health Hazard
INHALATION, INGESTION OR SKIN ABSORPTION: Headache, weakness, nausea or dizziness, cyanosis, drowsiness, shortness of breath and collapse. Can burn eyes and skin.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. A skin irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also 2,4-DINITROTOLUENE
Environmental Fate
Biological. When 2,6-dinitrotoluene was statically incubated in the dark at 25 °C with yeast
extract and settled domestic wastewater inoculum, significant biodegradation with gradual
acclimation was followed by deadaptive process in subsequent subcultures. At a concentration of 5
mg/L, 82, 55, 47, and 29% losses were observed after 7, 14, 21, and 28-d incubation periods,
respectively. At a concentration of 10 mg/L, only 57, 49, 35, and 13% were observed after 7, 14,
21, and 28-d incubation periods, respectively (Tabak et al., 1981). Under anaerobic and aerobic
conditions, a sewage inoculum degraded 2,6-dinitrotoluene to aminonitrotoluene (Hallas and
Alexander, 1983).
Photolytic. Simmons and Zepp (1986) estimated the photolytic half-life of 2,6-dinitrotoluene in
surface water to range from 2 to 17 h.
Low et al. (1991) reported that the nitro-containing compounds (e.g., 2,4-dinitrophenol) undergo
degradation by UV light in the presence of titanium dioxide yielding ammonium, carbonate, and
nitrate ions. By analogy, 2,6-dinitrotoluene should degrade forming identical ions.
Chemical/Physical. 2,6-Dinitrotoluene will not hydrolyze (Kollig, 1993).
At influent concentrations of 1.0, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 mg/L, the GAC adsorption capacities
were 145, 70, 33, and 16 mg/g, respectively (Dobbs and Cohen, 1980).
Metabolic pathway
2-Amino-6-nitrotoluene, 2,6-dinitrobenzyl alcohol, 2- amino-6-nitrobenzyl alcohol, and the conjugates of the latter two alcohols are detected in the urine of male Wistar rats as metabolites of 2,6-dinitrotoluene (2,6- DNT). In addition to the metabolites identified in the urine, 2,6-dinitrobenzaldehyde is detected in the rat bile. Incubation of 2,6-DNT with a hepatic microsomal preparation gives 2,6-dinitrobenzyl alcohol. Incubation of benzyl alcohol with a microsomal plus cytosol preparation gives 2,6-dinitrobenzaldehyde, and incubation of 2,6-dinitrobenzaldehyde with cytosol preparations gives 2,6-dinitrobenzyl alcohol and 2,6- dinitrobenzoic acid.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from acetone. EXPLOSIVE when dry.[Beilstein 5 III 761, 5 IV 866.]
Properties of 2,6-Dinitrotoluene
| Melting point: | 56-61 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 300°C |
| Density | 1.2833 |
| vapor pressure | 3.5(x 10-4 mmHg) at 20 °C (quoted, Howard, 1989)5.67(x 10-4 mmHg) at 25 °C (Banerjee et al., 1990) |
| refractive index | 1.4790 |
| Flash point: | 207°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in ethanol (Weast, 1986) and many other organic solvents including chloroform and
carbon tetrachloride. |
| Water Solubility | 0.0182 g/100 mL |
| BRN | 2052046 |
| Stability: | Stable, but shock sensitive. Incompatible with oxidizing agents, reducing agents, strong bases. Heating may cause explosion. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 606-20-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 65) 1996 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzene, 2-methyl-1,3-dinitro-(606-20-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,6-Dinitrotoluene (606-20-2) |
Safety information for 2,6-Dinitrotoluene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H361:Reproductive toxicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for 2,6-Dinitrotoluene
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2,6-Dinitrotoluene CAS 606-20-2View Details
2,6-Dinitrotoluene CAS 606-20-2View Details
606-20-2 -
 2,6-Dinitrotoluene CAS 606-20-2View Details
2,6-Dinitrotoluene CAS 606-20-2View Details
606-20-2 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
