2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
Synonym(s):2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
- CAS NO.:88-06-2
- Empirical Formula: C6H3Cl3O
- Molecular Weight: 197.45
- MDL number: MFCD00002172
- EINECS: 201-795-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18
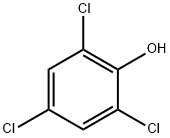
What is 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol?
Chemical properties
Yellow flakes; strong phenolic odor. Soluble in acetone, alcohol, and ether; insoluble in water. Nonflammable.
Physical properties
Colorless needles or yellow solid with a strong, phenolic, musty or rotten vegetable-type odor. At 40 °C, the lowest concentration at which an odor was detected was 380 μg/L. At 25 °C, the lowest concentration at which a taste was detected was >12 μg/L (Young et al., 1996).
The Uses of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is used as a broad range pesticide against insects, fungi, vegetation and bacteria. It has become a common environmental contaminant and probable human carcinogen.
The Uses of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
Fungicide, herbicide, defoliant.
The Uses of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
Wood preservative; disinfectant; fungicide, herbicide, defoliant.
What are the applications of Application
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is used as a broad range pesticide
Definition
ChEBI: A trichlorophenol with phenolic substituents on positions 2, 4 and 6.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 24, p. 1523, 1959 DOI: 10.1021/jo01092a034
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is incompatible with acid chlorides, acid anhydrides and oxidizing agents. 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol can be converted to the sodium salt by reaction with sodium carbonate. Forms ethers, esters and salts by reaction with metals and amines. Undergoes substitution reactions such as nitration, alkylation, acetylation and halogenation. Can be hydrolyzed by reaction with bases at elevated temperatures and pressures. Reacts with alkalis at high temperatures .
Health Hazard
In experimental animals, 2,4,6- trichlorophenol causes toxic effects to the liver and hematologic system and cancer. There is no reliable information regarding exposure and toxic effects in humans.
Fire Hazard
Literature sources indicate that 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is nonflammable.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic data. Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. A skin and severe eye irritant. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. Used as a germicide and preservative. See also CHLOROPHENOLS.
Carcinogenicity
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In activated sludge, only 0.3% mineralized to carbon dioxide after 5 d (Freitag et al.,
1985). In anaerobic sludge, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol degraded to 4-chlorophenol (Mikesell and Boyd,
1985). When 2,4,6-trichlorophenol was statically incubated in the dark at 25 °C with yeast extract
and settled domestic wastewater inoculum, significant biodegradation with rapid adaptation was
observed. At concentrations of 5 and 10 mg/L, 96 and 97% biodegradation, respectively, were
observed after 7 d (Tabak et al., 1981).
Photolytic. Titanium dioxide suspended in an aqueous solution and irradiated with UV light (λ
= 365 nm) converted 2,4,6-trinitrophenol to carbon dioxide at a significant rate (Matthews, 1986).
A carbon dioxide yield of 65.8% was achieved when 2,4,6-trichlorophenol adsorbed on silica gel
was irradiated with light (λ >290 nm) for 17 h (Freitag et al., 1985).
Chemical/Physical. An aqueous solution containing chloramine reacted with 2,4,6-trichlorophenol
to yield the following intermediate products after 2 h at 25 °C: 2,6-dichloro-1,4-
benzoquinone-4-(N-chloro)imine and 4,6-dichloro-1,2-benzoquinone-2-(N-chloro)imine (Maeda et
al., 1987).
Purification Methods
Crystallise the phenol from *benzene, EtOH or EtOH/water. [Beilstein 6 IV 1005.]
Properties of 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
| Melting point: | 64-66 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 246 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.49 |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 76.5 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5300 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 99 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 0.8g/l |
| form | Crystalline Mass or Crystalline Powder and Chunks |
| pka | 6.15 (Leuenberger et al., 1985) 6.10 (Blackman et al., 1955) 6.0 (Eder and Weber, 1980) |
| color | white to slightly brown |
| Water Solubility | 0.8 g/L |
| Merck | 14,9644 |
| BRN | 776729 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 9.07 at 25 °C (estimated, Leuenberger et al., 1985a) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 88-06-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol, 2,4,6-trichloro-(88-06-2) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 117) 2019 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol (88-06-2) |
Safety information for 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H351:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol 98%View Details
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol 98%View Details -
 88-06-2 98%View Details
88-06-2 98%View Details
88-06-2 -
 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, 98%+ CAS 88-06-2View Details
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol, 98%+ CAS 88-06-2View Details
88-06-2 -
 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol CAS 88-06-2View Details
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol CAS 88-06-2View Details
88-06-2 -
 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol CAS 88-06-2View Details
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol CAS 88-06-2View Details
88-06-2 -
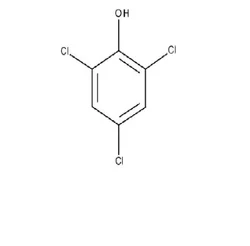 2,4,6 Tri Chloro PhenolView Details
2,4,6 Tri Chloro PhenolView Details
88-06-2 -
 2.4.6 Trichlorophenol , TCP, PowderView Details
2.4.6 Trichlorophenol , TCP, PowderView Details
88-06-2 -
 2,4,6 Trichloro Phenol Chemical, PowderView Details
2,4,6 Trichloro Phenol Chemical, PowderView Details
88-06-2
