2,3-Dimethylbutane
Synonym(s):Diisopropyl
- CAS NO.:79-29-8
- Empirical Formula: C6H14
- Molecular Weight: 86.18
- MDL number: MFCD00008925
- EINECS: 201-193-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
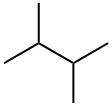
What is 2,3-Dimethylbutane?
Description
2,3-Dimethylbutane is a colorless liquid.Molecular weight= 86.20; Boiling point = 58℃; Flashpoint= 229℃; Autoignition temperature= 405℃.Explosive limits: LEL = 1.2%; UEL= 7.0%. HazardIdentification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System):Health 2, Flammability 3, Reactivity 0. Insoluble in water
Chemical properties
2,3-Dimethylbutane, C6H14, is a flammable liquid with a specific gravity of 0.66164. It is released into the atmosphere from automobile, biomass combustion, and gasoline vapor emissions.
Physical properties
Colorless liquid with a mild gasoline-like odor. An odor threshold concentration of 4.2 ppmv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
The Uses of 2,3-Dimethylbutane
2,3-Dimethylbutane is a branched saturated hydrocarbon for proteomics research. It is used in organic synthesis, catalytic agent, petrochemical additive.
The Uses of 2,3-Dimethylbutane
2,3-Dimethylbutane is used in high octane fuels and in organic synthesis. It is also used as a gas chromatography standard.
What are the applications of Application
2,3-Dimethylbutane is a branched saturated hydrocarbon for proteomics research
Production Methods
2,3-Dimethylbutane is produced from crude oil, natural liquid gases, and petroleum refining processes.
Definition
ChEBI: 2,3-dimethylbutane is an alkane that is butane substituted by a methyl group at positions 2 and 3. It is an alkane and a volatile organic compound. It derives from a hydride of a butane.
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a petroleum-like odor. Flash point -20°F. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Vapors heavier than air.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons, such as 2,3-DIMETHYLBUTANE, may be incompatible with strong oxidizing agents like nitric acid. Charring of the hydrocarbon may occur followed by ignition of unreacted hydrocarbon and other nearby combustibles. In other settings, aliphatic saturated hydrocarbons are mostly unreactive. They are not affected by aqueous solutions of acids, alkalis, most oxidizing agents, and most reducing agents. 2,3-DIMETHYLBUTANE is incompatible with oxidizing materials. 2,3-DIMETHYLBUTANE is also incompatible with oxygen. .
Health Hazard
Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Flammability and Explosibility
Flammable
Safety Profile
Probably an irritant and narcotic in high concentration. A very dangerous fire and explosion hazard when exposed to heat or flame; can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Keep away from heat and open flame. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Potential Exposure
2,3-Dimethylbutane is used in highoctane fuel and to make organic chemicals.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and i
Source
Comprised 1.6 to 2.6 vol % of total evaporated hydrocarbons from gasoline tank (quoted,
Verschueren, 1983). Schauer et al. (1999) reported 2,3-dimethylbutane in a diesel-powered
medium-duty truck exhaust at an emission rate of 570 μg/km.
California Phase II reformulated gasoline contained 2,3-dimethylbutane at a concentration of
12.9 g/kg. Gas-phase tailpipe emission rates from gasoline-powered automobiles with and without
catalytic converters were 2.14 and 298 mg/km, respectively (Schauer et al., 2002).
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. Major products reported from the photooxidation of 2,3-dimethylbutane with
nitrogen oxides are carbon monoxide and acetone. Minor products included formaldehyde,
acetaldehyde and peroxyacyl nitrates (Altshuller, 1983). Synthetic air containing gaseous nitrous
acid and exposed to artificial sunlight (λ = 300–450 nm) photooxidized 2,3-dimethylbutane into
acetone, hexyl nitrate, peroxyacetal nitrate, and a nitro aromatic compound tentatively identified
as a propyl nitrate (Cox et al., 1980).
Chemical/Physical. Complete combustion in air yields carbon dioxide and water vapor. 2,3-
Dimethylbutane will not hydrolyze because it has no hydrolyzable functional group.
storage
Color Code—Red: Flammability Hazard: Store ina flammable liquid storage area or approved cabinet awayfrom ignition sources and corrosive and reactive materials.Prior to working with 2,3-dimethylbutane you should betrained on its proper handling and storage. Before enteringconfined space where this chemical may be present, checkto make sure that an explosive concentration does not exist.2,3-Dimethylbutane must be stored to avoid contact withoxidizers (such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates,chlorates, and nitrates), since violent reactions occur.Sources of ignition, such as smoking and open flames, areprohibited where 2,3-dimethylbutane is handled, used, orstored. Metal containers involving the transfer of 5 gallonsor more of 2,3-dimethylbutane should be grounded andbonded. Drums must be equipped with self-closing valves,pressure vacuum bungs, and flame arresters. Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially when opening andclosing containers of 2,3-dimethylbutane. Wherever 2,3-dimethylbutane is used, handled, manufactured, or
Shipping
This compound requires a shipping label of“FLAMMABLE LIQUID.” It falls in Hazard Class 3 andPacking Group II.
Purification Methods
Distil it from sodium, pass it through a column of silica gel (activated by heating in nitrogen to 350o before use) to remove unsaturated impurities, and again distil it from sodium. Also distil it azeotropically with MeOH, then wash with water, dry (Na2SO4) it, and redistil it. [Beilstein 1 IV 371.]
Incompatibilities
Forms explosive mixture with air.Violent reaction with oxygen, strong oxidizers.
Properties of 2,3-Dimethylbutane
| Melting point: | -129 °C |
| Boiling point: | 58 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.662 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 7.41 psi ( 37.7 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | −28 °F |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | In methanol: 495, 593, 760, and 1,700 g/L at 5, 10, 15, and 20 °C, respectively. Miscible at higher
temperatures (Kiser et al., 1961). |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | >14 (Schwarzenbach et al., 1993) |
| color | Colorless |
| explosive limit | ~7.7% |
| Odor Threshold | 0.42ppm |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (1mg/ml @22°C), DMSO, ethanol, acetone. |
| BRN | 1730737 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 1.28(atm?m3/mol) at 25 °C (Mackay and Shiu, 1981) |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH TLV: TWA and STEL for all isomers except n-hexane are 500 and
1,000 ppm, respectively (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 1.8899999999999999 |
| Stability: | Stable. Flammable. Readily forms explosive mixtures with air. Note low flash point. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, oxygen. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 79-29-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,3-Dimethylbutane (79-29-8) |
Safety information for 2,3-Dimethylbutane
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H304:Aspiration hazard H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P331:Do NOT induce vomiting. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. |
Computed Descriptors for 2,3-Dimethylbutane
| InChIKey | ZFFMLCVRJBZUDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2,3-Dimethylbutane CAS 79-29-8View Details
2,3-Dimethylbutane CAS 79-29-8View Details
79-29-8 -
 2,3-Dimethylbutane CAS 79-29-8View Details
2,3-Dimethylbutane CAS 79-29-8View Details
79-29-8 -
 2,3-Dimethylbutane CAS 79-29-8View Details
2,3-Dimethylbutane CAS 79-29-8View Details
79-29-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1