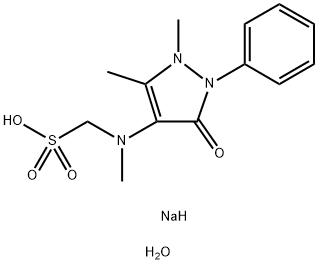
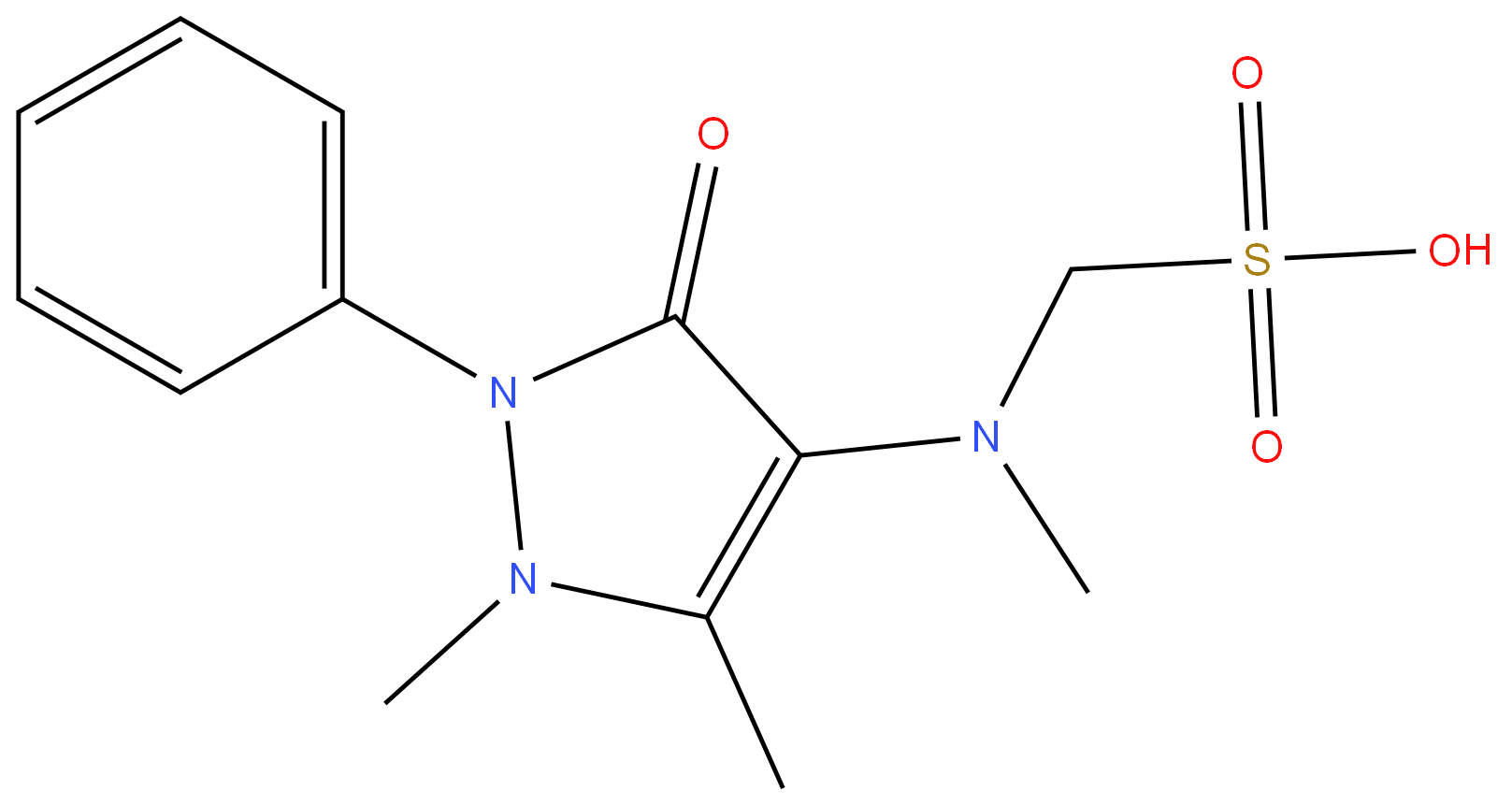
[(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid
- CAS NO.:50567-35-6
- Empirical Formula: C13H17N3O4S
- Molecular Weight: 311.36
- MDL number: MFCD00046078
- EINECS: 256-627-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
![[(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid Structural](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/50567-35-6.gif)
What is [(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid ?
Absorption
Metamizole is hydrolyzed to 4-methyl-amino-antipyrine (MAA) in gastric juice and is mostly absorbed in this form. MAA bioavailability differs based on the administration route. In patients given metamizole tablets, the bioavailability of MAA is 85%, in patients given drops, 89%, in patients given suppositories, 54%, and in patients given an intramuscular injection, 87%. There is a linear relationship between metamizole oral dose and MAA Cmax. After oral doses ranging between 0.75 and 3 g, the tmax is reached at 1.4-2.0 hours.
Toxicity
A metamizole overdose (7.5 g) may lead to gastrointestinal toxicity. If less than an hour has passed since metamizole ingestion, gastrointestinal decontamination and supportive measures are suggested as overdose treatment. Metamizole can also cause myelotoxicity, leading to drug-induced agranulocytosis.
Background
Metamizole (dipyrone) is a pyrazolone derivative that belongs to the group of nonacid nonopioids. It is considered a potent analgesic and antipyretic with favourable gastrointestinal tolerability. Metamizole was formerly marketed in the US as Dimethone tablets and injection, Protemp oral liquid, and other drug products, and was withdrawn due to its association with potentially fatal agranulocytosis. Approvals of the NDA's for metamizole drug products were withdrawn on June 27, 1977 (see the Federal Register of June 17, 1977, 42 FR 30893). In 1963, metamizole was withdrawn from the Canadian market and banned in the UK, France, Sweden, Norway and Australia. Metamizole is still used in certain countries in Europe, Asia and South America.
Indications
Metamizole is banned in several countries, where it was previously used as a powerful analgesic and fever reducer. In countries where it is still available, metamizole is indicated for acute severe pain after injuries or surgeries, colic, tumor pain, and acute or severe pain symptoms, as well as high fever if other treatments are unsuccessful.
Definition
ChEBI: A pyrazole that is antiipyrine substituted at C-4 by a methyl(sulfomethyl)amino group, the sodium salt of which, metamizole sodium, was widely used as a powerful analgesic and antipyretic, but withdrawn from many markets from the 1970s due to a risk of cau ing risk of causing agranulocytosis.
Pharmacokinetics
Metamizole is a strong analgesic and antipyretic with spasmolytic properties. It has weak anti-inflammatory or antithrombotic properties and does not follow the same mechanism of action as conventional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Metamizole can lead to agranulocytosis, a life-threatening side effect where a patient’s neutrophil count falls below 500 cells per microliter. It has been shown that metamizole-induced agranulocytosis is caused by the development of drug-dependent anti-neutrophil antibodies requiring covalent binding of neutrophils to metamizole and its metabolites.
Metabolism
Metamizole undergoes rapid hydrolysis to the active moiety 4-methyl-amino-antipyrine (MAA). MAA is then metabolized to 4-formyl-amino-antipyrine (FAA) via c-oxidation and 4-amino-antipyrine (AA) via N-demethylation. The N-demethylation of MAA is mainly mediated by CYP3A4, although CYP2B6, CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 may also be involved. FAA is an end metabolite, while AA is acetylated by N-acetyl-transferase to form 4-acetyl-amino-antipyrine (AAA). The unchanged drug may be present in plasma following the intravenous administration of metamizole; however, following oral administration, it cannot be detected in plasma or urine.
Properties of [(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid
| Density | 1.46±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Melting point: | 131-132 °C (decomp) |
| pka | 1.32±0.50(Predicted) |
Safety information for [(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid
Computed Descriptors for [(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid
[(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid manufacturer
Venkatasai Life Sciences
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

![[(2,3-dihydro-1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methylamino]methanesulphonic acid](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/50567-35-6.gif)
You may like
-
 50567-35-6 Metamizole 99%View Details
50567-35-6 Metamizole 99%View Details
50567-35-6 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1