2-Naphthylamine
Synonym(s):β-Naphthylamine;2-Aminonaphthalene
- CAS NO.:91-59-8
- Empirical Formula: C10H9N
- Molecular Weight: 143.19
- MDL number: MFCD00004112
- EINECS: 202-080-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-08 13:49:10
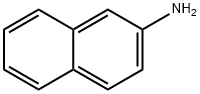
What is 2-Naphthylamine?
Chemical properties
2-Naphthylamine is a white to red crystals with a faint, aromatic odor. Darkens in air to a reddish-purple color.
Physical properties
White crystals becomes purplish-red on exposure to air. Odor threshold concentrations ranged from 1.4 to 1.9 mg/m3 (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992).
The Uses of 2-Naphthylamine
2-Naphthylamine was widely used in themanufacture of dyes and in rubber. Currently, its use is curtailed because of thehealth hazard.
The Uses of 2-Naphthylamine
It is listed as a known human carcinogen. Used in manufacturing of dyes, as antioxidant in rubber
The Uses of 2-Naphthylamine
An amine compound used for research purposes
Definition
ChEBI: 2-naphthylamine is a naphthylamine carrying the amino group at position 2. It has a role as a carcinogenic agent.
Production Methods
2-Naphthylamine was previously produced in substantial
amounts for nearly 50 years but is no longer produced
commercially. It is now used exclusively for research, and
only rarely. It was formerly used in the manufacture of
dyestuffs and as an antioxidant in the rubber industry.
Prior to termination of its domestic production and use in
the dye and rubber industries, an estimated 1000 U.S. workers
were possibly exposed to 2-naphthylamine by inhalation
and dermal routes. Currently, laboratory technicians and
scientists who use the compound for research purposes may
constitute the group with the greatest risk of potential exposure.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 75, p. 2014, 1953 DOI: 10.1021/ja01104a525
Synthesis, p. 830, 1980 DOI: 10.1055/s-1980-29225
General Description
A white to reddish colored solid in the form of flakes. Slightly soluble in hot water and denser than water. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Used to make dyes and agricultural chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
2-Naphthylamine darkens in air to a reddish-purple color (oxidizes). Slightly soluble in hot water and denser than water. Napthyl amines can be slowly hydrolyzed, releasing NH3 as a byproduct [N.L. Drake, Org. React. 1, (1942), 105].
Reactivity Profile
2-Naphthylamine is a weak base. 2-Naphthylamine is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents and strong acids. 2-Naphthylamine is also incompatible with nitrous acid. 2-Naphthylamine reduces warm ammoniacal silver nitrate.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion, inhalation, skin absorption; a confirmed carcinogen. Causes bladder cancer.
Health Hazard
2-Naphthylamine poses a severe health haz ard because of its carcinogenicity. Admin istration of this compound by all routesresulted in cancers in various tissues in testanimals. It caused tumors in the kidney, blad der, liver, lungs, skin, and blood tissues.There is sufficient evidence that this com pound causes bladder cancer in humans aftera latent period of several years.The toxicity of 2-naphthylamine is lowto moderate. However, high doses can pro duce severe acute toxic effects. The routesof exposures are ingestion, skin contact, andinhalation of its dusts or vapors. The acutetoxic symptoms are similar to those produced by 1-naphthylamine: hemorrhagic cystitis or methemoglobinemia (causing hypoxiaor inadequate supply of oxygen to tissues),respiratory distress, and hematuria (blood inurine).LD50 value, oral (rats): 727 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Safety Profile
Confirmed human carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic and tumorigenic data. Long and continued exposure to even small amounts may produce tumors and cancers of the bladder. Poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. A very toxic chemical in any of its physical forms, such as flake, lump, dust, liquid, or vapor. It can be absorbed into the body through the lungs, the gastrointestinal tract, or the skin. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. At elevated temperatures it evolves a vapor that is flammable and explosive. Incompatible with nitrous acid. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Toxicology
2-Naphthylamine is a human carcinogen that leads predominately to formation of tumors in the epithelium of the bladder. The conclusive epidemiological studies on humans are backed up by a wealth of animal data. However, although a proven carcinogen in mouse, hamster, dog, and monkey, 2-naphthylamine exhibits little, if any, carcinogenicity in rat or rabbit. Several metabolic pathways have been identified, but the main one involves N-hydroxylation followed by rearrangement to 2-amino-1- hydroxynaphthalene. Only the former is a proven animal carcinogen.
Potential Exposure
2-Naphthylamine is presently used only for research purposes. It is present as an impurity in α-naphthylamine. It is as an intermediate in the preparation of other compounds. 2-Naphthylamine was widely used in the manufacture of dyestuffs; as an antioxidant for rubber; and in rubber coated cables.
Carcinogenicity
2-Naphthylamine is known to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans.
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. Low et al. (1991) reported that the photooxidation of aqueous primary amine
solutions by UV light in the presence of titanium dioxide resulted in the formation of ammonium
and nitrate ions.
Chemical/Physical. Kanno et al. (1982) studied the aqueous reaction of 2-naphthylamine and
other substituted aromatic hydrocarbons (aniline, toluidine, 1-naphthylamine, phenol, cresol,
pyrocatechol, resorcinol, hydroquinone, and 1-naphthol) with hypochlorous acid in the presence of
ammonium ion. They reported that the aromatic ring was not chlorinated as expected but was
cleaved by chloramine forming cyanogen chloride. At lower pHs, the amount of cyanogen
chloride formed increased (Kanno et al., 1982).
2-Naphthylamine will not hydrolyze because it does not contain a hydrolyzable functional group
(Kollig, 1993).
At influent concentrations of 10, 1.0, 0.1, and 0.01 mg/L, the GAC adsorption capacities were 300,
150, 75, and 37 mg/g, respectively (Dobbs and Cohen, 1980).
Shipping
UN1650 β-Naphthylamine, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Sublime the amine at 180o in a stream of nitrogen. Crystallise it from hot water (charcoal) or *benzene. Dry it under vacuum in a drying pistol. The styphnate has m 194-195o (from EtOH). [Beilstein 12 H 1265, 12 III 2989, 12 IV 3122.] CARCINOGEN.
Incompatibilities
A weak base. Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Incompatible with nitrous acid.
Waste Disposal
Controlled incineration whereby oxides of nitrogen are removed from the effluent gas by scrubber, catalyst, or thermal device. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.
Properties of 2-Naphthylamine
| Melting point: | 111-113 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 306 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.061 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 2.56 x 10-4 mmHg at 20–30 °C (quoted, Mercer et al., 1990) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | Solubility Soluble in hot water, ethanol, ether |
| form | powder |
| pka | 4.16(at 25℃) |
| color | pink to purple |
| PH Range | Non& uorescence (2.8) to violet & uorescence (4.4) |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 22 ºC |
| Merck | 13,6425 |
| BRN | 3939429 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.01 x 10-9 atm?m3/mol at 25 °C (quoted, Mercer et al., 1990) |
| Exposure limits | Since it is a carcinogen, there is no TLV TWA for this compound. Recognized Carcinogen (ACGIH); Carcinogen (OSHA);
Human Sufficient Evidence (IARC). |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Major Application | Microelectronics, power transmission & fluid, insulators for electronic devices, photoresists, display device, imaging process, semiconductors, diesel fuel additives, battery, adhesive, paints, inks, chalk, leather, textiles, dye synthesis, soil products |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 91-59-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Naphthalenamine(91-59-8) |
| IARC | 1 (Vol. 4, Sup 7, 99, 100F) 2012 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Naphthalenamine (91-59-8) |
Safety information for 2-Naphthylamine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H350:Carcinogenicity H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Naphthylamine
| InChIKey | JBIJLHTVPXGSAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 2-Naphthylamine CAS 91-59-8View Details
2-Naphthylamine CAS 91-59-8View Details
91-59-8 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
