2-Methyl-2-butanol
Synonym(s):tert-Amyl alcohol;2-Methyl-2-butanol;Amylenehydrate, 2-Methyl-2-butanol, tert-Pentyl alcohol, Dimethyl ethyl carbinol;tert-Amyl alcohol;tert-PenOH
- CAS NO.:75-85-4
- Empirical Formula: C5H12O
- Molecular Weight: 88.15
- MDL number: MFCD00004478
- EINECS: 200-908-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
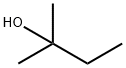
What is 2-Methyl-2-butanol?
Chemical properties
colourless liquid with a camphor-like odour
Chemical properties
Amyl alcohol is produced during the fermentation of grains, potatoes, and beets. It is also produced during the acid hydrolysis of petroleum fraction. Amyl alcohol is widely used in industry. For example, in the manufacturing of lacquers, paints, varnishes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, plastics, rubber, explosives, hydraulic fl uids, for the extraction of fats, is also used in the petroleum refi nery industries
Chemical properties
Amyl alcohols (pentanols) have eight isomers. All are flammable, colorless liquids, except the isomer 2,2- dimethyl-1-propanol, which is a crystalline solid.
Chemical properties
tert-Amyl alcohol is a volatile liquid.2-Methyl-2-butanol has a sour odor, a threshold value of 8.2 mg/m3 (2.3 ppm), an absolute perception limit of 0.04 ppm, and a 100% recognition level of 0.23 ppm .
The Uses of 2-Methyl-2-butanol
2-Methyl-2-butanol is used as a solvent in flavors, pharmaceuticals, corrosion inhibitors, resins, gums, coating materials and in organic synthesis. It acts as a frothing agent (ore flotation), surfactant (petroleum recovery) and stabilizing agent. Further, it is used in processing aids.
The Uses of 2-Methyl-2-butanol
Pharmaceutic aid (solvent).
The Uses of 2-Methyl-2-butanol
2-Methyl-2-butanol has been used in evaluating esterification rate of natural antioxidants like cinnamic acid and ascorbic acid using HPLC.
What are the applications of Application
2-Methyl-2-butanol is an organic solvent used for organic synthesis and biotransformation
Definition
ChEBI: A tertiary alcohol that is propan-1-ol in which both of the hydrogens at position 1 have been replaced by methyl groups.
Production Methods
tert-Amyl alcohol is prepared by hydrating 2-methyl-2- butenes. It can also be prepared by reducing pivalic acid.
General Description
A clear, colorless liquid with an odor of camphor. Flash point 70°F. Density 0.81 g / cm3. Slightly soluble in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Slightly soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
2-Methyl-2-butanol attacks plastics [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 236]. Reacts violently with acetyl bromide [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Mixtures of alcohols with concentrated sulfuric acid and strong hydrogen peroxide can cause explosions. Example: an explosion will occur if dimethylbenzylcarbinol is added to 90% hydrogen peroxide then acidified with concentrated sulfuric acid. Mixtures of ethyl alcohol with concentrated hydrogen peroxide form powerful explosives. Mixtures of hydrogen peroxide and 1-phenyl-2-methyl propyl alcohol tend to explode if acidified with 70% sulfuric acid [Chem. Eng. News 45(43):73 1967; J, Org. Chem. 28:1893 1963]. Alkyl hypochlorites are violently explosive. They are readily obtained by reacting hypochlorous acid and alcohols either in aqueous solution or mixed aqueous-carbon tetrachloride solutions. Chlorine plus alcohols would similarly yield alkyl hypochlorites. They decompose in the cold and explode on exposure to sunlight or heat. Tertiary hypochlorites are less unstable than secondary or primary hypochlorites [NFPA 491 M, 1991]. Base-catalysed reactions of isocyanates with alcohols should be carried out in inert solvents. Such reactions in the absence of solvents often occur with explosive violence [Wischmeyer 1969].
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk.
Health Hazard
Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control may cause pollution.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of the vapors of amyl alcohol causes tearing, pain, redness, swelling, irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, nose, throat, and upper respiratory tract and of thskin. Acute and long-term exposure to amyl alcohol causes nausea, vomiting, headache, vertigo, and muscular weakness. Vomiting may cause aspiration into the lungs, resulting in chemical pneumonia. After a prolonged period of exposure to amyl alcohol, workers develop dizziness, double vision, shortness of breath, delirium, and related narcotic effects. In severe cases, inhalation leads to pulmonary edema, kidney injury, effects on the heart and becomes fatal. Occupational workers with pre-existing skin disorders, eye problems, or impaired liver, kidney, or respiratory function, may be more susceptible to the effects of amyl alcohol.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic to humans by an unspecified route. Moderately toxic experimentally by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and rectal routes. Narcotic in high concentration. Flammable liquid when exposed to heat, flame, or oxiduing materials. Moderately explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. A hypnotic agent. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Potential Exposure
(n-isomer); Suspected reprotoxic hazard, Primary irritant (w/o allergic reaction), (iso-, primary): Possible risk of forming tumors, Primary irritant (w/o allergic reaction), (sec-, active primary-, and other isomers) Primary irritant (w/o allergic reaction). Used as a solvent in organic synthesis and synthetic flavoring, pharmaceuticals, corrosion inhibitors; making plastics and other chemicals; as a flotation agent. The (n-isomer) is used in preparation of oil additives, plasticizers, synthetic lubricants, and as a solvent.
Shipping
UN2811 Pentanols, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3- Flammable liquid. UN1987 Alcohols, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Purification Methods
Reflux it with K2CO3, CaH2, CaO or sodium, then fractionally distil. The near-dry alcohol is further dried by refluxing with Mg activated with iodine, as described for ethanol. Further purification is possible using fractional crystallisation and zone refining at <-10o or preparative gas chromatography. [Beilstein 1 IV 1668.]
Incompatibilities
Forms an explosive mixture with air. Contact with strong oxidizers and hydrogen trisulfide may cause fire and explosions. Incompatible with strong acids. Violent reaction with alkaline earth metals forming hydrogen, a flammable gas.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Precautions
During handling and use of amyl alcohol, persons with pre-existing skin disorders, eye problems, or impaired liver, kidney, or respiratory function, should be careful since these workers/persons are more susceptible to the effects of amyl alcohol
Properties of 2-Methyl-2-butanol
| Melting point: | -12 °C |
| Boiling point: | 102 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.805 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 15.5 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 20 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with alcohol, ether, benzene, chloroform, glycerol, oils and acetone. |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 15.38±0.29(Predicted) |
| color | Clear colorless |
| PH | 6.0 (118g/l, H2O, 20℃)neutral |
| Odor | pungent |
| explosive limit | 1.3-9.6%(V) |
| Odor Threshold | 0.088ppm |
| Water Solubility | 120 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,7140 |
| BRN | 1361351 |
| Dielectric constant | 11.7(20℃) |
| Stability: | Light sensitive. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-85-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Butanol, 2-methyl-(75-85-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Methyl-2-butanol (75-85-4) |
Safety information for 2-Methyl-2-butanol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Methyl-2-butanol
2-Methyl-2-butanol manufacturer
ARRAKIS INDUSTRIES LLP
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2-Methyl-2-butanol, 99% CAS 75-85-4View Details
2-Methyl-2-butanol, 99% CAS 75-85-4View Details
75-85-4 -
 tert-Amyl alcohol CAS 75-85-4View Details
tert-Amyl alcohol CAS 75-85-4View Details
75-85-4 -
 Tert Amyl Alcohol CASView Details
Tert Amyl Alcohol CASView Details -
 tert-Amyl alcohol, GR 99%+ CAS 75-85-4View Details
tert-Amyl alcohol, GR 99%+ CAS 75-85-4View Details
75-85-4 -
 tert-Amyl Alcohol CAS 75-85-4View Details
tert-Amyl Alcohol CAS 75-85-4View Details
75-85-4 -
 tert-AMYL ALCOHOL For Synthesis CAS 75-85-4View Details
tert-AMYL ALCOHOL For Synthesis CAS 75-85-4View Details
75-85-4 -
 tert-AMYL ALCOHOL AR & HPLC CAS 75-85-4View Details
tert-AMYL ALCOHOL AR & HPLC CAS 75-85-4View Details
75-85-4 -
 2-Methyl-2-butanol CAS 75-85-4View Details
2-Methyl-2-butanol CAS 75-85-4View Details
75-85-4