2-Hexylthiophene
- CAS NO.:18794-77-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H16S
- Molecular Weight: 168.3
- MDL number: MFCD00022535
- EINECS: 242-579-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-08-07 19:09:42
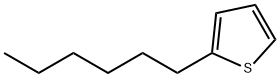
What is 2-Hexylthiophene?
Description
Thanksgiving traditionally means turkey; and turkey means the aromas that waft throughout the house while it’s roasting. But what’s responsible for these delicious smells?
Answer: the Maillard reaction. Discovered by French chemist Louis-Camille Maillard in 1912, the “reaction” is actually a complex series of steps that begins with the interaction between carbonyl groups of open-chain sugars and amine groups of amino acids to form N-aldosylamines. Eventually, depending on the food being heated, the sequence ends with the creation of multiple chemical entities, including many heterocyclic compounds.
These reactions occur when foodstuffs are heated to 140–165 oC. In addition to the aromas they produce, they are responsible for browning baked, grilled, or roasted foods such as breads, vegetables, and meats. Browning is accelerated in an alkaline environment.
All of which brings us back to turkey. As with other roasted meats, the Maillard reaction produces numerous compounds. Two that have been reported in the literature are 2-pentylpyridine and 2-hexylthiophene, shown here. (No systematic study of all of the Maillard products from turkey appears to have been conducted.)
So, when your host serves you delicious roasted turkey with all the fixings, please compliment her or him on an excellent helping of 2-pentylpyridine and 2-hexylthiophene.
Chemical properties
Light yellow liquid
Chemical properties
Colorless to pale yellow liquid; meat-like aroma
Occurrence
Reported found in beef, cranberry, mushroom and turkey.
The Uses of 2-Hexylthiophene
2-n-Hexylthiophene is used as a important raw material and intermediate used in organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals.
Definition
ChEBI: 2-Hexylthiophene is a heteroarene.
Aroma threshold values
High strength odor, sulfurous type; recommend smelling in a 0.10% solution or less
Properties of 2-Hexylthiophene
| Melting point: | -39.15°C (estimate) |
| Boiling point: | 228-230°C |
| Density | 0.932 g/mL at 25 °C |
| refractive index | 1.4960 |
| FEMA | 4137 | 2-HEXYLTHIOPHENE |
| Flash point: | 107°C |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | <1 g/l (est.) |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | colorless to pale yellow liquid |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Odor | at 0.10 % in dipropylene glycol. floral fruity gassy green meaty |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in most organic solvents and ethanol Soluble . Insoluble in water. |
| λmax | 234nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| JECFA Number | 1764 |
| BRN | 110220 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 18794-77-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for 2-Hexylthiophene
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H413:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Hexylthiophene
| InChIKey | QZVHYFUVMQIGGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
Sapala Organics Private Limited
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


![3,3-DIMETHYL-11-(2-THIENYL)-2,3,4,5,10,11-HEXAHYDRO-1H-DIBENZO[B,E][1,4]DIAZEPIN-1-ONE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB2209722.gif)
You may like
-
 2-Hexylthiophene 98%View Details
2-Hexylthiophene 98%View Details -
 2-Hexylthiophene CAS 18794-77-9View Details
2-Hexylthiophene CAS 18794-77-9View Details
18794-77-9 -
 2-Hexylthiophene CAS 18794-77-9View Details
2-Hexylthiophene CAS 18794-77-9View Details
18794-77-9 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4