2-Ethylhexanoic acid
Synonym(s):2-Ethylcaproic acid;2-Ethylhexanoic acid;3-Heptanecarboxylic acid, α-Ethylcaproic acid
- CAS NO.:149-57-5
- Empirical Formula: C8H16O2
- Molecular Weight: 144.21
- MDL number: MFCD00002675
- EINECS: 205-743-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-29 17:45:46
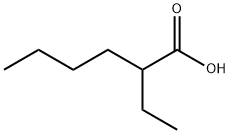
What is 2-Ethylhexanoic acid?
Chemical properties
colourless liquid
The Uses of 2-Ethylhexanoic acid
2-Ethylhexanoic acid is used in the preparation of metal derivatives, which act as a catalyst in polymerization reactions. For example, tin 2-ethylhexanoate is used in the manufacturing of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). It is also used as a stabilizer for polyvinyl chlorides. It is also involved in solvent extraction and dye granulation. Further, it is used to prepare plasticizers, lubricants, detergents, flotation aids, corrosion inhibitors and alkyd resins. In addition to this, it serves as a catalyst for polyurethane foaming.
The Uses of 2-Ethylhexanoic acid
Paint and varnish driers (metallic salts). Ethylhexoates of light metals are used to convert some mineral oils to greases. Its esters are used as plasticizers.
The Uses of 2-Ethylhexanoic acid
2-Ethylhexanoic acid can be used:
- As a reactant in esterification , decarboxylative alkynylation , and preparation of alkyl coumarins via decarboxylative coupling reactions.
- In the organocatalytic medium for the preparation of various 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones/thiones by Biginelli reaction.
What are the applications of Application
2-Ethylhexanoic acid is an acid used to prepare metal derivatives
Definition
ChEBI: 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is a branched-chain fatty acid.
Preparation
In a dry 1L three-neck bottle, Add isooctyl aldehyde (80g, 0.62mol) And the solvent 2-ethylhexanoic acid (240g, 1.66mol), ligand L8 (5.24mg, 0.007mmol), cesium carbonate (18.24mg, 0.056mmol), potassium acetate 160mg, placed in a water bath, mechanical under nitrogen atmosphere Stir, after the temperature rises to 30 ° C, Air flow was started at a flow rate of 11.9 g/h, and the reaction temperature was maintained at 30-35 ° C by adding cooling water to the water bath. After 6 hours of reaction, the conversion of isooctyl aldehyde was calculated to be 99.6%. The selectivity of 2-ethylhexanoic acid was 99.5%, and the yield was 99.10%.
General Description
2-Ethylhexanoic acid is a colorless to light yellow liquid with a mild odor. 2-Ethylhexanoic acid will burn though 2-Ethylhexanoic acid may take some effort to ignite. 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is slightly soluble in water. 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is corrosive to metals and tissue. 2-Ethylhexanoic acid is used to make paint dryers and plasticizers.
Reactivity Profile
2-Ethylhexanoic acid is a carboxylic acid. Carboxylic acids donate hydrogen ions if a base is present to accept them. They react in this way with all bases, both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic. Their reactions with bases, called "neutralizations", are accompanied by the evolution of substantial amounts of heat. Neutralization between an acid and a base produces water plus a salt. Carboxylic acids with six or fewer carbon atoms are freely or moderately soluble in water; those with more than six carbons are slightly soluble in water. Soluble carboxylic acid dissociate to an extent in water to yield hydrogen ions. The pH of solutions of carboxylic acids is therefore less than 7.0. Many insoluble carboxylic acids react rapidly with aqueous solutions containing a chemical base and dissolve as the neutralization generates a soluble salt. Carboxylic acids in aqueous solution and liquid or molten carboxylic acids can react with active metals to form gaseous hydrogen and a metal salt. Such reactions occur in principle for solid carboxylic acids as well, but are slow if the solid acid remains dry. Even "insoluble" carboxylic acids may absorb enough water from the air and dissolve sufficiently in 2-Ethylhexanoic acid to corrode or dissolve iron, steel, and aluminum parts and containers. Carboxylic acids, like other acids, react with cyanide salts to generate gaseous hydrogen cyanide. The reaction is slower for dry, solid carboxylic acids. Insoluble carboxylic acids react with solutions of cyanides to cause the release of gaseous hydrogen cyanide. Flammable and/or toxic gases and heat are generated by the reaction of carboxylic acids with diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides. Carboxylic acids, especially in aqueous solution, also react with sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates (to give H2S and SO3), dithionites (SO2), to generate flammable and/or toxic gases and heat. Their reaction with carbonates and bicarbonates generates a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) but still heat. Like other organic compounds, carboxylic acids can be oxidized by strong oxidizing agents and reduced by strong reducing agents. These reactions generate heat. A wide variety of products is possible. Like other acids, carboxylic acids may initiate polymerization reactions; like other acids, they often catalyze (increase the rate of) chemical reactions.
Health Hazard
Harmful if swallowed, inhaled or absorbed through skin. Material is extremely destructive to tissues of mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract, eyes and skin. Inhalation may be fatal as a result of spasm, inflammation and edema of the larynx, bronchii, chemical pneumonitis and pulmonary edema. Symptoms of exposure may include burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea and vomiting.
Fire Hazard
2-Ethylhexanoic acid is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. An experimental teratogen. A skin and severe eye irritant. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition, it emits acrid and irritating fumes.
Properties of 2-Ethylhexanoic acid
| Melting point: | -59 °C |
| Boiling point: | 228 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.906 |
| vapor density | 4.98 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.01 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 230 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 1.4g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | pK1:4.895 (25°C) |
| color | Clear |
| Odor | Mild odour |
| PH Range | 3 at 1.4 g/l at 20 °C |
| PH | 3 (1.4g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| explosive limit | 1.04%, 135°F |
| Water Solubility | 2 g/L (20 ºC) |
| BRN | 1750468 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents, bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 149-57-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hexanoic acid, 2-ethyl-(149-57-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Ethylhexanoic acid (149-57-5) |
Safety information for 2-Ethylhexanoic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for 2-Ethylhexanoic acid
| InChIKey | OBETXYAYXDNJHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
2-Ethylhexanoic acid manufacturer
Madhu Chemicals
M. J. Chemicals
C.H. Chemicals
Manav Biochem Impex Private Limited
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
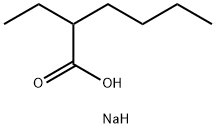
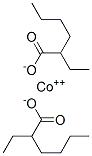
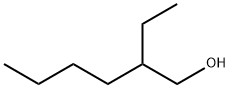
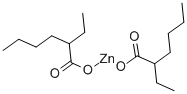
You may like
-
 2-ETHYL HEXANOIC ACID 99%View Details
2-ETHYL HEXANOIC ACID 99%View Details -
 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid extrapure CAS 149-57-5View Details
2-Ethylhexanoic Acid extrapure CAS 149-57-5View Details
149-57-5 -
 2-Ethylhexanoic acid CAS 149-57-5View Details
2-Ethylhexanoic acid CAS 149-57-5View Details
149-57-5 -
 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid CASView Details
2-Ethylhexanoic Acid CASView Details -
 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid CASView Details
2-Ethylhexanoic Acid CASView Details -
 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid (Octoic Acid), Grade Standard: Technical Grade, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
2-Ethylhexanoic Acid (Octoic Acid), Grade Standard: Technical Grade, Packaging Type: DrumView Details
149-57-5 -
 2 Ethyl Hexanoic AcidView Details
2 Ethyl Hexanoic AcidView Details
149-57-5 -
 Powder 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid, CAS Number: 149-57-5, Packaging Size: 25 KgsView Details
Powder 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid, CAS Number: 149-57-5, Packaging Size: 25 KgsView Details
149-57-5
