2-BUTANOL
- CAS NO.:15892-23-6
- Empirical Formula: C4H10O
- Molecular Weight: 74.12
- MDL number: MFCD00004569
- EINECS: 201-158-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-09 09:30:53
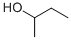
What is 2-BUTANOL?
Definition
ChEBI: Butan-2-ol is a secondary alcohol that is butane substituted by a hydroxy group at position 2. It derives from a hydride of a butane.
Potential Exposure
Butyl alcohols are used as solvents for paints, lacquers, varnishes, natural and synthetic resins, gums, vegetable oils, dyes, camphor, and alkaloids. They are also used as an intermediate in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and chemicals; in the manufacture of artificial leather, safety glass; rubber and plastic cements, shellac, raincoats, photographic films, perfumes; and in plastic fabrication.
Shipping
UN1120 Butanols, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3— Flammable liquid. UN1212 Isobutanol or Isobutyl alcohol, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3—Flammable liquid
Purification Methods
Purification methods are the same as for n-Butanol. These include drying with K2CO3 or CaSO4, followed by filtration and fractional distillation, refluxing with CaO, distillation, then refluxing with magnesium and redistillation, and refluxing with, then distilling from CaH2. Calcium carbide has also been used as a drying agent. The anhydrous alcohol is obtained by refluxing with sec-butyl phthalate or succinate. (For method see Ethanol.) Small amounts of alcohol can be purified via conversion to the alkyl hydrogen phthalate and recrystallisation [Hargreaves J Chem Soc 3679 1956]. For purification of optical isomers, see Timmermans and Martin [J Chem Phys 25 411 1928]. [Beilstein 2 III 1566.]
Incompatibilities
Butyl alcohols may form explosive mixture with air. In all cases they are Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks some plastics, rubber and coatings. n-Butanol is incompatible with strong acids; halogens, caustics, alkali metals; aliphatic amines; isocyanates. sec-Butanol forms an explosive peroxide in air. Ignites with chromium trioxide. Incompatible with strong oxidizers; strong acids; aliphatic amines; isocyanates, organic peroxides. tert-Butanol is incompatible with strong acids (including mineral acid), including mineral acids; strong oxidizers or caustics, aliphatic amines; isocyanates, alkali metals (i.e., lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium, francium). isoButanol is incompatible with strong acids; strong oxidizers; caustics, aliphatic amines; isocyanates, alkali metals and alkali earth. May react with aluminum at high temperatur
Waste Disposal
Incineration, or bury absorbed waste in an approved land fill.
Properties of 2-BUTANOL
| Melting point: | −115 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 98 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 0.808 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 12.5 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 80 °F |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 15892-23-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for 2-BUTANOL
Computed Descriptors for 2-BUTANOL
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1