(2-Bromoethyl)benzene
Synonym(s):(2-Bromoethyl)benzene;2-Phenylethyl bromide
- CAS NO.:103-63-9
- Empirical Formula: C8H9Br
- Molecular Weight: 185.06
- MDL number: MFCD00000240
- EINECS: 203-130-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-27 18:34:20
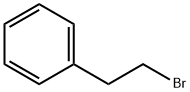
What is (2-Bromoethyl)benzene?
Description
Phenethylbromide is an analytical reference material that is structurally categorized as an organobromide. It is used in the synthesis of a variety of compounds, including fentanyl. Phenethylbromide is combined with 4-piperidinone to produce N-phenethyl-4-piperidone, which, as a precursor in the synthesis of fentanyl (Item Nos. ISO60197 | 14719), is scheduled as a List I chemical in the United States. Phenethylbromide may be found as in impurity in samples of fentanyl produced using this pathway.
Chemical properties
colourless to yellow liquid. It is miscible with ether and benzene, but insoluble in water.
The Uses of (2-Bromoethyl)benzene
(2-Bromoethyl)benzene is used in the preparation of phenelzine by reacting with hydrazine. It is also used as a starting material to prepare various beta-phenethyl derivatives, active pharmaceutical ingredients, and fragrances. It finds application as a flame retardant.
The Uses of (2-Bromoethyl)benzene
(2-Bromoethyl)benzene is an important starting material for the production of various b-phenethyl derivatives, pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other fine chemicals.
Preparation
(2-Bromoethyl)benzene is synthesized by the reaction of phenethyl alcohol with hydrogen bromide.
Reaction: The phenethyl alcohol was heated to 110°C, hydrogen bromide was slowly introduced, and the reaction was refluxed. The reaction was completed, cooled, washed with water, 10% sodium carbonate solution, and water in turn. After drying with anhydrous potassium carbonate, fractional distillation under reduced pressure was carried out to collect fractions at 97-99°C (2.0 kPa) with a yield of over 90%.
Preparation
Analogous to the preparation of most 1-bromoalkanes, 2-Phenylethyl bromide is prepared by free-radical addition of hydrogen bromide to styrene. These conditions lead to anti-Markovnikov addition, giving the 1-bromo derivatives.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 29, p. 2317, 1964 DOI: 10.1021/jo01031a051
Synthetic Communications, 20, p. 2349, 1990 DOI: 10.1080/00397919008053179
Safety
Store at 2-8° C in a tightly closed container in a dry, well-ventilated place. Containers that are opened must be carefully resealed and kept upright to prevent leakage. (2-Bromoethyl)benzene is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. This chemical is harmful if swallowed and causes severe eye irritation.
Synthesis
Phenethylbromide is commonly synthesized through the addition of HBr to styrene via a free-radical reaction. This process is typically carried out in a glasslined reactor by introducing gaseous HBr into a solution of styrene in an inert solvent that contains a free-radical initiator. The reaction, which is fast and releases a moderate amount of heat, can be managed by introducing HBr at a rate that matches its consumption. Once all the styrene has been converted, any remaining excess HBr can be reclaimed using different methods before the solvent and product are recovered through distillation.
Purification Methods
Wash the bromide with conc H2SO4, water, aqueous 10% Na2CO3 and water again, then dry it with CaCl2 and fractionally distil it just before use. [Beilstein 5 IV 907.]
References
1. Shukla, P.; Sharma, A.; Pallavi, B.; Cheng, C. H. Nickel-catalyzed reductive Heck type coupling of saturated alkyl halides with acrylates and oxabenzonorbornadiene. Tetrahedron 2015, 71 (15), 2260-2266. DOI:10.1016/J.TET.2015.02.067
2. Huang, Y. B.; Yan, L.; Chen, M. Y.; Guo, Q. X.; Fu, Y. Selective hydrogenolysis of phenols and phenyl ethers to arenes through direct C-O cleavage over ruthenium-tungsten bifunctional catalysts. Green Chem. 2015, 17 (5), 3010-3017. DOI:10.1039/C5GC00326A
3. Justice, D.E.A.D.o. Control of a chemical precursor used in the illicit manufacture of fentanyl as a List I chemical. Final rule. Federal Register 73(144), 43355-43357 (2008). PMID: 18949877
Properties of (2-Bromoethyl)benzene
| Melting point: | -56 °C |
| Boiling point: | 220-221 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.355 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 193 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 0.039g/l |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Clear colorless to pale yellow |
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE |
| BRN | 507487 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 103-63-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 1-Bromo-2-phenylethane(103-63-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzene, (2-bromoethyl)- (103-63-9) |
Safety information for (2-Bromoethyl)benzene
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for (2-Bromoethyl)benzene
| InChIKey | WMPPDTMATNBGJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
(2-Bromoethyl)benzene manufacturer
NSR Amino Organics
Sontara Organo Industries
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2-Phenylethyl bromide 99%View Details
2-Phenylethyl bromide 99%View Details -
 2-Phenylethyl bromide, 98% CAS 103-63-9View Details
2-Phenylethyl bromide, 98% CAS 103-63-9View Details
103-63-9 -
 (2-Bromoethyl)benzene CAS 103-63-9View Details
(2-Bromoethyl)benzene CAS 103-63-9View Details
103-63-9 -
 98% Phenylethyl Bromide (103-63-9), For Pharmaceuticals, Industrial GradeView Details
98% Phenylethyl Bromide (103-63-9), For Pharmaceuticals, Industrial GradeView Details
103-63-9 -
 Beta Phenyl Ethyl Bromide, Grade Standard: Industrial GradeView Details
Beta Phenyl Ethyl Bromide, Grade Standard: Industrial GradeView Details
103-63-9 -
 CAS 103-63-9 (2-Bromoethyl)benzeneView Details
CAS 103-63-9 (2-Bromoethyl)benzeneView Details
103-63-9 -
 2-Bromoethyl)Benzene CAS 103-63-9View Details
2-Bromoethyl)Benzene CAS 103-63-9View Details
103-63-9 -
 2 - Phenylethyl BromideView Details
2 - Phenylethyl BromideView Details
103-63-9
