1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE
- CAS NO.:253-72-5
- Empirical Formula: C8H6N2
- Molecular Weight: 130.15
- MDL number: MFCD00059750
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
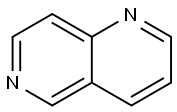
What is 1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE?
Description
Naphthalene is an aromatic organic compound that consists of two fused benzene rings. Diazanaphthalenes have the naphthalene structure with nitrogen atoms in place of two of the CH groups. There are two structural classes of diazanaphthalenes: benzodiazines, in which both nitrogen atoms are in the same ring, and naphthyridines, with one nitrogen atom in each ring.
Six naphthyridine isomers exist, based on the positions of the nitrogen atoms; they can be in the 1,5, 1,6 (shown here), 1,7, 1,8, 2,6, or 2,7 positions. All are white solids with a surprisingly wide span of melting points: 1,6-Naphthyridine’s is the lowest at <40 oC; 2,6-naphthyridine’s is the highest at 114–115 oC.
Quinoline derivatives such as naphthyridines that have nitrogen atoms in the 1-position are usually synthesized via the Skraup reaction, in which an aminopyridine and a glycerol derivative are heated in the presence of an oxidizing agent (e.g., nitrobenzene) and sulfuric acid. This is often a violent, runaway reaction, so it is perhaps fortunate that the synthesis of 1,6-naphthyridine from 4-aminopyridine was not originally successful.
Refinements of the Skraup reaction, however, did eventually lead to preparations of 1,6-naphthyridine in modest yields. One modification used 4-aminopyridine-N-oxide as the starting material; the resulting 1,6-naphthyridine-N-oxide was then reduced to the free base.
1,6-Naphthyridine and some of its derivatives have been reported to have medicinal, electronic, and catalytic properties. But none of these investigations has yet resulted in any practical applications.
Definition
ChEBI: 1,6-naphthyridine is a naphthyridine.
Properties of 1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE
| Melting point: | 231-233°C |
| Boiling point: | 267.3±13.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.183±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 35 °C |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | unreported |
| form | powder to crystal |
| appearance | white to pale yellow or light brown solid or liquid |
| pka | 3.70±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 253-72-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,6-Naphthyridine (253-72-5) |
Safety information for 1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


![3-[(E)-3-(DIMETHYLAMINO)-2-PROPENOYL]-2-METHYL-1,6-NAPHTHYRIDINE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB8402581.gif)



You may like
-
 1,6-Naphthyridine CAS 253-72-5View Details
1,6-Naphthyridine CAS 253-72-5View Details
253-72-5 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1