1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE
- CAS NO.:99-35-4
- Empirical Formula: C6H3N3O6
- Molecular Weight: 213.1
- MDL number: MFCD00059179
- EINECS: 202-752-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18
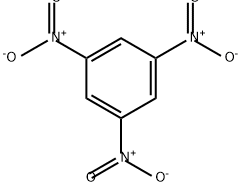
What is 1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE?
Chemical properties
Trinitrobenzene is a yellow crystalline solid.
The Uses of 1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE
Explosive. 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is a vulcanizing agent for natural rubber. Indicator for pH 12.0-14.0.
The Uses of 1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE
Trinitrobenzene is used as an explosive. It is obtained by oxidation of trinitrotoluene.
The Uses of 1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE
1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene can be used for direct analysis in real time mass spectrometry for fast screening of explosives.
Definition
ChEBI: A trinitrobenzene in which each of the nitro groups is meta- to the other two.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 22, p. 1046, 1957 DOI: 10.1021/jo01360a012
General Description
A light yellow crystalline sludge or slurry. Burns but may require some effort to ignite. A high explosive when dry. Easily ignited and burns very vigorously when dry. Soluble in alcohol and ether; insoluble in water. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Aromatic nitro compounds, such as TRINITROBENZENE, range from slight to strong oxidizing agents. If mixed with reducing agents, including hydrides, sulfides and nitrides, they may begin a vigorous reaction that culminates in a detonation. The aromatic nitro compounds may explode in the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide even in the presence of water or organic solvents. The explosive tendencies of aromatic nitro compounds are increased by the presence of multiple nitro groups.
Health Hazard
Some are toxic and may be fatal if inhaled, swallowed or absorbed through skin. Contact may cause burns to skin and eyes. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Health Hazard
The toxic effects from ingestion of the solid or inhalation of its dusts include irritation of respiratory tract, headache, dyspnea, and cyanosis. Other effects noted in animals were degenerative changes in the brain. The oral LD50 values in rats and mice are 450 and 570 mg/kg, respectively.
Fire Hazard
Trinitrobenzene is a high explosive, similar to trinitrotoluene. However, it is less sensitive to impact than the latter. Its brisance and power are higher than those of TNT. It detonates when heated rapidly. The dry material is highly sensitive to shock and heat.Slow and careful heating of a small amount of material does not cause detonation. Trinitrobenzene is a flammable solid. It reacts vigorously with reducing substances. It emits highly toxic oxides of nitrogen on decomposition. .
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. Mutation data reported. A severe explosion hazard when shocked or exposed to heat. Trinitrobenzene is considered a powerful high explosive and has more shattering power than TNT. Although it is less sensitive to impact than TNT, it is not used much because it is difficult to produce. The complex with potassium trimethyl stannate explodes at room temperature. Forms heat-sensitive explosive complexes with alkyl or aryl metallates (e.g., lithium or potassium salts of trimethyl-, triethyl-, or triphenyl-germanate, -silanate, or -stamate). Can react vigorously with reducing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx and explodes. See also NITRO COMPOUNDS of AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS.
Synthesis
One synthesis route of 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene is through the decarboxylation of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzoic acid (obtained from TNT by oxidation with chromic acid) by heating in aqueous medium.
Potential Exposure
Trinitrobenzene is explosive when dry. Used as an explosive; as a vulcanizing agent for natural rubber. Trinitrobenzene may be more powerful than TNT; and is reported to be less sensitive to impact than TNT. However it is difficult to produce, and is not used as widely as TNT.
Storage
Storage and shipping are similar to those used for TNT and other high explosives. Trinitrobenzene is stored in a permanent magazine well separatedfrom initiator explosive, combustible and oxidizing materials, and heat sources. It is shipped in metal containers enclosed in wooden boxes or strong siftproof cloth or paper bags in amounts not exceeding 60 lb net weight (NFPA 1997).
Shipping
UN0214 Trinitrobenzene, dry or wetted with <30% water, by mass, Hazard Class: 1.1D; Labels:1.1DExplosives (with a mass explosion hazard); D-Substances or articles which may mass detonate (with blast and/or fragment hazard) when exposed to fire. UN1354 Trinitrobenzene, wetted with not <30% water, by mass, Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from glacial acetic acid, CHCl3, CCl4, EtOH aqueous EtOH or EtOH/*benzene, after (optionally) heating with dilute HNO3. Dry it in air. Fuse it and crystallise it under vacuum. [Beilstein 5 H 271, 5 I 140, 5 II 203, 5 III 643, 5 IV 754.]
Incompatibilities
Sensitive to shock and heat. Incompatible with initiating explosives, combustible materials. Aromatic nitro compounds, such as trinitrobenzene, range from slight to strong oxidizing agents. Keep away from strong reducing agents, including hydrides, alkali metals; aluminium and other metal powder; phosphorus; sulfides and nitrides, alkaline material, strong bases; contact may initiate vigorous reactions that culminates in a detonation. The aromatic nitro compounds may explode in the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide even in the presence of water or organic solvents. The aromatic nitro compounds may explode in the presence of a base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide even in the presence of water or organic solvents. Incompatible with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Dissolve in a combustible solvent and spray into an incinerator equipped with afterburner and scrubber.
Properties of 1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE
| Melting point: | 122°C |
| Boiling point: | 315°C |
| Density | d420 1.76; d4152 1.4775 |
| refractive index | 1.6600 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 2℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Solubility Slightly soluble in water; soluble in ethanol |
| form | crystals |
| color | Light yellow |
| PH Range | 12(colourless)-13.4(orange) |
| Water Solubility | 357.7mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,9726 |
| Dielectric constant | 89.0(18℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 99-35-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene (99-35-4) |
Safety information for 1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H228:Flammable solids H301:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H351:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P241:Use explosion-proof electrical/ventilating/lighting/…/equipment. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P281:Use personal protective equipment as required. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for 1,3,5-TRINITROBENZENE
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
Potassium Hydroxide 90%View Details
1310-58-3 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
