1,3-Dinitrobenzene
Synonym(s):1,3-DNB
- CAS NO.:99-65-0
- Empirical Formula: C6H4N2O4
- Molecular Weight: 168.11
- MDL number: MFCD00007222
- EINECS: 202-776-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18
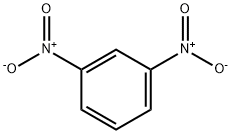
What is 1,3-Dinitrobenzene?
Description
1,3-Dinitrobenzene (1,3-DNB) is an impurity present in the manufacture of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Workers in munitions plants are at risk of exposure. While it does not bioaccumulate, it persists in the environments (air, water, and soil) with slow rates of degradation. Metabolism in animals (rabbits) results in reduction of the nitro functionalities to amine functionalities to produce 2,4-diaminophenol, m-nitroaniline, m-phenylenediamine, and 2-amino-4-nitrophenol. Human exposure is generally dermal contact or inhalation of vapor.
Chemical properties
orange to yellow crystalline powder. Freely soluble in benzene, chloroform, ethyl acetate, soluble in alcohol, slightly soluble in water. Can evaporate with water vapour.
The Uses of 1,3-Dinitrobenzene
1,3-Dinitrobenzene (1,3-DNB) is an impurity present in the manufacture of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Dinitrobenzene (as a mixture of 1,2-dinitro- 1,3-dinitro- and 1,4-dinitro-isomers) is used in the manufacture of dyes and explosives, and in organic syntheses.
Definition
ChEBI: 1,3-dinitrobenzene is a dinitrobenzene that is benzene disubstituted at positions 1 and 3 with nitro groups. It has a role as a neurotoxin.
Preparation
1,3-Dinitrobenzene is accessible by nitration of nitrobenzene. The reaction proceeds under acid catalysis using sulfuric acid. The directing effect of the nitro group of nitrobenzene leads to 93% of the product resulting from nitration at the meta-position. The ortho- and para-products occur in only 6% and 1%, respectively.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 38, p. 4243, 1973 DOI: 10.1021/jo00964a007
Synthesis, p. 1085, 1992 DOI: 10.1055/s-1992-26309
General Description
1,3-Dinitrobenzene is a yellow solid with a slight odor. Sinks in water. (USCG, 1999)
Air & Water Reactions
Slowly mixes with water.
Reactivity Profile
All three isomers have similar properties and may react vigorously with oxidizing materials. Their reaction with nitric acid (nitration) will lead to a mixture of trinitrobenzenes possessing high-explosive properties [Urbanski, 1967, vol. 3, p. 290]. If heat and reaction conditions of the nitration are not controlled, detonation comparable to TNT may occur [Anon., J. R. Inst. Chem., 1960, 84, p. 451]. Mixture of 1,3-dinitrobenzene with tetranitromethane was found highly explosive [Urbanski, 1964, vol. 1, 592]. 1,2-dinitrobenzene is a severe explosion hazard when shocked or exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition all dinitrobenzens emit toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 1374].
Health Hazard
Inhalation or ingestion causes loss of color, nausea, headache, dizziness, drowsiness, and collapse. Eyes are irritated by liquid. Stains skin yellow; if contact is prolonged, can be absorbed into blood and cause same symptoms as for inhalation.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: May explode
Safety Profile
Suspected carcinogen. Human poison by ingestion. Experimental poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects by skin contact: cyanosis and motor activity changes. Experimental reproductive effects. An eye irritant. Mutation data reported. Mixture with nitric acid is a high explosive. Mixture with tetranitromethane is a hgh explosive very sensitive to sparks. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also 0and pDINITROBENZENE.
Environmental Fate
Biological. Under anaerobic and aerobic conditions using a sewage inoculum, 1,3-
dinitrobenzene degraded to nitroaniline (Hallas and Alexander, 1983). In activated sludge
inoculum, following a 20-d adaptation period, no degradation was observed (Pitter, 1976).
Photolytic. Low et al. (1991) reported that the nitro-containing compounds (e.g., 2,4-
dinitrophenol) undergo degradation by UV light in the presence of titanium dioxide yielding
ammonium, carbonate, and nitrate ions. By analogy, 1,3-dinitrobenzene should degrade forming
identical ions.
Chemical/Physical. Releases toxic nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and
Lewis, 1987). 1,3-Dinitrobenzene will not hydrolyze in water (Kollig, 1993).
Solubility in organics
Soluble in acetone, ether, pyrimidine (Weast, 1986), alcohol (27 g/L), pyridine (3,940 g/kg at 20–25 °C) (Dehn, 1917); freely soluble in benzene, chloroform, ethyl acetate (Windholz et al., 1983), and toluene.
Purification Methods
Crystallise 1,3-dinitrobenzene from alkaline EtOH solution (20g in 750mL 95% EtOH at 40o, plus 100mL of 2M NaOH) by cooling and adding 2.5L of H2O. The precipitate, after filtering off, is washed with H2O, sucked dry, and crystallised from 120mL, then 80mL of absolute EtOH [Callow et al. Biochem J 32 1312 1938]. Alternatively crystallise it from MeOH, CCl4 or EtOAc. It can be sublimed in a vacuum. [Tanner J Org Chem 52 2142 1987, Beilstein 5 IV 739.]
Toxicity evaluation
Cultured astrocytes and brain capillary endothelial cells were exposed to 1 mM concentrations for 1 day in an in vitro blood–brain barrier (BBB) model, resulting in cell death.
Properties of 1,3-Dinitrobenzene
| Melting point: | 86 °C |
| Boiling point: | 297 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.575 |
| vapor pressure | 8.15 x 10-4 mmHg at 35 °C (Hine et al., 1963) |
| refractive index | 1.4660 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 150 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Very Slightly) |
| form | solid |
| color | White to yellowish crystals |
| Specific Gravity | 1.368 |
| Water Solubility | 500 mg/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,3273 |
| BRN | 1105654 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.8(20.0℃) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 1, IDLH 50; OSHA PEL: TWA 1; ACGIH TLV:
TWA 0.15 ppm for all isomers (adopted). |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with reducing agents, oxidizing agents, strong bases. May explode if heated. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 99-65-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzene, 1,3-dinitro-(99-65-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | m-Dinitrobenzene (99-65-0) |
Safety information for 1,3-Dinitrobenzene
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P314:Get medical advice/attention if you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for 1,3-Dinitrobenzene
1,3-Dinitrobenzene manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 m-Dinitrobenzene CAS 99-65-0View Details
m-Dinitrobenzene CAS 99-65-0View Details
99-65-0 -
 m-Dinitrobenzene, GR 99%+ CAS 99-65-0View Details
m-Dinitrobenzene, GR 99%+ CAS 99-65-0View Details
99-65-0 -
 m-Dinitrobenzene, pract CAS 99-65-0View Details
m-Dinitrobenzene, pract CAS 99-65-0View Details
99-65-0 -
 m-DINITROBENZENE For Synthesis CAS 99-65-0View Details
m-DINITROBENZENE For Synthesis CAS 99-65-0View Details
99-65-0 -
 m-DINITROBENZENE AR CAS 99-65-0View Details
m-DINITROBENZENE AR CAS 99-65-0View Details
99-65-0 -
 1,3-Dinitrobenzene CAS 99-65-0View Details
1,3-Dinitrobenzene CAS 99-65-0View Details
99-65-0 -
 meta- DINITROBENZENE 98%, For SynthesisView Details
meta- DINITROBENZENE 98%, For SynthesisView Details
99-65-0 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
