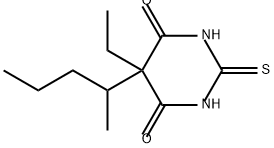
(+/-)-THIOPENTAL
Synonym(s):(±)-Thiopental;5-Ethyl-5-(1-methylbutyl)-2-thiobarbituric acid;Pentothal
- CAS NO.:76-75-5
- Empirical Formula: C11H18N2O2S
- Molecular Weight: 242.34
- MDL number: MFCD00057564
- EINECS: 200-984-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
What is (+/-)-THIOPENTAL?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed.
Toxicity
Overdosage may occur from rapid or repeated injections. Too rapid injection may be followed by an alarming fall in blood pressure even to shock levels. Apnea, occasional laryngospasm, coughing and other respiratory difficulties with excessive or too rapid injections may occur. Lethal blood levels may be as low as 1 mg/100 mL for short-acting barbiturates; less if other depressant drugs or alcohol are also present.
Chemical properties
Off-White Solid
Originator
Pentothal,Abbott
The Uses of (+/-)-THIOPENTAL
A thio-derivative of Barbituric acid. Controlled substance (depressant). Anesthetic
Background
A barbiturate that is administered intravenously for the induction of general anesthesia or for the production of complete anesthesia of short duration. It is also used for hypnosis and for the control of convulsive states. It has been used in neurosurgical patients to reduce increased intracranial pressure. It does not produce any excitation but has poor analgesic and muscle relaxant properties. Small doses have been shown to be anti-analgesic and lower the pain threshold. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p920)
Indications
For use as the sole anesthetic agent for brief (15 minute) procedures, for induction of anesthesia prior to administration of other anesthetic agents, to supplement regional anesthesia, to provide hypnosis during balanced anesthesia with other agents for analgesia or muscle relaxation, for the control of convulsive states during or following inhalation anesthesia or local anesthesia, in neurosurgical patients with increased intracranial pressure, and for narcoanalysis and narcosynthesis in psychiatric disorders.
Definition
ChEBI: Thiopental is a barbiturate, the structure of which is that of 2-thiobarbituric acid substituted at C-5 by ethyl and sec-pentyl groups. It has a role as an anticonvulsant, a sedative, an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic, a drug allergen and an intravenous anaesthetic. It is functionally related to a 2-thiobarbituric acid. It is a conjugate acid of a thiopental(1-).
Manufacturing Process
130 g of ethyl (1-methylbutyl) malonic ester is added to a concentrated solution of sodium ethylate prepared from 34 g of sodium in absolute alcohol; with stirring, 60 g of finely divided thiourea is added, and, the mixture refluxed for 10 hours. Most or all of the solvent is evaporated and the residual mass is dissolved in cold water. The barbituric acid derivative so formed is precipitated by the addition of dilute hydrochloric acid. It may be 1 purified by solution in dilute ammonium hydroxide solution and precipitated by carbon dioxide, followed by recrystallization from 95% alcohol. The ethyl (1- methylbutyl)thiobarbituric acid so obtained is a white crystalline solid, melting at 158-159°C and readily forming salts with alkalies.
brand name
Thiopental is BAN.
Therapeutic Function
Narcotic analgesic, Anesthetic
Pharmacokinetics
Thiopental, a barbiturate, is used for the induction of anesthesia prior to the use of other general anesthetic agents and for induction of anesthesia for short surgical, diagnostic, or therapeutic procedures associated with minimal painful stimuli. Thiopental is an ultrashort-acting depressant of the central nervous system which induces hypnosis and anesthesia, but not analgesia. It produces hypnosis within 30 to 40 seconds of intravenous injection. Recovery after a small dose is rapid, with some somnolence and retrograde amnesia. Repeated intravenous doses lead to prolonged anesthesia because fatty tissues act as a reservoir; they accumulate Pentothal in concentrations 6 to 12 times greater than the plasma concentration, and then release the drug slowly to cause prolonged anesthesia
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal, intravenous, and rectal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Human mutation data reported. A short-acting intravenous anesthetic. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx
Metabolism
Thiopental is extensively metabolized, primarily in the liver, resulting in only 0.3% of an administered dose being excreted unchanged in the urine. Ring desulfuration leads to the generation of an active metabolite, pentobarbital, that exists in concentrations approximately 3-10% that of the parent concentration. Thiopental and pentobarbital are also subject to both oxidation and hydroxylation to carboxylic acids and alcohols, respectively, all of which are pharmacologically inert.
While many of the specifics regarding thiopental biotransformation have not been elucidated, including the enzymes responsible, the oxidation of thiopental to its carboxylic acid may be the major driver of thiopental detoxification as this product appears to account for 10-25% of renally excreted drug.
Properties of (+/-)-THIOPENTAL
| Melting point: | 158-160°C |
| Density | 1.1789 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5440 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: complete50mg/mL |
| pka | 7.11±0.40(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | 50mg/L(25 ºC) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 76-75-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 4,6(1H,5H)-Pyrimidinedione, 5-ethyldihydro-5-(1-methylbutyl)-2-thioxo- (76-75-5) |
Safety information for (+/-)-THIOPENTAL
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for (+/-)-THIOPENTAL
(+/-)-THIOPENTAL manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![THIOPENTAL, [2-14C]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB2167813.gif)
![5-ALLYL-5-[1-METHYLBUTYL]-2-THIOBARBITURIC ACID](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/77-27-0.gif)
You may like
-
 76-75-5 Thiopental 98%View Details
76-75-5 Thiopental 98%View Details
76-75-5 -
 76-75-5 98%View Details
76-75-5 98%View Details
76-75-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8