(-)-Huperzine A
Synonym(s):(−)-Selagine;Kimpukan A
- CAS NO.:102518-79-6
- Empirical Formula: C15H18N2O
- Molecular Weight: 242.32
- MDL number: MFCD01714949
- EINECS: 600-320-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-25 18:47:31
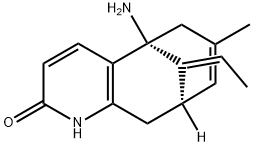
What is (-)-Huperzine A?
Description
Huperzine A is obtained from Huperzia serrata, which is the perennial fern. It shows activities in antipyretic, hemostasis, and dehumidification and is used for the treatment in folk of pneumonia, lung abscess, hematemesis, hematochezia, traumatic injury, etc.
Chemical properties
Pale Brown Solid
Physical properties
Appearance: white crystalline powder. Bitter with hygroscopicity. Solubility: easily soluble in chloroform, soluble in methanol and ethanol, and slightly soluble in water. Melting point: 211–216?°C.
History
In the 1980s, Chinese scholars isolated huperzine A from Lycopodiales,
Huperziaceae, Phlegmariurus fordii, and Huperzia serrata (Thunb.) Trevis.
At present, about 120 chemical components have been isolated and identified from
the plant, including 90 lycopodium alkaloids and 32 lycopodium triterpenes.
Huperzine A has the most potent inhibition on acetylcholinesterase activity, followed by huperzine B and 6β-hydroxy huperzine A.?These three compounds belong
to lycodine-type lycopodium alkaloids. The full synthesis of
huperzine A is complex and costly. Therefore, it is a focus to develop biotransformation or semisynthesis with other alkaloids as lead compounds on the basis of the
intrinsic relationship among different kinds of alkaloids
After the determination of chemical structure of huperzine A in 1986, it was
found to be the same alkaloid as selagine separated from Lycopodium selago by
Valenta in the 1960s, so it was classified as lycodine-type alkaloid. Huperzine A is
a potent reversible inhibitor of AChE, and its ability to improve learning and memory has been validated in animal models. It was approved for treatment in Alzheimer’s
disease (AD) in China in 1996
Due to the high cost of extraction of huperzine A, research on its chemical synthesis has been the focus at home and abroad since 1986. It has been found that the
chiral structure of huperzine A is essential for its biological activity; the inhibitory
activity on AChE of natural products (-)?- huperzine A is twice as its raceme and
38–50 times as its enantiomer (+)?- huperzine A which is not a natural product, so
the chemical synthesis of natural product (-)?- huperzine A has received extensive
attention. The chemical preparation method of (-)?- huperzine A can be divided into
asymmetric synthesis and raceme separation and is limited to a small amount preparation in laboratory for the high cost.
Considering the difficulty of realizing unique bridge ring and amino structure of
(-)?- huperzine A and achieving its full synthesis and structural modification, scientists are trying to synthesize analogues of huperzine A with simple structure and
AchE inhibitory activity. It was found that the activity of spearmint huperzine A was
similar to that of huperzine A, with improved selectivity and poor chemical stability.
It was modified structurally to obtain ZT-1 .
The Uses of (-)-Huperzine A
Huperzine A is a potential therapeutic agent for Alzheimer disease that reversible alkaloid inhibitor of AChE which crosses the blood-brain barrier. It reduces cell death induced by glutamate in primary cultures derived from forebrain, hippocampus, cortex and cere.
In China, it is approved for use in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Huperzine A was classified as a dietary supplement by the FDA in 1997. As a nutraceutical, it is available in American health food stores or via the Internet, labeled as a memory aid.
Background
Huperzine A, is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid found in the extracts of the firmoss Huperzia serrata. The botanical has been used in China for centuries for the treatment of swelling, fever and blood disorders. Recently in clinical trials in China, it has demonstrated neuroprotective effects. It is currently being investigated as a possible treatment for diseases characterized by neurodegeneration – particularly Alzheimer’s disease.
Indications
Investigated for use/treatment in alzheimer's disease.
What are the applications of Application
(?)-Huperzine A is an inhibitor of AChE and antagonist of NMDA receptors
Definition
ChEBI: Huperzine A is a sesquiterpene alkaloid isolated from a club moss Huperzia serrata that has been shown to exhibit neuroprotective activity. It is also an effective inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase and has attracted interest as a therapeutic candidate for Alzheimer's disease. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, a neuroprotective agent, a plant metabolite and a nootropic agent. It is a sesquiterpene alkaloid, a pyridone, a primary amino compound and an organic heterotricyclic compound. It is a conjugate base of a huperzine A(1+).
Indications
Huperzine A is purified from Chinese club moss and has been traditionally used in China for the treatment of swelling, fever, inflammation, blood disorders, and schizophrenia. It was mainly applied to age-related memory dysfunction and Alzheimer and has a good effect on improving memory function. It can be used to treat various types of Alzheimer's disease and also myasthenia gravis.
Preparation
(-)-Huperzine A, a Lyco-podium alkaloid isolated in 1986 from the club moss Huperzia serrata, has drawn considerable attention after it was revealed to be a potent, selective, and reversible AChE inhibitor.
The total synthesis of Lycopodium alkaloid (-)-huperzine A has been accomplished in 10 steps with 17% overall yield from commercially abundant (R)-pulegone. The synthetic route features an efficient synthesis of 4 via a Buchwald–Hartwig coupling reaction, a dianion-mediated highly stereoselective alkylation of 4, and a rare example of an intramolecular Heck reaction of an enamine-type substrate. The stereoselective β-elimination and the accompanying Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement are of particular interest.
[1] RUI DING Guo Q L Bing Feng Sun*. An Efficient Total Synthesis of (-)-Huperzine A [J]. Organic Letters, 2012, 14 17: 4446-4449. DOI:10.1021/ol301951r.
[2] RUI DING. Divergent Total Synthesis of the Lycopodium Alkaloids Huperzine A, Huperzine B, and Huperzine U[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2013, 79 1: 240-250. DOI:10.1021/jo402419h.
[3] TUN M K M, WüSTMANN D J, HERZON S B. A robust and scalable synthesis of the potent neuroprotective agent (-)-huperzine A [J]. Chemical Science, 2011, 11: 2251-2253. DOI:10.1039/C1SC00455G.
Pharmacokinetics
Huperzine A is an alkaloid derived from Huperzia serrata (which is available as an herbal product in the US). It is under investigation as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Clinical trials in China have shown that huperzine A is comparably effective to the drugs currently on the market, and may even be somewhat safer in terms of side effects.
Pharmacology
Huperzine A has the ability to enhance learning and memory, improve spatial memory, and can be used for age-related dementia, vascular dementia, and other neurodegenerative diseases. Compared with the current anti-AD drugs, huperzine A can go through the blood-brain barrier, with a high oral bioavailability and longer time
inhibition on AChE.
As a highly selective AChE reversible inhibitor, huperzine A can inhibit AChE,
reduce acetylcholine hydrolysis, and improve the level of acetylcholine in the synaptic gap. This inhibition is reversible, lasts for a long time, shows no drug dependence if repeated administration, and does not induce significant liver toxicity.
X-ray diffraction results show that the direct binding of huperzine A to AChE active
sites inhibits the binding of AChE to its substrate.
In addition to the potent inhibition on AChE, huperzine A only shows a weak
inhibitory effect on the butyrylcholinesterase; also protects neurons by inhibiting
oxidative stress, reducing somatostatin, reducing the content of glutamate, decreasing the increased intracellular calcium, and inhibiting neuronal apoptosis; further
improves AD-related cognitive function and reduces the symptoms of AD patients.
Clinical Use
Since 1994, huperzine A has been approved for clinical use in improving memory and cognitive impairment in old patients with memory loss and dementia. A large number of domestic clinical studies have found that huperzine A shows therapeutic effect on learning and cognitive dysfunction of vascular dementia, mental retardation, and schizophrenia patients with mild adverse reactions.
Metabolism
Not Available
storage
+4°C (desiccate)
Properties of (-)-Huperzine A
| Melting point: | 211-216oC |
| Boiling point: | 505.0±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D -147° (c = 0.36 in CH3OH) (Ayer); D24.5 -150.4° (c = 0.498 in MeOH) (Liu) |
| Density | 1.20±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; ≥12.12 mg/mL in DMSO; ≥23.13 mg/mL in EtOH |
| form | neat |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 12.25±0.60(Predicted) |
| color | White to Almost white |
| optical activity | [α]/D -153±5°, c = 0.5 in methanol |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 102518-79-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for (-)-Huperzine A
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for (-)-Huperzine A
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran







You may like
-
 Huperzine A 98.00% CAS 102518-79-6View Details
Huperzine A 98.00% CAS 102518-79-6View Details
102518-79-6 -
 (-)-Huperzine A CAS 102518-79-6View Details
(-)-Huperzine A CAS 102518-79-6View Details
102518-79-6 -
 (-)-Huperzine A, 98%+ CAS 102518-79-6View Details
(-)-Huperzine A, 98%+ CAS 102518-79-6View Details
102518-79-6 -
 (−)-Huperzine A CAS 102518-79-6View Details
(−)-Huperzine A CAS 102518-79-6View Details
102518-79-6 -
 366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 Riveroxaban 98%View Details
366789-02-8 -
 Carvedilol 98%View Details
Carvedilol 98%View Details
72956-09-3 -
 73590-58-6 Omeprazole 98%View Details
73590-58-6 Omeprazole 98%View Details
73590-58-6 -
 Sertraline HCl 98%View Details
Sertraline HCl 98%View Details
79559-97-0
