(-)-ANABASINE
Synonym(s):2-(3-Pyridyl)piperidine;Neonicotine
- CAS NO.:13078-04-1
- Empirical Formula: C10H14N2
- Molecular Weight: 162.23
- MDL number: MFCD00871391
- EINECS: 621-972-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-15 16:23:17
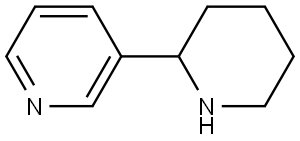
What is (-)-ANABASINE?
Description
Anatabine is an alkaloid found in the root, fibrous roots, or bark of Alangium chinense (Lour) Harms. The herb was recorded in “Jianyi Bencao,” “Bencao Gangmu Shiyi,” and “Zhi Wu Ming Shi Tu Kao.” Alangium chinense is widely distributed in the east and south of China. It is also called “Bailongxu” in Shaanxi, Yunnan, and Guizhou provinces, “Baijintiao” in Guangxi province, and “Bajiaowutong,” “Bajiaojinpan,” or “Laolongxu” in Jiangxi and Hubei provinces. This plant is commonly used as a traditional Chinese medicine. The Alangium species includes more than 30 plants which are distributed in Asia, Oceania, and Africa. Nine of these plants are distributed in China. The root and the stem parts of Alangium plants are toxic.
Description
Anabasine [(±)-3-(2-piperidinyl)pyridine] is a pyridine alkaloid, closely related to nicotine. It has been used historically as an insecticide. Its isolation from the shrub?Anabasis aphylla?L. was reported by A. P. Orekhov and G. P. Men’shikov in 1931. Anabasine is also a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist, and, in high doses, can cause symptoms similar to those of nicotine poisoning.
Chemical properties
Colourless Oil
Physical properties
Appearance: Colorless to yellow liquid. Solubility: Soluble in water and common organic solvents. Boiling point: 110?°C. Refractive index: 1.5418. Density: 1.0516?g cm?3.
History
Alangium chinense contains alkaloids, sugars, saponins, steroids, triterpenes, anthraquinones and their glycosides, and other ingredients. In 1974, dl-anabasine was isolated from the fibrous roots of Alangium chinense . Four isoquinoline alkaloids including two new alkaloids (?)-10-O-dimethyl-eugenol base and 10-O-dimethyl-eugenol base were isolated. P-amyrin acetate, triacontanol, and β-sitosterol were then found in its leaves . Seven glycosides were isolated from the water-soluble fraction of dried leaves of Alangium chinense, and eight glycosides were also isolated from the n-butanol soluble part . Three new lignincompounds including 2-O-(β-apio-furanosyl)-β-glucoside, E ferulic acid ester, and Z ferulic acid ester were extracted from Alangium chinense, and their structures were determined. Nakamoto et?al. extracted 7-O-acetylmaleic acid from Alangium chinense and determined the structure. There are also long-chain fatty acids and short-chain alkanes in Alangium chinense leaves. The volatile oil was then analyzed, and 59 components are identified by GC-MS.?The total alkaloid content in the Alangium chinense was found to be fibrous root > fine root > coarse root > branch wood > leaf.
The Uses of (-)-ANABASINE
A nicotinic receptor agonist
The Uses of (-)-ANABASINE
insecticide
The Uses of (-)-ANABASINE
Anabasine, a tobacco alkaloid, was used as a biomarker of active tobacco use.
What are the applications of Application
(R,S)-Anabasine is a AChR (nicotinic receptor) agonist
Definition
ChEBI: A pyridine alkaloid that is pyridine substituted by a piperidin-2-yl group at position 3.
General Description
Anabasine inhibited androstenedione conversion to estrogen in a dose-dependent manner.
Pharmacology
Alangium plants have wide pharmacological effects including muscle relaxation, central inhibition, anticancer, antibacterial, and so on. The “Jisong-II” injection has presynaptic and postsynaptic effects on the neuromuscular junction, and it acts as noncompetitive muscular relaxant . In 1979, the respiratory suppression experiments showed that Alangium chinense is a central nervous system depressant . The extract of Alangium chinense significantly inhibits the growth of P388 lymphoblastic leukemia and Gardner lymphosarcoma in mice, but it has no effect on Gross virus-induced leukemia, Warner myelomonocytic leukemia, and B16 melanoma . Another study reported that the anabasine could excite respiratory similar to nicotine and lobeline. Anabasine also induces high blood pressure and bradycardia. The components in the Alangium chinense extract can bind to the M, 5-HT and dopamine receptors indicating that Alangium chinense affects the central nervous system.
Clinical Use
The Alangium chinense was used for treating rheumatoid arthritis.
Properties of (-)-ANABASINE
| Melting point: | 9 °C |
| Boiling point: | 270 °C |
| Density | 1.05 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.5440 |
| Flash point: | 93 °C |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: 10 mg/mL |
| form | liquid |
| pka | 8.98±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | colorless to yellow |
| Merck | 14,619 |
| BRN | 82639 |
Safety information for (-)-ANABASINE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for (-)-ANABASINE
| InChIKey | MTXSIJUGVMTTMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![N-{4-[(2-PYRIDIN-3-YLPIPERIDIN-1-YL)SULFONYL]PHENYL}ACETAMIDE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure5/GIF/CB7779798.gif)

You may like
-
 (+/-)-Anabasine CAS 13078-04-1View Details
(+/-)-Anabasine CAS 13078-04-1View Details
13078-04-1 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Guanine , 99%View Details
Guanine , 99%View Details
73-40-5 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
Octadecyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)propionate 98% (GC)View Details
2082-79-3 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
