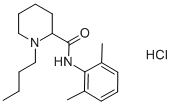
(±)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
- CAS NO.:38396-39-3
- Empirical Formula: C18H28N2O
- Molecular Weight: 288.43
- MDL number: MFCD00243007
- EINECS: 253-911-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-11 20:33:26
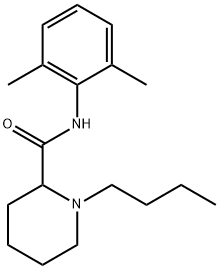
What is (±)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide ?
Absorption
Systemic absorption of local anesthetics is dose- and concentration-dependendent on the total drug administered. Other factors that affect the rate of systemic absorption include the route of administration, blood flow at the administration site, and the presence or absence of epinephrine in the anesthetic solution.
Bupivacaine formulated for instillation with meloxicam produced varied systemic measures following a single dose of varying strength. In patients undergoing bunionectomy, 60 mg of bupivacaine produced a Cmax of 54 ± 33 ng/mL, a median Tmax of 3 h, and an AUC∞ of 1718 ± 1211 ng*h/mL. For a 300 mg dose used in herniorrhaphy, the corresponding values were 271 ± 147 ng/mL, 18 h, and 15,524 ± 8921 ng*h/mL. Lastly, a 400 mg dose used in total knee arthroplasty produced values of 695 ± 411 ng/mL, 21 h, and 38,173 ± 29,400 ng*h/mL.
Toxicity
The mean seizure dosage of bupivacaine in rhesus monkeys was found to be 4.4 mg/kg with mean arterial plasma concentration of 4.5 mcg/mL. The intravenous and subcutaneous LD 50 in mice is 6 to 8 mg/kg and 38 to 54 mg/kg respectively. Recent clinical data from patients experiencing local anesthetic induced convulsions demonstrated rapid development of hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis with bupivacaine within a minute of the onset of convulsions. These observations suggest that oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production are greatly increased during local anesthetic convulsions and emphasize the importance of immediate and effective ventilation with oxygen which may avoid cardiac arrest.
Description
Bupivacaine is a sodium channel blocker and local anesthetic. It inhibits sodium currents in rat dorsal horn neurons in a concentration-dependent manner and inhibits synaptic transmission in rat sympathetic ganglia, increasing the firing threshold when used at a concentration of 200 nM. Bupivacaine (10 μM) blocks cardiac sodium channels in a use-dependent manner and inhibits respiration in cardiac cell mitochondria when palmitoyl-carnitine or acetyl-carnitine are used as substrates (IC50s = 0.78 and 0.37 mM, respectively). It also reduces thermal hyperplasia in a rat model of sciatic ligation injury when 0.6 ml of a 0.5% solution is administered into the perinerve space, and the duration of this effect is extended by co-administration of the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 . Formulations containing bupivacaine have been used as local anesthetics for surgery, oral surgery, and dental procedures and for anesthetic purposes in research studies using animals.
The Uses of (±)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
Bupivacaine acts as a potent and long-acting local anesthetic agent in vivo. At 100 μM, it has been reported to inhibit the uptake of dopamine in striatal synaptosomes by 47%.
Indications
As an implant, bupivacaine is indicated in adults for placement into the surgical site to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 24 hours following open inguinal hernia repair.
Bupivacaine, in liposome suspension, is indicated in patients aged 6 years and older for single-dose infiltration to produce postsurgical local analgesia. In adults, it is also indicated as an interscalene brachial plexus nerve block to produce postsurgical regional analgesia.
Bupivacaine, in combination with meloxicam, is indicated for postsurgical analgesia in adult patients for up to 72 hours following foot and ankle, small-to-medium open abdominal, and lower extremity total joint arthroplasty surgical procedures.
Bupivacaine, alone or in combination with epinephrine, is indicated in adults for the production of local or regional anesthesia or analgesia for surgery, dental and oral surgery procedures, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for obstetrical procedures. Specific concentrations and presentations are recommended for each type of block indicated to produce local or regional anesthesia or analgesia. Finally, its use is not indicated in all blocks given clinically significant risks associated with use.
Background
Bupivacaine is a widely used local anesthetic agent.
What are the applications of Application
Bupivacaine Free Base is local anesthetic which binds to the intracellular portion of sodium channels and blocks sodium influx into the nerve cells
Definition
ChEBI: A piperidinecarboxamide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of N-butylpipecolic acid with the amino group of 2,6-dimethylaniline.
Pharmacokinetics
Bupivacaine is a widely used local anesthetic agent. Bupivacaine is often administered by spinal injection prior to total hip arthroplasty. It is also commonly injected into surgical wound sites to reduce pain for up to 20 hours after surgery. In comparison to other local anesthetics it has a long duration of action. It is also the most toxic to the heart when administered in large doses. This problem has led to the use of other long-acting local anaesthetics:ropivacaine and levobupivacaine. Levobupivacaine is a derivative, specifically an enantiomer, of bupivacaine. Systemic absorption of local anesthetics produces effects on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. At blood concentrations achieved with therapeutic doses, changes in cardiac conduction, excitability, refractoriness, contractility, and peripheral vascular resistance are minimal. However, toxic blood concentrations depress cardiac conduction and excitability, which may lead to atrioventricular block, ventricular arrhythmias and to cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in fatalities. In addition, myocardial contractility is depressed and peripheral vasodilation occurs, leading to decreased cardiac output and arterial blood pressure. Following systemic absorption, local anesthetics can produce central nervous system stimulation, depression or both.
Metabolism
Amide-type local anesthetics such as bupivacaine are metabolized primarily in the liver via conjugation with glucuronic acid. The major metabolite of bupivacaine is 2,6-pipecoloxylidine, which is mainly catalyzed via cytochrome P450 3A4.
Properties of (±)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
| Melting point: | 106-110℃ |
| Boiling point: | 423.4±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.032±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO:25.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);86.68(Max Conc. mM) DMF:30.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);104.01(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:30.0(Max Conc. mg/mL);104.01(Max Conc. mM) Ethanol:PBS (pH 7.2) (1:1):0.5(Max Conc. mg/mL);1.73(Max Conc. mM) |
| form | Cyrstalline powder |
| pka | 14.85±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water, ethanol, chloroform (slightly ), and acetone (slightly ). |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2-Piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)- (38396-39-3) |
Safety information for (±)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H310:Acute toxicity,dermal H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P320:Specific treatment is urgent (see … on this label). P330:Rinse mouth. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for (±)-1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 38396-39-3 Bupivacaine Base (IHS) 99%View Details
38396-39-3 Bupivacaine Base (IHS) 99%View Details
38396-39-3 -
 38396-39-3 98%View Details
38396-39-3 98%View Details
38396-39-3 -
 Rac-Bupivacaine 98%View Details
Rac-Bupivacaine 98%View Details
38396-39-3 -
 Bupivacaine 98% (HPLC) CAS 38396-39-3View Details
Bupivacaine 98% (HPLC) CAS 38396-39-3View Details
38396-39-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4