9002-85-1
Product Name:
VINYLIDENE CHLORIDE LATEX
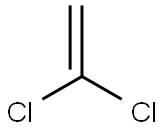
Formula:
C2H2Cl2
Synonyms:
CV301150;CV301230
Inquiry
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Vinylidene chloride, stabilized appears as a clear colorless liquid with a chloroform-like odor. Flash point 0 °F. Boiling point 99 °F. Denser (at 10.1 lb / gal) than water and insoluble in water. Hence sinks in water. May polymerize exothermically if heated or contaminated. If the polymerization takes place inside a container, the container may rupture violently. Vapors heavier than air. |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Mild, sweet odor resembling that of chloroform |
| Boiling Point | 89.1 °F at 760 mmHg (NTP, 1992) |
| Melting Point | -188.5 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Flash Point | 14 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Solubility | 5 to 10 mg/mL at 70 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density | 1.21 at 68 °F (USCG, 1999) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Density | 3.25 (NTP, 1992) - Heavier than air; will sink (Relative to Air) |
| Vapor Pressure | 500 mmHg at 68 °F ; 591 mmHg at 77 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| LogP | log Kow = 2.13 |
| Henry's Law Constant | Henry's Law constant = 2.61X10-2 atm-cu m/mole @ 24 °C |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable under recommended storage conditions. Contains the following stabilizer(s): Mequinol (0.02%). |
| Autoignition Temperature | 1058 °F (USCG, 1999) |
| Decomposition | Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides, hydrogen chloride gas. |
| Viscosity | 0.3302 cP at 20 °C |
| Corrosivity | Vinylidene chloride may be corrosive or unstable in the presence of steel. |
| Heat of Combustion | 1095.9 kJ/mole at 25 °C |
| Heat of Vaporization | 26.48 kJ/mole at 25 °C |
| Surface Tension | 24 dynes/cm at 15 °C (Inhibited) |
| Ionization Potential | 10.00 eV |
| Polymerization | Hazardous polymerization may occur. Usually contains inhibitors to prevent polymerization. Polymerization may be caused by elevated temperature, oxidizers, peroxides, or air. Uninhibited monomer vapor may form polymer in vents and other confined spaces. |
| Odor Threshold | Odor threshold (air) = 2000-5500 mg/cu m |
| Refractive Index | Index of refraction: 1.4249 at 20 °C/D |
| Relative Evaporation Rate | ... The evaporation half-life of a dilute aqueous solution of vinylidene chloride (1 ppm w/w) in an open container stirred at 200 rpm at 25 °C /was/ 22 min, 90% of the compound was lost in 89 min. |
| Kovats Retention Index | 513 513 517 517 519 517.2 498 508.9 498 513 513.1 509.4 512 511 512 511 515 519 520 515 |
| Other Experimental Properties | Heat of polymerization: -185 cal/g; vapor specific gravity: 3.3 |
| Chemical Classes | Plastics & Rubber -> Vinyl Halides |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 96.94 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 0 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Exact Mass | 95.9533555 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 95.9533555 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 0 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 4 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 27 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
1, 1-Dichloroethene is an industrial chemical that is not found naturally in the environment. It is a colorless liquid with a mild, sweet smell. It is also called vinylidene chloride. 1, 1-Dichloroethene is used to make certain plastics, such as flexible films like food wrap, and in packaging materials. It is also used to make flame retardant coatings for fiber and carpet backings, and in piping, coating for steel pipes, and in adhesive applications.