CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 655.5 |
| Solubility | 1.00e-01 g/L |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 358.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | -1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Exact Mass | 358.15624311 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 358.15624311 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 155 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 519 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
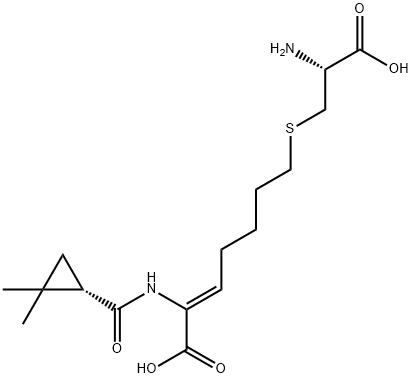
Cilastatin is the thioether resulting from the formal oxidative coupling of the thiol group of L-cysteine with the 7-position of (2Z)-2-({[(1S)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropyl]carbonyl}amino)hept-2-enoic acid. It is an inhibitor of dehydropeptidase I (membrane dipeptidase, 3.4.13.19), an enzyme found in the brush border of renal tubes and responsible for degrading the antibiotic imipenem. Cilastatin is therefore administered (as the sodium salt) with imipenem to prolong the antibacterial effect of the latter by preventing its renal metabolism to inactive and potentially nephrotoxic products. Cilastatin also acts as a leukotriene D4 dipeptidase inhibitor, preventing the metabolism of leukotriene D4 to leukotriene E4. It has a role as a protease inhibitor, an EC 3.4.13.19 (membrane dipeptidase) inhibitor, a xenobiotic and an environmental contaminant. It is a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid, a L-cysteine derivative, an organic sulfide and a carboxamide. It is a conjugate acid of a cilastatin(1-).