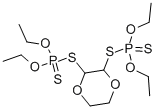
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Dioxathion appears as tan liquid (technical grade is brown). Used for the control of insects and mites on grapes, citrus, walnuts, ornamentals, apples, pears, and quince. Also used as a spray or dip for the control of ticks, lice, hornfly, and sheep ked on cattle, goats, sheep, and hogs. (EPA, 1998) |
|---|---|
| Color/Form | TAN LIQUID |
| Boiling Point | 140 to 154 °F at 0.5 mmHg (NTP, 1992) |
| Melting Point | -4 °F (EPA, 1998) |
| Solubility | less than 0.1 mg/mL at 68 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| Density | 1.257 at 78.8 °F (EPA, 1998) - Denser than water; will sink |
| Vapor Pressure | 17.8 mmHg at 77 °F (NTP, 1992) |
| LogP | 3.0 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | STABLE IN WATER AT NEUTRAL PH, BUT HYDROLYSED BY ALKALI OR ON HEATING. UNSTABLE TO IRON OR TIN SURFACES OR WHEN MIXED WITH CERTAIN CARRIERS. |
| Viscosity | 117 CENTIPOISES @ 25 °C |
| Refractive Index | INDEX OF REFRACTION: 1.5420 @ 20 °C/D |
| Collision Cross Section | 197.29 Ų [M+Cl]- 195.86 Ų [M+Na]+ 199.36 Ų [M+HCOO]- |
| Kovats Retention Index | 1714 1740.8 1742 1742.7 1728 1751.5 |
| Other Experimental Properties | NONVOLATILE |
| Chemical Classes | Pesticides -> Organophosphate Insecticides |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 456.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Exact Mass | 456.00874723 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 456.00874723 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 170 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 395 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
Dioxathion appears as tan liquid (technical grade is brown). Used for the control of insects and mites on grapes, citrus, walnuts, ornamentals, apples, pears, and quince. Also used as a spray or dip for the control of ticks, lice, hornfly, and sheep ked on cattle, goats, sheep, and hogs. (EPA, 1998)